How To Manage Normal Blood Sugar Levels? Easy Guide
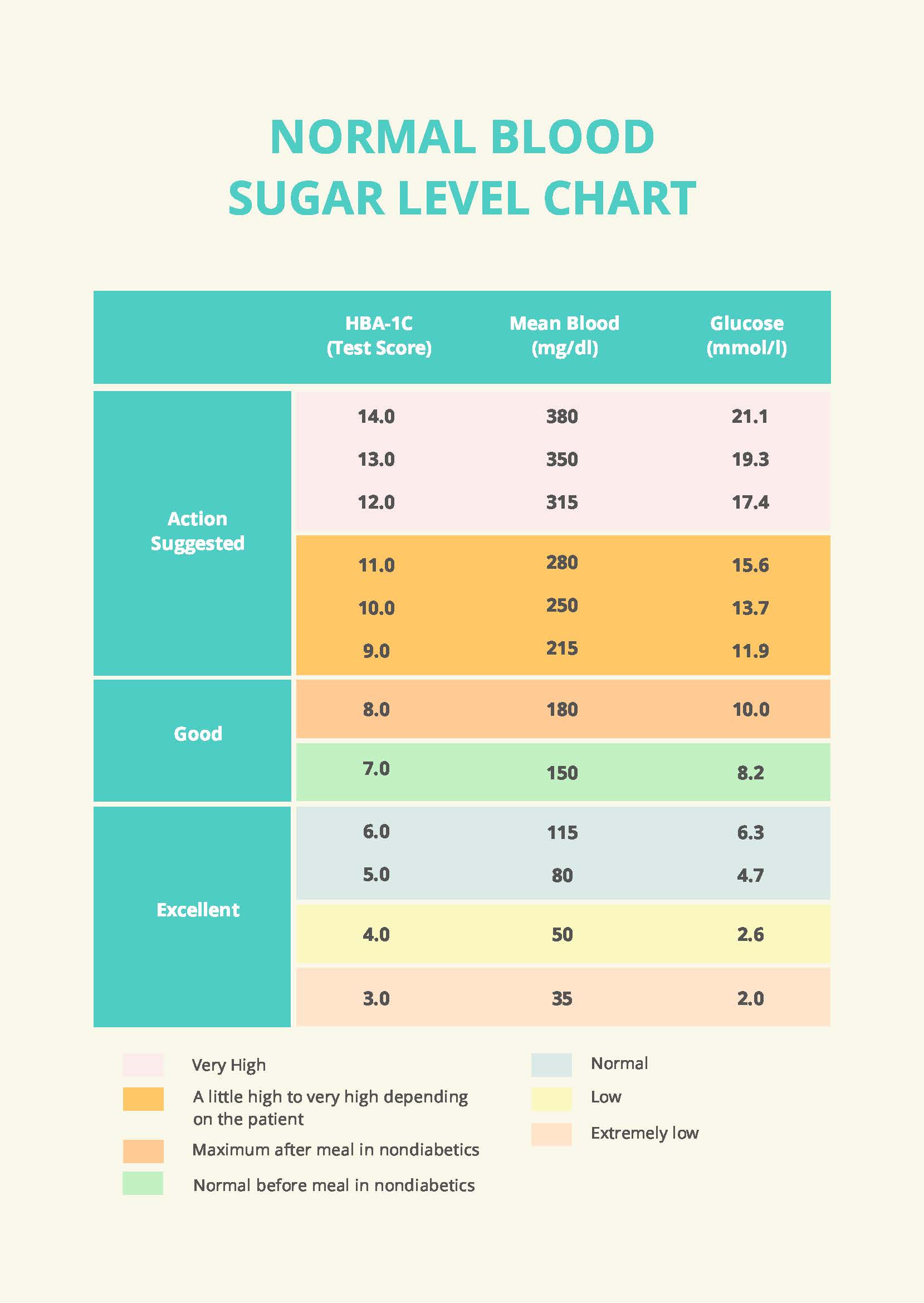
Managing normal blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health, as it helps prevent complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. Normal blood sugar levels are typically between 70 and 140 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) after eating and less than 100 mg/dL when fasting. Achieving and maintaining these levels requires a combination of healthy lifestyle habits, dietary adjustments, and, in some cases, medication. Here’s an easy guide to help you manage normal blood sugar levels:
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
Before diving into management strategies, it’s essential to understand what blood sugar levels are and how they’re affected by different factors. Blood sugar, or glucose, is the primary energy source for your body’s cells. It’s obtained from the food you eat, primarily from carbohydrates, and is regulated by insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas. When you eat, your body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which is then absorbed into your bloodstream. In response, your pancreas releases insulin, which helps your cells absorb glucose for energy.
Dietary Adjustments
Diet plays a critical role in managing blood sugar levels. Here are some dietary adjustments you can make:
- Choose Complex Carbohydrates: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods like vegetables, whole grains, and fruits. These foods are rich in fiber, which helps slow down the absorption of glucose into your bloodstream, preventing spikes in blood sugar levels.
- Incorporate Protein and Healthy Fats: Protein and healthy fats like those found in nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil can help regulate blood sugar levels by slowing down the digestion of carbohydrates and reducing inflammation.
- Avoid Sugary Drinks and Refined Carbohydrates: Beverages and foods high in added sugars and refined carbohydrates can cause a rapid increase in blood sugar levels. Limit your intake of soft drinks, sports drinks, energy drinks, sweets, and refined grains like white bread and sugary cereals.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water can help your body regulate blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. Aim for at least 8 cups (64 ounces) of water per day.
Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is another crucial component of blood sugar management. Exercise helps your body use insulin more efficiently, which can lower your blood sugar levels. Here are some tips for incorporating physical activity into your routine:
- Aim for 150 Minutes of Moderate Exercise: Engage in moderate-intensity exercises like brisk walking, cycling, or swimming for at least 150 minutes per week. You can break this down into 30 minutes per day, 5 days a week.
- Include High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): HIIT involves short bursts of high-intensity exercise followed by brief periods of rest. This type of exercise has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels.
- Strength Training: Incorporate strength training exercises at least twice a week to build muscle. Muscle tissue is more sensitive to insulin than fat tissue, which can help lower blood sugar levels.
Stress Management
Stress can raise your blood sugar levels and worsen diabetes symptoms. Here are some strategies to manage stress:
- Practice Yoga or Meditation: These mindfulness practices can help reduce stress and improve your body’s response to insulin.
- Get Enough Sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night to helpyour body regulate stress hormones and maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
- Engage in Relaxing Activities: Activities like reading, listening to music, or taking a warm bath can help reduce stress.
Monitoring and Medication
If you have diabetes or are at risk of developing it, monitoring your blood sugar levels and, in some cases, taking medication, is crucial:
- Use a Blood Glucose Meter: Check your blood sugar levels regularly, as recommended by your healthcare provider, to understand how different foods, activities, and medications affect your levels.
- Follow Your Medication Plan: If you’re prescribed medication for diabetes, take it exactly as directed by your healthcare provider. Medications can help lower your blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications.
Conclusion
Managing normal blood sugar levels is a multifaceted approach that involves dietary adjustments, regular physical activity, stress management, and, when necessary, monitoring and medication. By incorporating these strategies into your lifestyle, you can help maintain healthy blood sugar levels, reduce your risk of diabetes complications, and improve your overall well-being.
What role does fiber play in managing blood sugar levels?
+Fiber helps slow down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, which can prevent spikes in blood sugar levels. Foods high in fiber include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes.
How often should I check my blood sugar levels if I have diabetes?
+The frequency of checking your blood sugar levels depends on the type of diabetes you have, your treatment plan, and how well your blood sugar levels are controlled. Your healthcare provider will recommend how often you should check your blood sugar levels.
Can I manage my blood sugar levels without medication if I have diabetes?
+For some people with type 2 diabetes, it may be possible to manage blood sugar levels through lifestyle changes alone, such as diet and exercise. However, this should be done under the guidance of a healthcare provider, and medication may still be necessary to achieve and maintain target blood sugar levels.