Levothyroxine Side Effects: Manage Symptoms Easily

When it comes to managing hypothyroidism, levothyroxine is a commonly prescribed medication that helps restore thyroid hormone levels to a normal range. However, like any medication, levothyroxine can cause side effects, which can be uncomfortable and affect daily life. Understanding the potential side effects of levothyroxine and knowing how to manage them is crucial for individuals taking this medication.
Introduction to Levothyroxine
Levothyroxine, also known as T4, is a synthetic form of the thyroid hormone thyroxine. It works by replacing the missing thyroid hormone in the body, which helps to regulate various bodily functions, such as metabolism, energy production, and growth. Levothyroxine is often prescribed for individuals with hypothyroidism, a condition where the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone.
Common Levothyroxine Side Effects
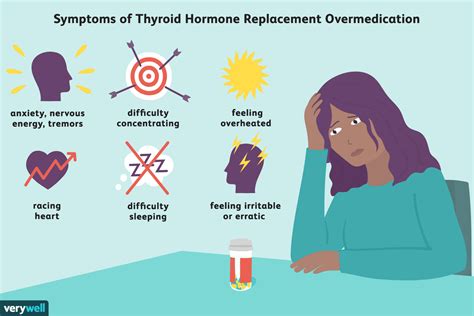
While levothyroxine is generally well-tolerated, some individuals may experience side effects, especially when first starting the medication or when the dose is adjusted. Common side effects of levothyroxine include:
- Fatigue or weakness
- Weight loss or gain
- Hair loss
- dry skin
- Cold intolerance
- Constipation or diarrhea
- Nervousness or anxiety
- Mood changes, such as depression or irritability
- Sleep disturbances, such as insomnia or vivid dreams
Serious Levothyroxine Side Effects
In rare cases, levothyroxine can cause more serious side effects, which require immediate medical attention. These include:
- Allergic reactions, such as hives, itching, or difficulty breathing
- Chest pain or irregular heartbeat
- Seizures or convulsions
- Severe headache or confusion
- Vomiting or diarrhea that is severe or persistent
Managing Levothyroxine Side Effects
While side effects can be uncomfortable, there are several ways to manage them and minimize their impact on daily life. Here are some tips:
- Take the medication as directed: Follow the prescribed dosage and schedule to minimize the risk of side effects.
- Monitor thyroid levels: Regular blood tests can help ensure that thyroid hormone levels are within a normal range, reducing the risk of side effects.
- Eat a balanced diet: A healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein can help alleviate side effects such as fatigue and weight changes.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help with dry skin and constipation.
- Exercise regularly: Gentle exercise, such as yoga or walking, can help improve mood and reduce fatigue.
- Get enough sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night to help regulate thyroid hormone levels and alleviate sleep disturbances.
Comparing Levothyroxine to Other Thyroid Medications
Levothyroxine is just one of several medications available to treat hypothyroidism. Other medications, such as liothyronine (T3) and natural desiccated thyroid (NDT), may be prescribed in certain situations. Here’s a brief comparison:
- Liothyronine (T3): This medication contains the active form of thyroid hormone and is often prescribed for individuals who have difficulty converting T4 to T3.
- Natural Desiccated Thyroid (NDT): This medication is derived from animal thyroid tissue and contains both T4 and T3. It’s often prescribed for individuals who prefer a more natural approach or who have difficulty tolerating synthetic medications.
| Medication | Active Ingredient | Prescription Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Levothyroxine | T4 | Hypothyroidism |
| Liothyronine | T3 | Difficulty converting T4 to T3 |
| Natural Desiccated Thyroid | T4 and T3 | Hypothyroidism, preference for natural approach |
Historical Evolution of Levothyroxine
Levothyroxine has been used to treat hypothyroidism for over 50 years. The medication was first synthesized in the 1950s and was initially used to treat severe cases of hypothyroidism. Over the years, the manufacturing process has been refined, and the medication has become more widely available.
Step 1: Synthesis of Levothyroxine
Levothyroxine was first synthesized in the 1950s using a combination of chemical and biological processes.
Step 2: Clinical Trials
Clinical trials were conducted to test the safety and efficacy of levothyroxine in treating hypothyroidism.
Step 3: FDA Approval
Levothyroxine was approved by the FDA in the 1960s for the treatment of hypothyroidism.
Future Trends in Thyroid Treatment
As research continues to advance, new treatments and medications are being developed to manage hypothyroidism. Some potential future trends include:
- Personalized medicine: Tailoring treatment to an individual’s specific needs and genetic profile.
- Alternative therapies: Exploring non-pharmacological approaches, such as dietary changes and stress management.
- Gene therapy: Developing treatments that target the underlying genetic causes of hypothyroidism.
What are the most common side effects of levothyroxine?
+The most common side effects of levothyroxine include fatigue, weight changes, hair loss, dry skin, and mood changes.
How can I minimize the risk of side effects when taking levothyroxine?
+To minimize the risk of side effects, take the medication as directed, monitor thyroid levels regularly, and maintain a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise.
Can I take levothyroxine with other medications?
+It's essential to consult with a healthcare provider before taking levothyroxine with other medications, as interactions can occur. Certain medications, such as blood thinners and diabetes medications, may require dosage adjustments when taken with levothyroxine.
In conclusion, while levothyroxine can cause side effects, these can be managed with the right approach. By understanding the potential side effects, working closely with a healthcare provider, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, individuals can minimize the risk of side effects and ensure that the medication is working effectively. As research continues to advance, new treatments and medications are being developed to manage hypothyroidism, offering hope for improved management and treatment of this condition.