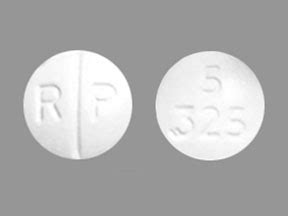
I can provide information on Hydrocodone Acetate. Hydrocodone Acetate, with the imprint code 5325, is a medication that belongs to the class of opioids, specifically a semi-synthetic opioid derived from codeine and thebaine. It is commonly used in combination with other substances like acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen to treat moderate to severe pain.
Introduction to Hydrocodone Acetate
Hydrocodone Acetate works by binding to opioid receptors in the brain and spinal cord, altering the way the body perceives and responds to pain. It is available in various formulations, including tablets, capsules, and liquid suspensions, and is administered orally. The presence of acetaminophen or ibuprofen in combination products helps to enhance the pain-relieving effects of hydrocodone and can also reduce fever.
Uses of Hydrocodone Acetate
The primary use of hydrocodone acetate is for the relief of moderate to moderately severe pain. It is often prescribed for short-term management of acute pain, such as after surgery or injury, and for chronic pain management in cases where other treatments have failed. Due to its potential for dependency and abuse, hydrocodone products are controlled substances and are subject to strict prescribing and dispensing regulations.
Side Effects and Risks
Like all opioid medications, hydrocodone acetate carries a range of potential side effects and risks. Common side effects include drowsiness, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, constipation, and headache. More serious risks include respiratory depression, which can be life-threatening, especially when hydrocodone is combined with other central nervous system depressants like alcohol or benzodiazepines. Additionally, long-term use can lead to physical dependence and addiction.
Safety Precautions
Due to the risks associated with hydrocodone acetate, several safety precautions are advised: - Use as Directed: Only use hydrocodone acetate as directed by a healthcare provider. Do not increase the dose or frequency of use without medical advice. - Avoid Combination with Other Substances: Unless directed by a healthcare provider, avoid combining hydrocodone with other central nervous system depressants, as this can increase the risk of serious side effects. - Monitor for Signs of Dependence: Be aware of the signs of physical dependence or addiction, such as needing to take more medication to achieve the same effect, and report these to a healthcare provider. - Dispose of Medication Properly: Unused hydrocodone acetate should be disposed of properly to prevent misuse.
Drug Interactions
Hydrocodone acetate can interact with a variety of drugs, including but not limited to: - Central Nervous System Depressants: Alcohol, benzodiazepines, sedatives, tranquilizers, and certain antidepressants can increase the risk of respiratory depression. - Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs): The use of MAOIs with hydrocodone can increase the risk of serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition.
Overdose and Emergency
In case of an overdose, symptoms may include extreme drowsiness, confusion, slow or stopped breathing, slow heart rate, cold and clammy skin, and loss of consciousness. If an overdose is suspected, immediate medical attention is required. Naloxone, an opioid antagonist, is used as an antidote for opioid overdose and can be administered by emergency responders or, in some cases, by family members or caregivers trained in its use.
Conclusion
Hydrocodone acetate, found in medications like those with the imprint code 5325, is a potent opioid analgesic used for pain relief. While it can be an effective treatment for moderate to severe pain, its use must be carefully managed due to the risks of side effects, dependence, and overdose. Always follow the advice of a healthcare provider and report any concerns or side effects promptly.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Hydrocodone Acetate used for?
+Hydrocodone Acetate is primarily used for the relief of moderate to moderately severe pain. It is often prescribed for both acute and chronic pain management.
Can Hydrocodone Acetate be addictive?
+Yes, Hydrocodone Acetate carries a risk of physical dependence and addiction. Long-term use can lead to tolerance and dependence, and its use should be closely monitored by a healthcare provider.
What are the common side effects of Hydrocodone Acetate?
+
How should unused Hydrocodone Acetate be disposed of?
+Unused Hydrocodone Acetate should be disposed of properly to prevent misuse. This can be done through drug take-back programs, household trash disposal by mixing the medication with an undesirable substance like coffee grounds and sealing it in a container, or by using a DEA-authorized drug disposal facility.