Check Blood Sugar Levels: Master Your Monitoring Routine
Managing blood sugar levels is a critical aspect of maintaining overall health, particularly for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. Blood sugar monitoring is an essential tool in this endeavor, enabling individuals to track their glucose levels, identify patterns, and make informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and medication. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of blood sugar monitoring, exploring the importance of regular checks, the different methods available, and providing expert tips on how to master your monitoring routine.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
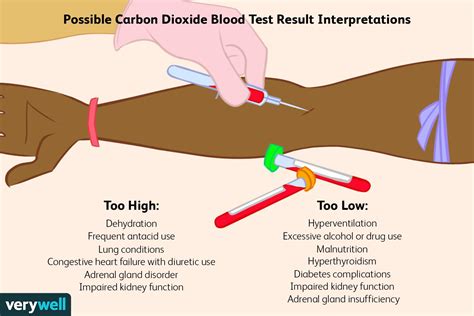
Before diving into the monitoring aspect, it’s crucial to understand what blood sugar levels are and why they’re vital. Blood sugar, or glucose, is a type of sugar that serves as the primary source of energy for the body’s cells. The level of glucose in the blood is measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). Normal blood sugar levels typically range from 70 to 140 mg/dL, though these levels can fluctuate throughout the day based on factors such as diet, physical activity, and sleep.
The Importance of Blood Sugar Monitoring
Monitoring blood sugar levels is essential for several reasons:
Diabetes Management: For individuals with diabetes, regular monitoring helps in adjusting medication, diet, and exercise to maintain blood sugar levels within a target range. This is crucial for preventing complications associated with diabetes, such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage.
Identifying Patterns: Through regular monitoring, individuals can identify patterns in their blood sugar levels. This information can be used to make informed decisions about meal planning, physical activity, and stress management.
Preventing Hypoglycemia and Hyperglycemia: Monitoring helps in the early detection of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and hyperglycemia (high blood sugar), allowing for prompt intervention to prevent serious health complications.
Methods of Blood Sugar Monitoring
Several methods are available for monitoring blood sugar levels, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages:
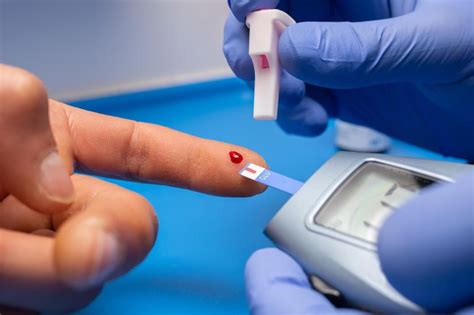
1. Fingerstick Testing
- Description: This is the most common method, involving pricking the fingertip with a lancet to collect a blood sample, which is then placed on a test strip and inserted into a glucose meter.
- Advantages: Quick, relatively painless, and provides immediate results.
- Disadvantages: May not always provide accurate results, especially if not done correctly, and can be painful for some individuals.
2. Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
- Description: CGMs involve wearing a small sensor under the skin, typically on the abdomen or arm, which measures glucose levels throughout the day and night.
- Advantages: Provides real-time glucose data, alerts for high or low levels, and reduces the need for fingerstick testing.
- Disadvantages: Can be expensive, may cause skin irritation, and requires calibration with a blood glucose meter.
3. Flash Glucose Monitoring
- Description: Similar to CGM but does not require calibration with a blood glucose meter. It involves scanning a sensor worn on the skin with a reader device.
- Advantages: Easy to use, does not require fingerstick calibration, and provides immediate glucose levels and trending information.
- Disadvantages: The sensor must be replaced regularly, and the system may not be as widely available or reimbursed as CGM.
Mastering Your Monitoring Routine
To get the most out of blood sugar monitoring, follow these expert tips:
1. Set a Schedule
- Regular monitoring at the same times each day can help identify patterns and trends in blood sugar levels.
2. Keep a Log
- Recording blood sugar levels, along with the time of day, meals, exercise, and any medications taken, can provide valuable insights into how different factors affect glucose levels.
3. Understand Your Targets
- Work with your healthcare provider to set realistic blood sugar targets and to understand how to adjust your lifestyle and medication based on your monitoring results.
4. Stay Hydrated
- Adequate hydration is essential for overall health and can impact blood sugar levels. Aim for at least eight glasses of water per day.
5. Be Active
- Regular physical activity can help lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week.
6. Manage Stress
- High levels of stress can increase blood sugar levels. Engage in stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
Conclusion
Mastering a blood sugar monitoring routine is a personalized and ongoing process that requires patience, dedication, and the right tools. By understanding the importance of blood sugar monitoring, choosing the most appropriate method for your needs, and implementing expert tips into your daily routine, you can better manage your blood sugar levels, reduce the risk of complications, and improve your overall health and well-being.
Practical Application Guide
For individuals looking to integrate blood sugar monitoring into their daily lives, consider the following steps:
- Consult with a Healthcare Provider: Discuss the best monitoring method for your specific needs and health status.
- Set Realistic Goals: Work with your provider to set achievable targets for your blood sugar levels.
- Choose the Right Equipment: Select a glucose meter or CGM system that fits your lifestyle and preferences.
- Develop a Monitoring Schedule: Decide on the best times of the day to check your blood sugar levels based on your daily routine and activities.
- Keep Track of Your Progress: Use a log or mobile app to record your blood sugar levels, noting any factors that may influence your readings.
FAQ Section
What is the ideal frequency for checking blood sugar levels?
+The ideal frequency for checking blood sugar levels varies depending on the individual's health status, type of diabetes, and treatment plan. Generally, individuals with type 1 diabetes or those using insulin may need to check their levels more frequently than those with type 2 diabetes managed through diet and exercise. It's essential to follow the advice of a healthcare provider for personalized guidance.
Can I use blood sugar monitoring results to adjust my medication on my own?
+No, it's not recommended to adjust your medication based solely on blood sugar monitoring results without consulting your healthcare provider. While monitoring provides valuable information, medication adjustments should be made under professional guidance to ensure safety and effectiveness.
How often should I calibrate my Continuous Glucose Monitor (CGM)?
+The calibration frequency for a CGM varies by device and individual needs. Typically, calibration is required at the start of each sensor session and may need to be repeated during the session as per the manufacturer's instructions or based on readings that suggest a need for recalibration. Always refer to the user manual or consult with a healthcare provider for specific guidance.
By embracing blood sugar monitoring as a core component of your health management strategy, you can empower yourself with the knowledge and insights necessary to achieve better glucose control, enhance your quality of life, and reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications. Remember, every small step towards understanding and managing your blood sugar levels is a significant move towards a healthier, happier you.