Ladies Heart Attack
When it comes to heart attacks, there’s a common misconception that they primarily affect men. However, the reality is that heart disease is the leading cause of death for women in the United States, accounting for about 1 in every 5 deaths. Women’s heart health is a critical issue that requires attention, understanding, and action. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the world of ladies’ heart attacks, exploring the symptoms, risk factors, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies.
Understanding Heart Attacks in Women
Heart attacks, also known as myocardial infarctions, occur when the blood flow to the heart is blocked, causing damage to the heart muscle. This blockage is often the result of a blood clot that forms in a coronary artery, which supplies blood to the heart. Women’s heart attacks can be different from men’s in several ways, including symptoms, severity, and outcomes. It’s essential to recognize these differences to provide timely and effective care.
Symptoms of Heart Attacks in Women
Unlike men, who often experience the classic symptom of chest pain, women may exhibit a more diverse range of symptoms. These can include:
- Chest pain or discomfort, which may feel like pressure, tightness, or heaviness
- Pain or discomfort in the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Cold sweats, nausea, or lightheadedness
- Fatigue or weakness
- Palpitations or irregular heartbeats
Some women may not experience any symptoms at all, or their symptoms may be mild and easily mistaken for other conditions. This is why it’s crucial for women to be aware of their risk factors and to seek medical attention immediately if they suspect something is wrong.
Risk Factors for Heart Attacks in Women
Several risk factors can increase a woman’s likelihood of having a heart attack. These include:
- Age: The risk of heart disease increases with age, especially after menopause
- Family history: Having a family history of heart disease can increase a woman’s risk
- Smoking: Smoking is a significant risk factor for heart disease, as it damages the cardiovascular system and increases blood pressure
- High blood pressure: Uncontrolled high blood pressure can lead to heart disease and stroke
- High cholesterol: High levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol can increase the risk of heart disease
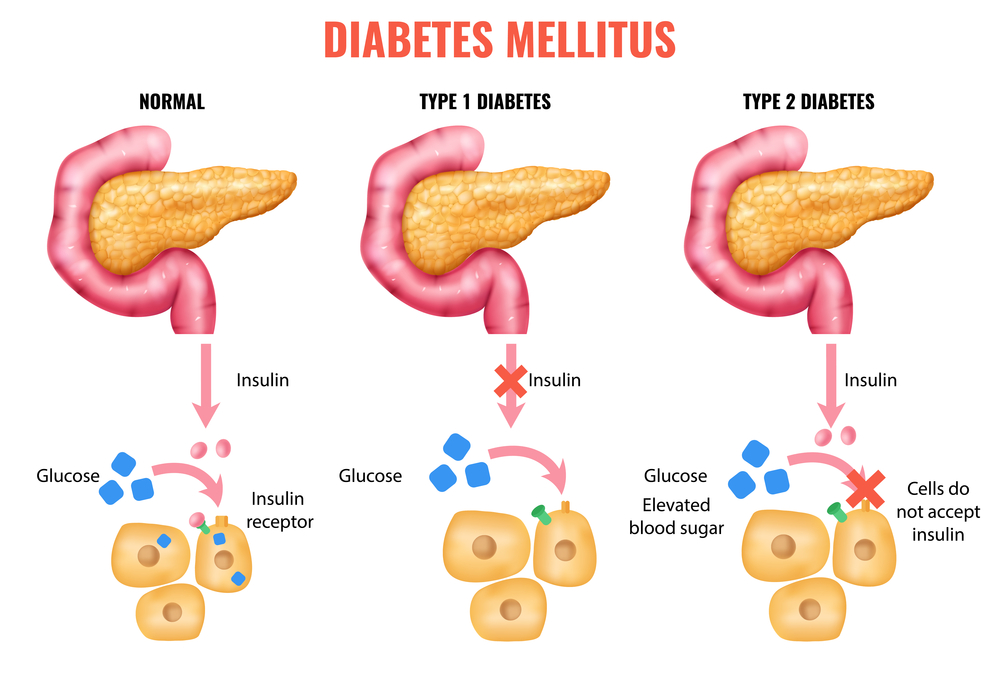
- Diabetes: Women with diabetes are more likely to develop heart disease than those without diabetes
- Obesity: Excess weight can increase the risk of heart disease, as well as other conditions like high blood pressure and diabetes
- Physical inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle can contribute to the development of heart disease
- Stress: Chronic stress can increase the risk of heart disease, as well as other conditions like high blood pressure and anxiety disorders
Diagnosis and Treatment of Heart Attacks in Women
Diagnosing heart attacks in women can be more challenging than in men, as their symptoms may be less typical. Doctors use a combination of medical history, physical examination, electrocardiogram (ECG), and blood tests to diagnose a heart attack. Treatment options may include medications to dissolve blood clots, improve blood flow, and reduce pain, as well as surgical procedures like angioplasty or coronary artery bypass grafting.
Preventing Heart Attacks in Women
Prevention is key when it comes to heart disease. Women can take several steps to reduce their risk of having a heart attack:
- Maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise
- Quit smoking and avoid exposure to secondhand smoke
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques like meditation or deep breathing
- Get enough sleep and practice good sleep hygiene
- Limit alcohol consumption and avoid binge drinking
- Stay up-to-date on recommended health screenings and check-ups
Heart health is a critical aspect of overall well-being, and women must take an active role in protecting their hearts. By understanding the symptoms, risk factors, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies, women can empower themselves to make informed decisions about their health. If you suspect you or someone else is having a heart attack, call emergency services immediately.
Personal Stories and Experiences
Hearing from women who have experienced heart attacks can provide valuable insights and inspiration. Their stories highlight the importance of being aware of risk factors, recognizing symptoms, and seeking medical attention promptly.
Conclusion
Women’s heart health is a vital concern that requires attention, awareness, and action. By understanding the complexities of ladies’ heart attacks, women can take control of their health and reduce their risk of having a heart attack. It’s essential to recognize the differences in symptoms, risk factors, and outcomes between men and women, as well as the importance of prevention and timely medical care.
FAQ Section
What are the most common symptoms of a heart attack in women?
+The most common symptoms of a heart attack in women include chest pain or discomfort, pain or discomfort in the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach, shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, cold sweats, nausea, or lightheadedness, fatigue or weakness, and palpitations or irregular heartbeats.
How can women reduce their risk of having a heart attack?
+Women can reduce their risk of having a heart attack by maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, managing stress, getting enough sleep, limiting alcohol consumption, and staying up-to-date on recommended health screenings and check-ups.
What is the importance of recognizing symptoms and seeking medical attention promptly?
+Recognizing symptoms and seeking medical attention promptly is crucial because it can significantly improve outcomes and reduce the risk of complications or death. Women should not hesitate to call emergency services if they suspect they or someone else is having a heart attack.