Thyroid Antibody Test
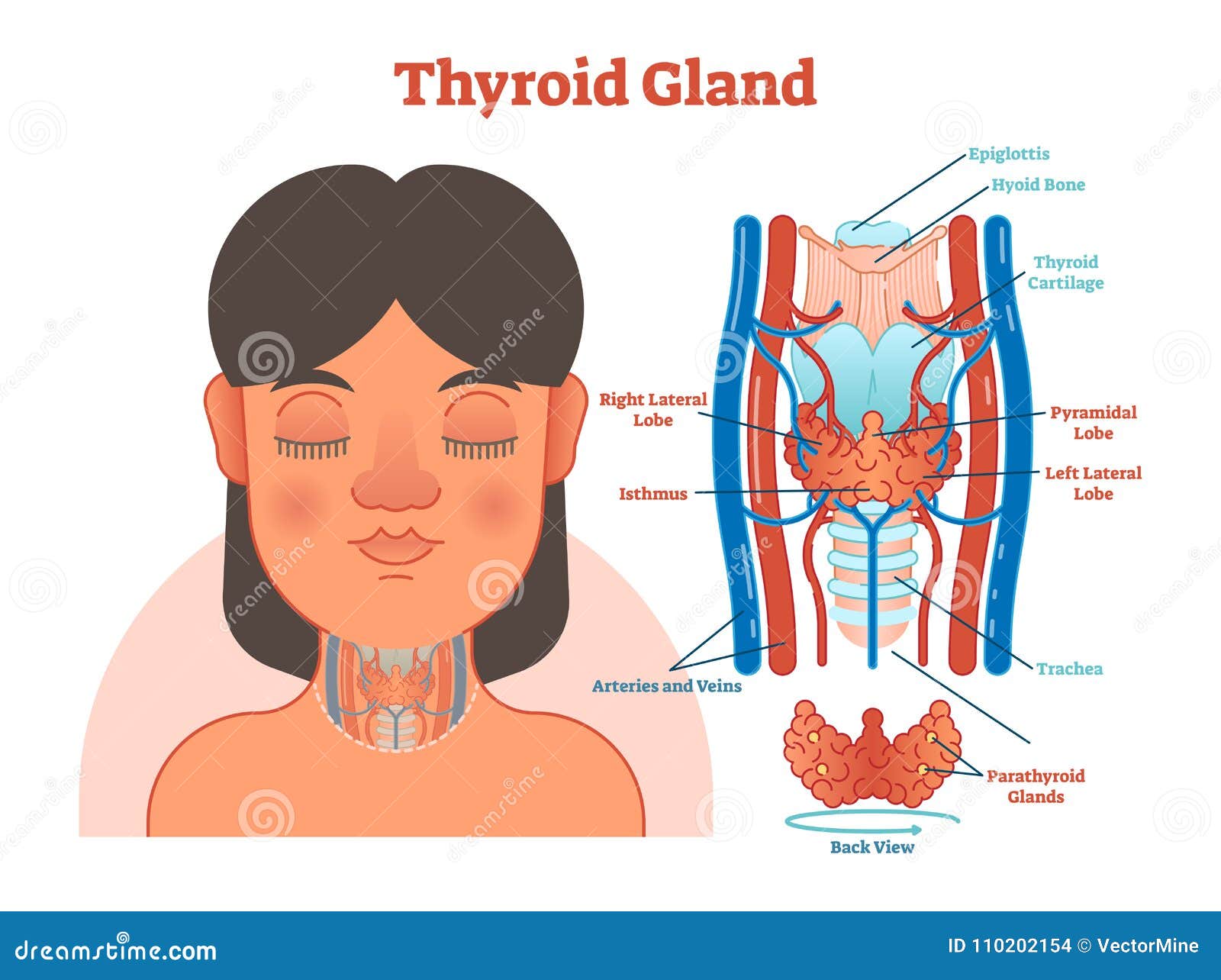
The thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped organ located in the neck, plays a vital role in regulating metabolism, energy generation, and overall hormonal balance. However, for some individuals, the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland, leading to the production of thyroid antibodies. This autoimmune response can disrupt thyroid function, causing a range of symptoms and health issues. The thyroid antibody test is a crucial diagnostic tool used to detect the presence of these antibodies, helping healthcare professionals diagnose and manage autoimmune thyroid diseases.
Understanding Thyroid Antibodies
Thyroid antibodies are proteins produced by the immune system that target the thyroid gland. There are several types of thyroid antibodies, but the most common ones include:
- Thyroid Peroxidase Antibodies (TPOAb): These antibodies attack the thyroid peroxidase enzyme, which is essential for the production of thyroid hormones.
- Thyroglobulin Antibodies (TgAb): These antibodies target thyroglobulin, a protein that helps produce and store thyroid hormones.
- Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Receptor Antibodies (TRAb): These antibodies bind to the thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) receptor, either stimulating or blocking the production of thyroid hormones.
Why Are Thyroid Antibody Tests Necessary?
The thyroid antibody test is essential for diagnosing and monitoring autoimmune thyroid diseases, such as:
- Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: An autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks the thyroid gland, leading to hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid).
- Graves’ Disease: An autoimmune condition where the immune system produces antibodies that stimulate the thyroid gland, leading to hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid).
- Postpartum Thyroiditis: A temporary autoimmune condition that occurs in some women after childbirth, causing thyroid inflammation and dysfunction.
How Is the Thyroid Antibody Test Performed?
The thyroid antibody test is a blood test that measures the levels of thyroid antibodies in the blood. The test is typically performed in a laboratory, and the results are usually available within a few days. The test may be ordered by a healthcare professional if:
- You are experiencing symptoms of thyroid dysfunction, such as fatigue, weight gain or loss, or mood changes.
- You have a family history of autoimmune thyroid diseases.
- You are pregnant or have recently given birth.
Interpreting Thyroid Antibody Test Results
The results of the thyroid antibody test can be complex and require interpretation by a healthcare professional. Here are some possible results:
- Positive: The presence of thyroid antibodies indicates an autoimmune response against the thyroid gland. The level of antibodies can help determine the severity of the condition.
- Negative: The absence of thyroid antibodies suggests that the thyroid dysfunction is not caused by an autoimmune response.
- Borderline: The results may indicate a borderline or equivocal result, which requires further testing or evaluation.
What Do Thyroid Antibody Test Results Mean for Your Health?
If you test positive for thyroid antibodies, it does not necessarily mean that you have an autoimmune thyroid disease. However, it does indicate an increased risk of developing thyroid dysfunction. Your healthcare professional may recommend:
- Monitoring: Regular blood tests to monitor thyroid function and antibody levels.
- Medications: Thyroid hormone replacement therapy or immunosuppressive medications to manage symptoms and prevent further damage.
- Lifestyle Changes: Dietary modifications, stress management, and exercise to help manage symptoms and support overall health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is the Normal Range for Thyroid Antibody Tests?
+The normal range for thyroid antibody tests varies depending on the laboratory and the specific test used. Generally, a positive result is indicated by a level of antibodies above a certain threshold, typically measured in international units per milliliter (IU/mL).
Can Thyroid Antibody Tests Be Used to Diagnose Other Conditions?
+Thyroid antibody tests are specific to autoimmune thyroid diseases and are not typically used to diagnose other conditions. However, some thyroid antibodies may be present in other autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus.
How Often Should I Get Thyroid Antibody Tests?
+The frequency of thyroid antibody tests depends on your individual health needs and medical history. Your healthcare professional may recommend regular testing to monitor thyroid function and antibody levels, especially if you have a family history of autoimmune thyroid diseases or are experiencing symptoms of thyroid dysfunction.
Conclusion
Thyroid antibody tests are a vital tool for diagnosing and managing autoimmune thyroid diseases. By understanding the different types of thyroid antibodies and the implications of test results, individuals can work with their healthcare professionals to develop effective treatment plans and manage symptoms. Remember, a positive test result does not necessarily mean that you have an autoimmune thyroid disease, but it does indicate an increased risk of developing thyroid dysfunction. With proper monitoring, medications, and lifestyle changes, it is possible to manage thyroid health and reduce the risk of complications.