Hmo And Ppo: Choose The Best Insurance Plan

Health insurance is an essential aspect of financial planning, providing a safety net against unexpected medical expenses. With numerous options available, selecting the right insurance plan can be overwhelming, especially when it comes to choosing between Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs) and Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs). In this article, we will delve into the details of both HMO and PPO plans, highlighting their advantages and disadvantages, to help you make an informed decision.
Understanding HMOs
HMOs are a type of health insurance plan that provides coverage for medical services through a network of healthcare providers. These providers have a contract with the HMO to offer discounted services to plan members. The primary goal of an HMO is to focus on preventive care, reducing the need for costly medical interventions. HMOs often have lower premiums compared to other types of insurance plans, but they also come with certain restrictions.
Some key characteristics of HMOs include:
- Network restrictions: HMOs have a limited network of healthcare providers. If you see a doctor or visit a hospital outside of this network, you may not be covered, or you may have to pay out-of-pocket expenses.
- Primary care physician (PCP) requirement: In most HMO plans, you need to choose a PCP who will coordinate your medical care and refer you to specialists when necessary.
- Referral requirements: To see a specialist, you typically need a referral from your PCP.
Pros and Cons of HMOs
HMOs offer several benefits, including:
- Lower premiums: HMOs often have lower premiums compared to PPOs or other types of insurance plans.
- Focus on preventive care: HMOs emphasize preventive care, which can help you stay healthy and reduce the need for costly medical interventions.
- Coordinated care: HMOs provide coordinated care through your PCP, who can help you navigate the healthcare system and ensure that you receive the necessary treatment.
However, HMOs also have some drawbacks:
- Limited flexibility: HMOs have strict network restrictions, which can limit your ability to see the doctor or specialist of your choice.
- Referral requirements: The need for referrals can be inconvenient and may delay your access to specialized care.
Understanding PPOs
PPOs are another type of health insurance plan that offers a network of healthcare providers, but with more flexibility compared to HMOs. In a PPO plan, you can see any healthcare provider, both in-network and out-of-network, without the need for referrals.
Some key characteristics of PPOs include:
- Network flexibility: PPOs have a larger network of healthcare providers, and you can see any doctor or visit any hospital, both in-network and out-of-network.
- No PCP requirement: In PPO plans, you do not need to choose a PCP, and you can see any specialist without a referral.
- Out-of-pocket expenses: While PPOs offer more flexibility, you may have to pay higher out-of-pocket expenses, especially if you see an out-of-network provider.
Pros and Cons of PPOs
PPOs offer several benefits, including:
- Flexibility: PPOs provide more flexibility, allowing you to see any healthcare provider, both in-network and out-of-network.
- No referral requirements: You can see a specialist without a referral, which can be convenient and help you access the care you need more quickly.
- Wider network: PPOs often have a larger network of healthcare providers, which can be beneficial if you travel frequently or have family members living in different areas.
However, PPOs also have some drawbacks:
- Higher premiums: PPOs often have higher premiums compared to HMOs.
- Higher out-of-pocket expenses: While PPOs offer more flexibility, you may have to pay higher out-of-pocket expenses, especially if you see an out-of-network provider.
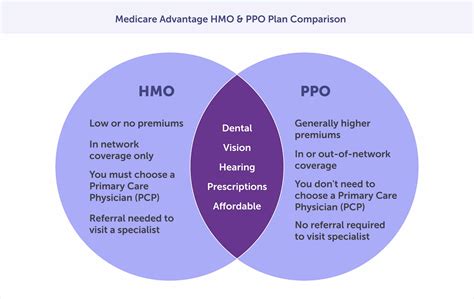
Comparative Analysis
When choosing between an HMO and a PPO, it’s essential to consider your individual needs and circumstances. Here’s a comparative analysis of the two:
| HMO | PPO | |
|---|---|---|
| Network restrictions | Limited network | Larger network, in-network and out-of-network options |
| PCP requirement | Required | Not required |
| Referral requirements | Required for specialists | Not required |
| Premiums | Lower | Higher |
| Out-of-pocket expenses | Lower | Higher, especially for out-of-network care |
| Flexibility | Limited | More flexible |
Decision Framework
To help you make an informed decision, consider the following factors:
- Healthcare needs: If you have ongoing health issues or require frequent medical care, an HMO might be a better option, as it provides coordinated care and lower out-of-pocket expenses.
- Budget: If you’re on a tight budget, an HMO might be more affordable, with lower premiums and out-of-pocket expenses.
- Flexibility: If you value flexibility and want to see any healthcare provider without restrictions, a PPO might be a better choice.
- Travel: If you travel frequently or have family members living in different areas, a PPO might provide better coverage, with a larger network of healthcare providers.
Conclusion
Choosing between an HMO and a PPO depends on your individual circumstances, healthcare needs, and budget. While HMOs offer lower premiums and a focus on preventive care, PPOs provide more flexibility and a wider network of healthcare providers. By considering your needs and weighing the pros and cons of each plan, you can make an informed decision and select the best insurance plan for you and your family.
What is the primary difference between an HMO and a PPO?
+The primary difference between an HMO and a PPO is the level of flexibility and network restrictions. HMOs have a limited network of healthcare providers and require referrals for specialists, while PPOs offer a larger network and more flexibility, with no referral requirements.
Which type of insurance plan is more affordable?
+HMOs are often more affordable, with lower premiums and out-of-pocket expenses, especially for preventive care and coordinated medical services.
Can I see any doctor or specialist with a PPO plan?
+Yes, with a PPO plan, you can see any healthcare provider, both in-network and out-of-network, without the need for referrals. However, you may have to pay higher out-of-pocket expenses for out-of-network care.
What is the role of a primary care physician (PCP) in an HMO plan?
+In an HMO plan, a PCP coordinates your medical care and refers you to specialists when necessary. This helps ensure that you receive the necessary treatment and can help reduce costs by preventing unnecessary medical interventions.
Can I change my insurance plan from an HMO to a PPO or vice versa?
+Yes, you can change your insurance plan during the annual open enrollment period or if you experience a qualifying life event, such as a change in employment or marriage. However, it’s essential to carefully review the terms and conditions of your new plan to ensure it meets your healthcare needs and budget.