Metformin: Lowest Dose For Diabetes Control
For individuals diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, managing blood sugar levels is crucial to prevent complications and improve quality of life. Among the various medications prescribed for diabetes control, metformin stands out as a first-line treatment due to its effectiveness, safety profile, and the fact that it does not cause significant weight gain, a common issue with many other diabetes drugs. When it comes to metformin, understanding the appropriate dosage is essential for maximizing its benefits while minimizing potential side effects.
Metformin works by decreasing glucose production in the liver, increasing insulin sensitivity, and thereby lowering blood sugar levels. It is available in several formulations, including immediate-release and extended-release tablets, as well as a liquid solution. The dosing of metformin can vary based on factors such as the severity of diabetes, the patient’s kidney function, and whether it is used alone or in combination with other diabetes medications.
Starting with the Lowest Effective Dose
The concept of starting with the lowest effective dose is rooted in the principle of minimizing side effects while achieving therapeutic goals. For metformin, the typical starting dose for adults with type 2 diabetes is 500 mg taken once or twice daily, depending on the formulation. This dose can be gradually increased by the physician based on the patient’s response to the medication, aiming to reach the maximum tolerated dose or the dose that provides the best control of blood sugar levels without causing undue side effects.
The immediate-release formulation of metformin is usually initiated at a dose of 500 mg once daily, with meals, to reduce gastrointestinal side effects such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain, which are more common when starting the medication but often resolve over time. The dose can be increased by 500 mg every 1-2 weeks, as tolerated, up to a maximum dose of 2000-2500 mg per day, given in divided doses.
For the extended-release formulation, which is designed to release the drug more slowly, allowing for once-daily dosing and potentially fewer gastrointestinal side effects, the starting dose is also 500 mg once daily with the evening meal. The dose can be increased to 1000 mg once daily after one week, and then increased by 500 mg every week, as needed, and as tolerated, up to a maximum dose of 2000-2500 mg once daily.
Importance of Dose Titration
Dose titration, or the gradual adjustment of the dose, is crucial with metformin. It helps in minimizing side effects, especially gastrointestinal, allowing the body to adjust to the medication. Patients are advised to take metformin with meals to reduce the risk of stomach upset. It’s also important to stay hydrated when taking metformin to minimize the risk of kidney problems.
Monitoring and Adjustments
During treatment with metformin, regular monitoring of blood glucose levels, as well as kidney function tests, is essential. The dose may need to be adjusted based on these results, or if significant side effects occur. The goal is to find the lowest effective dose that maintains blood glucose levels within a target range without causing significant side effects.
Combining Metformin with Other Treatments
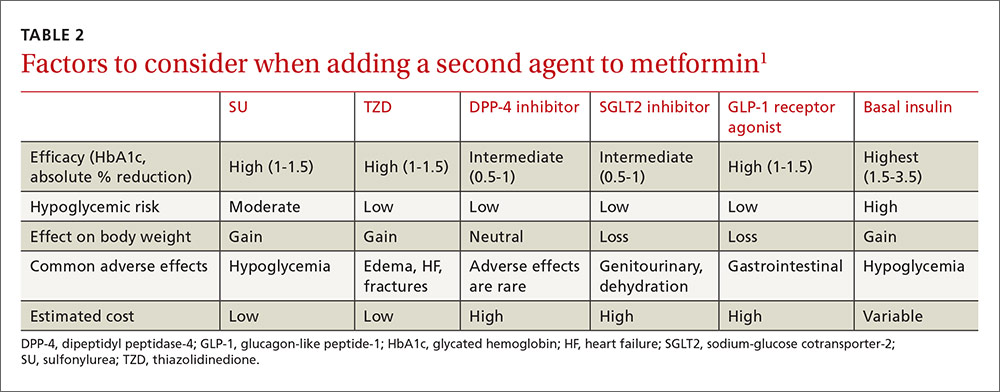
Often, metformin is used in combination with other diabetes medications, such as sulfonylureas, meglitinides, thiazolidinediones, DPP-4 inhibitors, GLP-1 receptor agonists, or insulin, to achieve better control of blood sugar levels. When combining metformin with other diabetes drugs, the dose of metformin may need to be adjusted based on the patient’s response and the potential for increased risk of hypoglycemia or other side effects.
Conclusion
Metformin is a cornerstone in the management of type 2 diabetes due to its efficacy and safety profile. Starting with the lowest effective dose and gradually increasing it as needed and as tolerated helps in achieving optimal blood sugar control while minimizing side effects. Regular monitoring and adjustments, as well as patient education on the proper use of metformin, are key components of effective diabetes management.
What is the usual starting dose of metformin for type 2 diabetes?
+The usual starting dose of metformin for adults with type 2 diabetes is 500 mg taken once or twice daily, depending on the formulation, with meals to reduce gastrointestinal side effects.
How is the dose of metformin adjusted?
+The dose of metformin can be increased by 500 mg every 1-2 weeks, as tolerated, to a maximum dose of 2000-2500 mg per day for the immediate-release formulation, and up to 2000-2500 mg once daily for the extended-release formulation, based on the patient’s response and side effects.
What are common side effects of metformin and how can they be minimized?
+Common side effects of metformin include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. These can be minimized by taking metformin with meals, starting with a low dose and gradually increasing it, and staying hydrated to reduce the risk of kidney problems.
Can metformin be used in combination with other diabetes medications?
+Yes, metformin is often used in combination with other diabetes medications to achieve better control of blood sugar levels. The dose of metformin may need to be adjusted when used in combination with other diabetes drugs to minimize the risk of side effects.
Why is regular monitoring important during treatment with metformin?
+Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels and kidney function tests during treatment with metformin is essential to adjust the dose as needed, ensure the medication is effective, and minimize potential side effects.