How Common Is Ectopic Pregnancy
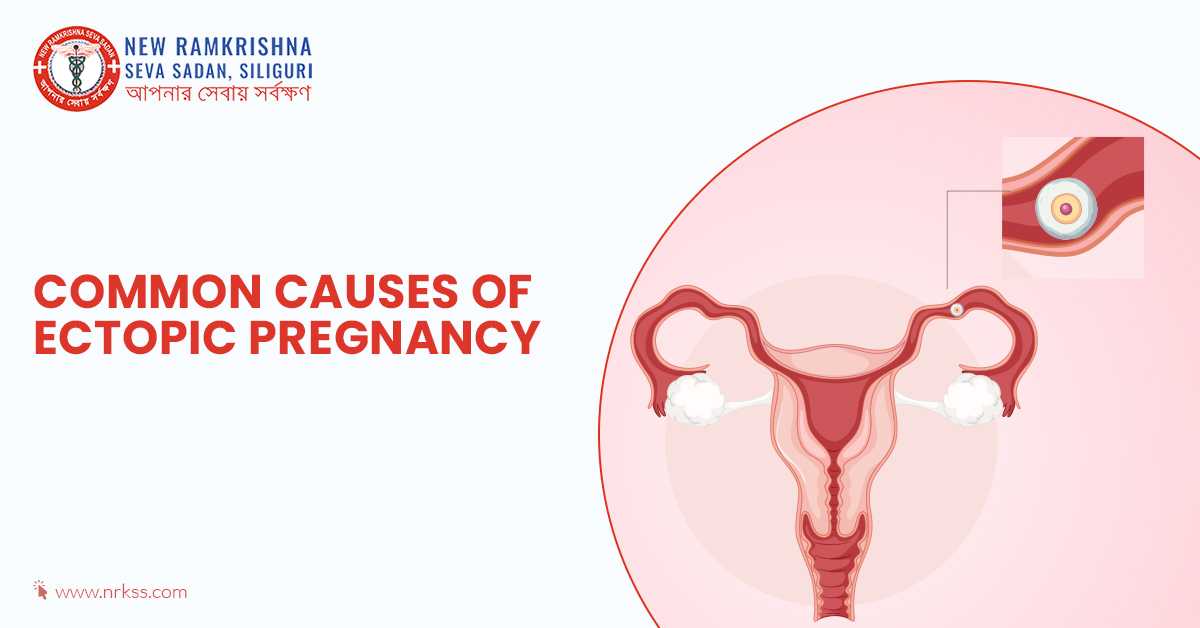
Ectopic pregnancy, a condition where a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, is a significant concern for women of childbearing age. The incidence of ectopic pregnancy varies depending on several factors, including geographic location, age, and underlying medical conditions. Understanding the frequency and risk factors associated with ectopic pregnancy is crucial for early detection and management.
According to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), ectopic pregnancy occurs in approximately 1 in 50 pregnancies in the United States. This translates to about 1-2% of all pregnancies. However, the actual incidence may be higher due to underreporting and variations in diagnostic criteria.
A study published in the Journal of Clinical Epidemiology found that the incidence of ectopic pregnancy has been increasing over the past few decades, with a reported rate of 19.7 per 1,000 pregnancies in 2017. This increase may be attributed to advances in diagnostic techniques, such as transvaginal ultrasound, which enable earlier detection of ectopic pregnancies.
Several factors contribute to the risk of developing an ectopic pregnancy. These include:
- Previous ectopic pregnancy: Women who have had a previous ectopic pregnancy are at increased risk of experiencing another ectopic pregnancy.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID): PID, often caused by chlamydia or gonorrhea, can lead to scarring in the fallopian tubes, increasing the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
- Assisted reproductive technology (ART): Women undergoing IVF or other fertility treatments are at higher risk of ectopic pregnancy due to the increased likelihood of multiple pregnancies.
- Smoking: Smoking has been linked to an increased risk of ectopic pregnancy, possibly due to the damaging effects of tobacco on the fallopian tubes.
- Age: Women over 35 years old are at higher risk of ectopic pregnancy, possibly due to decreased fallopian tube function with age.
Symptoms of ectopic pregnancy can be nonspecific, making early diagnosis challenging. Common symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain: Sharp, stabbing, or crampy pain in the lower abdomen
- Vaginal bleeding: Light to heavy bleeding, which may be accompanied by clotting
- Missed period: A missed menstrual period or irregular bleeding
- Nausea and vomiting: Morning sickness-like symptoms
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately. Early detection and treatment of ectopic pregnancy can significantly improve outcomes and reduce the risk of complications.
In conclusion, while ectopic pregnancy is a relatively rare condition, it is essential to be aware of the risk factors and symptoms to ensure early detection and management. By understanding the incidence and risk factors associated with ectopic pregnancy, women can take proactive steps to reduce their risk and seek medical attention if symptoms arise.
What are the most common symptoms of ectopic pregnancy?
+The most common symptoms of ectopic pregnancy include abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, missed period, and nausea and vomiting. However, symptoms can be nonspecific, making early diagnosis challenging.
Can ectopic pregnancy be prevented?
+While some risk factors for ectopic pregnancy cannot be prevented, practicing safe sex, avoiding smoking, and seeking prompt medical attention for pelvic inflammatory disease can reduce the risk of developing an ectopic pregnancy.
How is ectopic pregnancy diagnosed?
+Ectopic pregnancy is typically diagnosed using a combination of physical examination, ultrasound, and blood tests to detect the presence of a fertilized egg outside the uterus.
By prioritizing reproductive health and seeking medical attention if symptoms arise, women can reduce their risk of complications associated with ectopic pregnancy. Remember, early detection and treatment are critical for optimal outcomes. If you have any concerns or questions about ectopic pregnancy, consult with your healthcare provider for personalized guidance and support.