How Does Farxiga 10 Mg Work? Effective Treatment
Farxiga, also known by its generic name dapagliflozin, is a medication that has been widely used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes and, more recently, for certain cases of heart failure. It belongs to a class of drugs known as sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors. To understand how Farxiga 10 mg works, it’s essential to delve into its mechanism of action, its effects on the body, and the benefits it provides as an effective treatment for its indicated conditions.
Mechanism of Action
The primary function of Farxiga is to inhibit the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2), a protein found in the kidneys. Under normal circumstances, SGLT2 is responsible for reabsorbing glucose from the filtrate back into the bloodstream. By inhibiting this protein, dapagliflozin reduces the reabsorption of glucose into the bloodstream, thereby increasing the amount of glucose excreted in the urine. This action helps to lower blood glucose levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
Impact on Blood Glucose Levels
The reduction of glucose reabsorption in the kidneys leads to several beneficial effects for individuals with type 2 diabetes:
- Lower Blood Glucose Levels: By promoting the excretion of excess glucose in the urine, Farxiga helps to decrease blood glucose levels, which is crucial for managing type 2 diabetes.
- Weight Loss: The increased glucose excretion can also lead to a reduction in body weight, as the body loses calories that would otherwise be retained as glucose.
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Over time, the reduction in glucose levels can help improve the body’s sensitivity to insulin, making it easier for glucose to enter cells.
Heart Failure Treatment
Beyond its role in managing type 2 diabetes, Farxiga has been shown to be beneficial in the treatment of heart failure, particularly in reducing the risk of worsening heart failure or death from cardiovascular causes. The exact mechanisms through which SGLT2 inhibitors like dapagliflozin exert their beneficial effects on heart failure are not fully understood but are thought to involve a combination of factors, including:
- Diuretic Effect: The increased excretion of glucose and sodium can help reduce fluid retention in the body, decreasing the workload on the heart.
- Reduced Blood Pressure: SGLT2 inhibitors may help to lower blood pressure, further reducing the strain on the heart.
- Improved Cardiac Function: There is evidence to suggest that SGLT2 inhibitors may have direct beneficial effects on cardiac function and structure, though more research is needed to fully understand these mechanisms.
Administration and Dosage
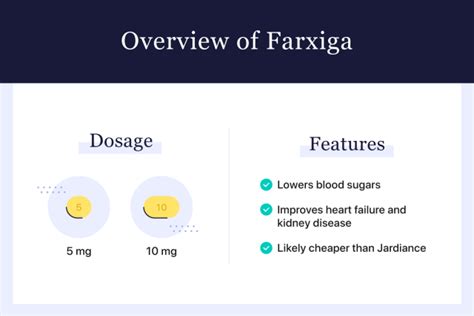
Farxiga is administered orally, once daily, with or without food. The recommended dosage for adults with type 2 diabetes is 5 mg once daily, which can be increased to 10 mg once daily for additional glycemic control if needed. It’s crucial to follow the prescribed dosage and not to exceed it without consulting a healthcare provider, as this can increase the risk of side effects.
Side Effects and Precautions
While effective, Farxiga can cause side effects, including but not limited to:
- Increased urine glucose excretion
- Genital mycotic infections
- Urinary tract infections
- Hypotension
- Hyperkalemia
It’s essential for patients to discuss any concerns, other medications they are taking, and their medical history with their healthcare provider before starting Farxiga. Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels, renal function, and other health parameters is also recommended.
Conclusion
In summary, Farxiga 10 mg, through its inhibition of the SGLT2 protein, offers an effective treatment option for managing type 2 diabetes by lowering blood glucose levels and aiding in weight loss. Its additional benefits in the treatment of heart failure make it a valuable medication in cardiovascular health as well. However, like all medications, it should be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider, with attention to potential side effects and interactions.