Lymph Node Biopsy: Diagnose Cancer Accurately
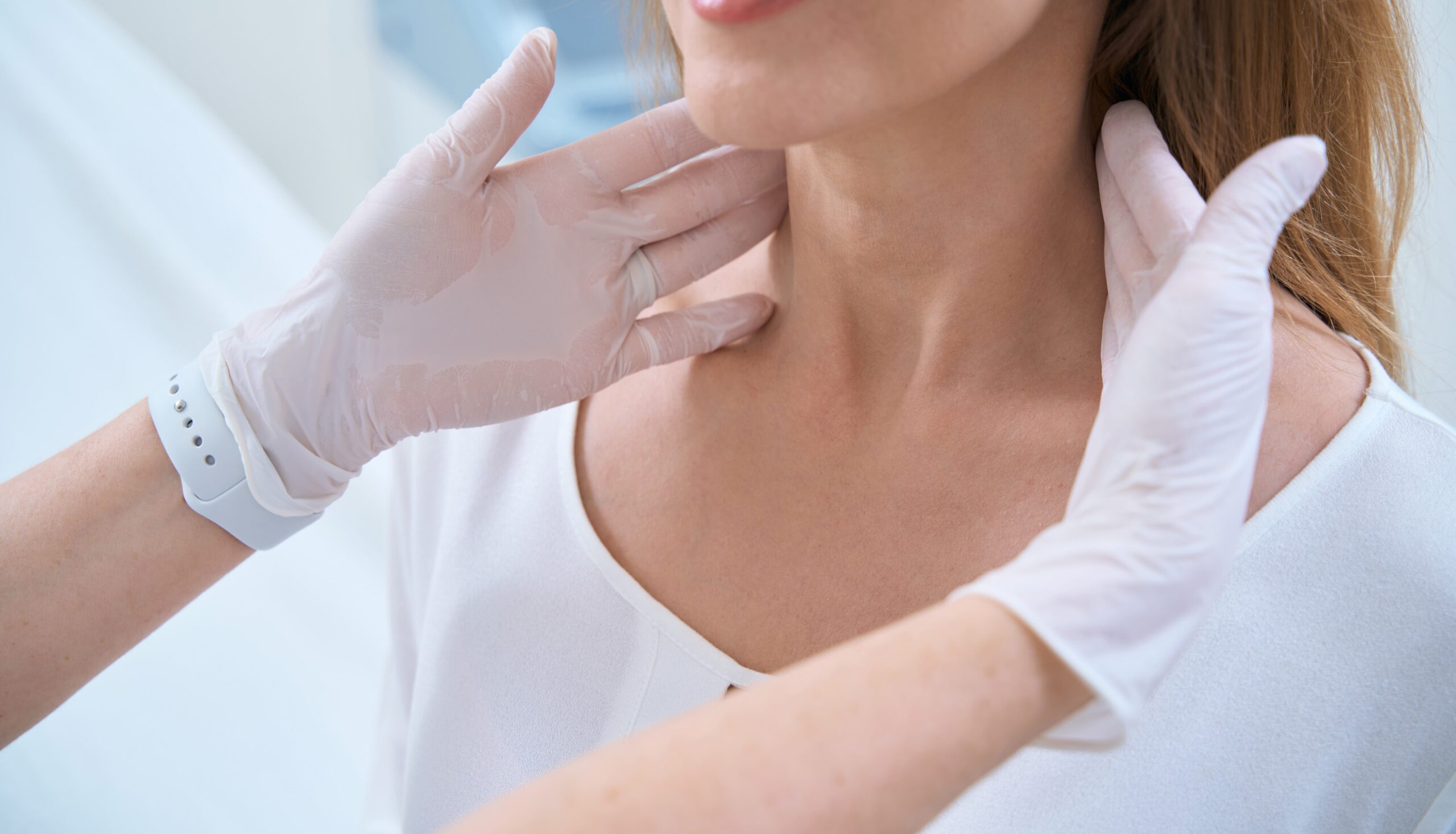
The complexity of the human body is a marvel, with intricate systems working in harmony to maintain health. One such system is the lymphatic system, comprising lymph nodes, vessels, and organs that play a pivotal role in immune function. Lymph nodes, small, bean-shaped structures, are scattered throughout the body and act as filters for harmful substances. They are also one of the first places where cancer can spread, making them a crucial focus in cancer diagnosis and treatment. A lymph node biopsy, a procedure to remove and examine lymph node tissue, is a critical diagnostic tool in determining the presence and spread of cancer.
Understanding Lymph Node Biopsy
A lymph node biopsy is typically recommended when a lymph node is enlarged or when cancer is suspected. This procedure can be performed in various ways, including a fine-needle aspiration biopsy, core needle biopsy, or surgical biopsy. Each method has its specific indications and advantages. For instance, a fine-needle aspiration biopsy is less invasive and can often be performed in a doctor’s office, making it a favorable initial approach. However, it may not always provide enough tissue for a definitive diagnosis, in which case a core needle biopsy or surgical biopsy might be necessary.
The Importance of Accurate Diagnosis
Accurate diagnosis is the cornerstone of effective cancer treatment. A lymph node biopsy provides critical information about the type of cancer, its stage, and whether it has spread to other parts of the body. This information guides treatment decisions, including the need for surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or a combination of these. For example, if a biopsy reveals that cancer has spread to the lymph nodes, it may indicate a more advanced stage of the disease, requiring a more aggressive treatment approach.
The Procedure: What to Expect
The lymph node biopsy procedure itself is generally well-tolerated. For a fine-needle aspiration or core needle biopsy, local anesthesia is used to numb the area, and the procedure typically takes about 30 minutes. Patients may experience some discomfort and bruising afterward, but these effects are usually temporary. A surgical biopsy, which involves removing an entire lymph node, requires general anesthesia and a longer recovery time. post-operative care instructions are provided to minimize the risk of complications and ensure a smooth recovery.
Interpreting Biopsy Results
After the biopsy, the tissue sample is sent to a pathology laboratory for examination. Pathologists look for abnormal cell growth, which could indicate cancer, and may perform additional tests to determine the type of cancer and its aggressiveness. The results are then communicated to the patient’s healthcare team, who will discuss the findings, explain the diagnosis, and outline treatment options. This process can be anxiety-provoking for patients, emphasizing the importance of clear communication and support from healthcare professionals.
Recent Advances in Biopsy Techniques
Advancements in medical technology have led to the development of more sophisticated biopsy techniques. For instance, sentinel lymph node biopsy, a procedure used primarily in breast cancer and melanoma, involves removing the first lymph node to which cancer cells are likely to spread. This approach can reduce the need for more extensive lymph node removal, potentially decreasing side effects. Additionally, the use of molecular diagnostics, such as PCR (polymerase chain reaction) and FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization), can provide more detailed information about the cancer, helping to tailor treatment to the individual’s specific disease characteristics.
Living with Cancer: Beyond Diagnosis
While a lymph node biopsy is a critical step in cancer diagnosis, it is only the beginning of the cancer journey. Living with cancer involves not just treating the disease but also managing its impact on daily life. This can include dealing with the emotional and psychological aspects of a cancer diagnosis, navigating changes in relationships, work, and overall well-being. Support systems, such as counseling services, support groups, and online resources, play a vital role in helping patients and their families cope with these challenges.
Future Directions in Cancer Diagnosis
The future of cancer diagnosis holds much promise, with ongoing research focused on developing even more precise and less invasive diagnostic tools. Liquid biopsies, which involve analyzing circulating tumor DNA in blood samples, are an exciting area of development. These tests could potentially detect cancer at its earliest stages, even before symptoms appear, revolutionizing the approach to cancer screening and treatment. Furthermore, advances in AI and machine learning are being explored to improve the accuracy of biopsy interpretations and to predict patient outcomes, further personalizing cancer care.
Conclusion
A lymph node biopsy is a powerful diagnostic tool in the fight against cancer, offering valuable insights into the disease’s extent and nature. As medical science continues to evolve, it is likely that biopsy techniques will become even more refined, contributing to earlier detection and more effective treatment of cancer. For now, patients facing a lymph node biopsy can take comfort in knowing that this procedure is a necessary step towards understanding their condition and developing an appropriate treatment plan. With the support of healthcare professionals, loved ones, and advancements in medical technology, the path forward, though challenging, can be navigated with hope and determination.
What is the purpose of a lymph node biopsy?
+A lymph node biopsy is performed to determine if cancer or infection is present in the lymph nodes. It helps in diagnosing the type of cancer and its stage, guiding treatment decisions.
How is a lymph node biopsy performed?
+A lymph node biopsy can be performed through a fine-needle aspiration, core needle biopsy, or surgical biopsy. The choice of method depends on the location and size of the lymph node, as well as the patient’s overall health.
What are the risks associated with a lymph node biopsy?
+Like any medical procedure, a lymph node biopsy carries risks such as bleeding, infection, and nerve damage. However, these risks are generally low, and the benefits of the procedure often outweigh them.
How long does it take to recover from a lymph node biopsy?
+Recovery time from a lymph node biopsy varies depending on the type of biopsy performed. For less invasive procedures, patients can usually return to their normal activities within a day or two. For surgical biopsies, recovery may take several days to a week.
Can a lymph node biopsy be used to treat cancer?
+A lymph node biopsy is primarily a diagnostic tool. While it can provide information necessary for planning cancer treatment, it is not a treatment in itself. Treatment options such as surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy are determined based on the biopsy results.