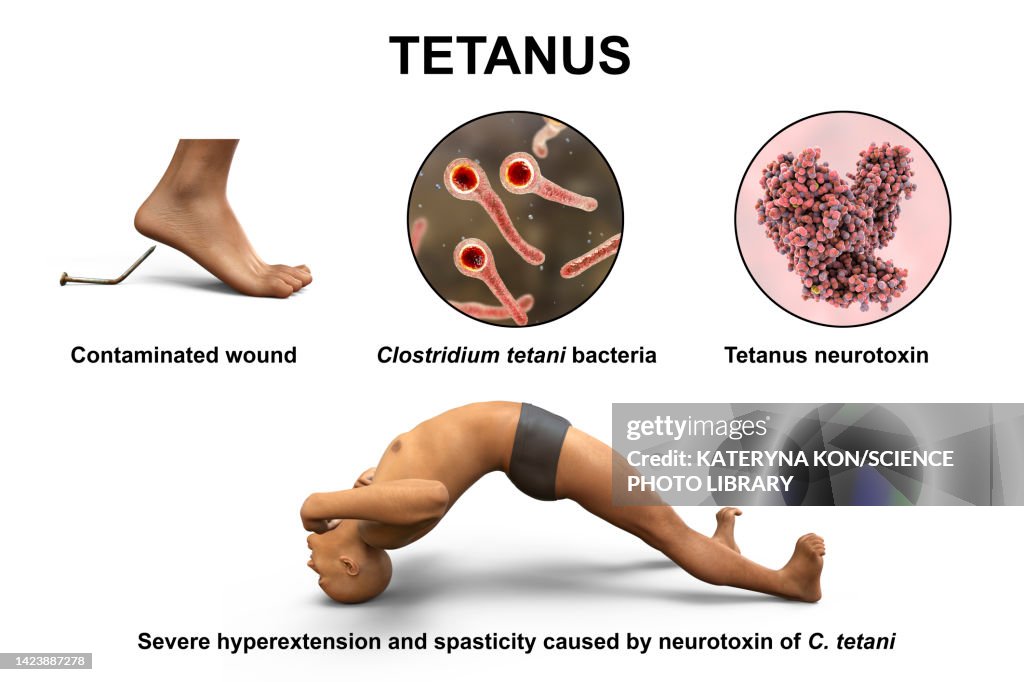
Ibuprofen Drug Class
Ibuprofen, a commonly used medication, belongs to a class of drugs known as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). NSAIDs are a group of medications that are used to reduce inflammation, relieve pain, and lower fever. They work by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins, which are chemical messengers in the body that cause pain and inflammation.
History of Ibuprofen
Ibuprofen was first introduced in the 1960s as a prescription drug, and it was later approved for over-the-counter (OTC) use in the 1980s. It is now one of the most widely used NSAIDs in the world, available under various brand names such as Advil, Motrin, and Nurofen. The development of ibuprofen marked a significant milestone in the treatment of pain and inflammation, offering an alternative to aspirin and other NSAIDs.
Mechanism of Action
Ibuprofen works by blocking the production of prostaglandins, which are produced by the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX). There are two types of COX enzymes: COX-1 and COX-2. COX-1 is involved in maintaining the health of the stomach lining and kidneys, while COX-2 is involved in the production of prostaglandins that cause pain and inflammation. Ibuprofen is a non-selective COX inhibitor, meaning it blocks both COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes. This can lead to both therapeutic effects, such as reduced pain and inflammation, and potential side effects, such as stomach upset and kidney damage.
Therapeutic Uses
Ibuprofen is used to treat a wide range of conditions, including:
- Pain relief: Ibuprofen is effective in relieving mild to moderate pain, such as headaches, toothaches, and menstrual cramps.
- Inflammation: Ibuprofen is used to reduce inflammation and swelling in conditions such as arthritis, sprains, and strains.
- Fever reduction: Ibuprofen can help to reduce fever in adults and children.
- Menstrual symptoms: Ibuprofen is often used to relieve menstrual cramps, bloating, and other symptoms associated with premenstrual syndrome (PMS).
Side Effects and Risks
While ibuprofen is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects and increase the risk of certain health problems. Common side effects of ibuprofen include:
- Stomach upset and nausea
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Dizziness or drowsiness
- Headaches or fatigue
Long-term use of ibuprofen can increase the risk of more serious health problems, such as:
- Stomach ulcers and bleeding
- Kidney damage
- Increased blood pressure
- Heart attack and stroke
Interactions and Contraindications
Ibuprofen can interact with other medications, including:
- Anticoagulants (blood thinners)
- Diabetes medications
- Blood pressure medications
- Lithium
Ibuprofen is contraindicated in people with certain medical conditions, such as:
- Active stomach ulcers or bleeding
- Kidney disease
- Heart failure
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Conclusion
Ibuprofen is a widely used NSAID that is effective in relieving pain, reducing inflammation, and lowering fever. However, it can cause side effects and increase the risk of certain health problems, especially with long-term use. Take ibuprofen as directed and consult a healthcare professional if any concerns or questions arise.
FAQ Section
What is the recommended dosage of ibuprofen for adults?
+The recommended dosage of ibuprofen for adults is 200-400mg every 4-6 hours as needed, not to exceed 1200mg in 24 hours.
Can ibuprofen be taken with other medications?
+Ibuprofen can interact with other medications, such as anticoagulants, diabetes medications, and blood pressure medications. Consult a healthcare professional before taking ibuprofen with other medications.
Is ibuprofen safe for people with kidney disease?
+Ibuprofen can increase the risk of kidney damage, especially with long-term use. People with kidney disease should consult a healthcare professional before taking ibuprofen.
Key Takeaways
- Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that relieves pain, reduces inflammation, and lowers fever.
- It works by blocking the production of prostaglandins, which cause pain and inflammation.
- Ibuprofen is available over-the-counter (OTC) and by prescription.
- Common side effects include stomach upset, diarrhea, and dizziness.
- Long-term use can increase the risk of stomach ulcers, kidney damage, and heart problems.
- Ibuprofen can interact with other medications and is contraindicated in people with certain medical conditions.
Additional Resources
For more information on ibuprofen and other NSAIDs, consult the following resources:
- National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
- American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP)
- American College of Rheumatology (ACR)