Metabolic Panel Test
The metabolic panel test, also known as a chemistry screen or chemistry panel, is a comprehensive blood test used to assess various aspects of a person’s metabolic function. This test is a crucial diagnostic tool for healthcare professionals, providing valuable insights into the body’s chemical balance, organ function, and potential underlying health issues.
What Does a Metabolic Panel Test Measure?
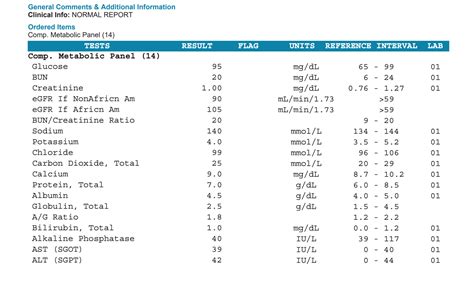
A standard metabolic panel test typically includes measurements of 14-20 different substances in the blood, although the exact components may vary depending on the laboratory or healthcare provider. The test is designed to evaluate:
- Electrolyte levels: Sodium, potassium, chloride, and carbon dioxide levels, which help regulate the body’s acid-base balance and hydration status.
- Blood sugar control: Glucose levels, which indicate how well the body is managing blood sugar.
- Kidney function: Waste products, such as urea and creatinine, which are filtered by the kidneys and can indicate kidney dysfunction.
- Liver function: Enzymes, such as alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST), which can indicate liver damage or disease.
- Protein levels: Albumin and total protein levels, which can indicate nutritional status, liver function, or kidney function.
- Mineral levels: Calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium levels, which are essential for maintaining healthy bones, muscles, and nerve function.
- Acid-base balance: The test measures the blood’s pH level and the levels of bicarbonate and carbon dioxide, which help regulate the body’s acid-base balance.
Why is a Metabolic Panel Test Ordered?
A metabolic panel test is often ordered as part of a routine health exam or to:
- Monitor existing medical conditions: Such as diabetes, kidney disease, or liver disease.
- Evaluate symptoms: Like fatigue, weakness, or changes in urination patterns.
- Assess medication effectiveness: Certain medications, such as diuretics or blood thinners, can affect electrolyte levels or kidney function.
- Screen for underlying conditions: Like kidney disease, liver disease, or hormonal imbalances.
How is a Metabolic Panel Test Performed?
The test is typically performed in a healthcare setting or laboratory, and involves:
- Blood draw: A healthcare professional will draw a blood sample from a vein in the arm.
- Sample preparation: The blood sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis.
- Analysis: The laboratory uses automated analyzers to measure the various components of the metabolic panel.
Interpreting the Results
The results of a metabolic panel test are typically reported in a table or graph, with each component measured in units such as milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or grams per deciliter (g/dL). Healthcare professionals will interpret the results in the context of the individual’s medical history, symptoms, and other diagnostic tests.
Abnormal Results: What Do They Mean?
Abnormal results can indicate various health issues, such as:
- Electrolyte imbalances: Abnormal sodium, potassium, or chloride levels can indicate dehydration, kidney disease, or hormonal imbalances.
- Blood sugar control issues: Elevated glucose levels can indicate diabetes or prediabetes.
- Kidney dysfunction: Elevated waste products, such as urea and creatinine, can indicate kidney disease or kidney failure.
- Liver damage: Elevated liver enzymes, such as ALT and AST, can indicate liver damage or disease.
Next Steps After an Abnormal Metabolic Panel Test
If the results of a metabolic panel test are abnormal, the healthcare provider may:
- Order additional tests: To confirm the diagnosis or rule out other conditions.
- Initiate treatment: Such as medication or lifestyle changes, to address the underlying condition.
- Monitor the condition: With regular follow-up tests to track the effectiveness of treatment.
In conclusion, the metabolic panel test is a valuable diagnostic tool that provides insights into various aspects of a person’s metabolic function. By understanding the components of the test and what abnormal results mean, individuals can better navigate their healthcare and work with their healthcare provider to address any underlying health issues.
What is the purpose of a metabolic panel test?
+The purpose of a metabolic panel test is to assess various aspects of a person’s metabolic function, including electrolyte levels, blood sugar control, kidney function, liver function, and protein levels.
What does a metabolic panel test measure?
+A metabolic panel test measures 14-20 different substances in the blood, including electrolytes, blood sugar, waste products, liver enzymes, protein levels, and mineral levels.
Why is a metabolic panel test ordered?
+A metabolic panel test is ordered to monitor existing medical conditions, evaluate symptoms, assess medication effectiveness, or screen for underlying conditions.
How is a metabolic panel test performed?
+The test is performed by drawing a blood sample from a vein in the arm, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis.
What do abnormal results mean?
+Abnormal results can indicate various health issues, such as electrolyte imbalances, blood sugar control issues, kidney dysfunction, or liver damage.