Metronidazole 500 Mg

Metronidazole, a medication belonging to the class of nitroimidazoles, is widely used to treat various infections caused by bacteria and protozoa. The 500 mg dosage of metronidazole is commonly prescribed for a range of conditions, including bacterial vaginosis, pelvic inflammatory disease, amoebiasis, and infections caused by susceptible organisms such as Giardia lamblia and Trichomonas vaginalis. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of metronidazole 500 mg, including its mechanisms of action, indications, dosage, side effects, interactions, and contraindications.
Mechanism of Action
Metronidazole works by entering the cells of the microorganisms and damaging their DNA, thereby inhibiting their ability to reproduce and ultimately leading to their death. This action is made possible by the reduction of the nitro group of metronidazole by the bacterial enzyme nitroreductase, which converts metronidazole into its active form. This active form then interferes with the DNA of the microbial cell, resulting in cell death.
Indications
Metronidazole 500 mg is used for a variety of infections:
- Bacterial Vaginosis: Metronidazole is effective against the bacteria that cause vaginal infections, restoring the natural balance of vaginal flora.
- Trichomoniasis: It is used to treat infections caused by Trichomonas vaginalis, a sexually transmitted parasite.
- Amoebiasis: Metronidazole is the drug of choice for treating amoebic dysentery and liver abscess caused by Entamoeba histolytica.
- Giardiasis: It is also effective against Giardia lamblia infections, which cause giardiasis.
- Intra-abdominal Infections: Metronidazole, often used in combination with other antibiotics, is effective in treating infections within the abdominal cavity caused by susceptible anaerobic bacteria.
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): It is part of the treatment regimen for PID, particularly for infections involving anaerobic bacteria.
Dosage
The dosage of metronidazole can vary based on the condition being treated. For metronidazole 500 mg:
- Bacterial Vaginosis: Typically, 500 mg twice daily for 7 days.
- Trichomoniasis: Usually, 2 grams as a single dose or 1 gram twice daily for 7 days.
- Amoebiasis: For intestinal amoebiasis, 500 to 750 mg three times daily for 5 to 10 days. For extraintestinal disease (e.g., liver abscess), 500 to 750 mg three times daily for 5 to 10 days.
- Giardiasis: Usually, 250 mg three times daily for 5 to 7 days, though the 500 mg dosage may be used in certain cases.
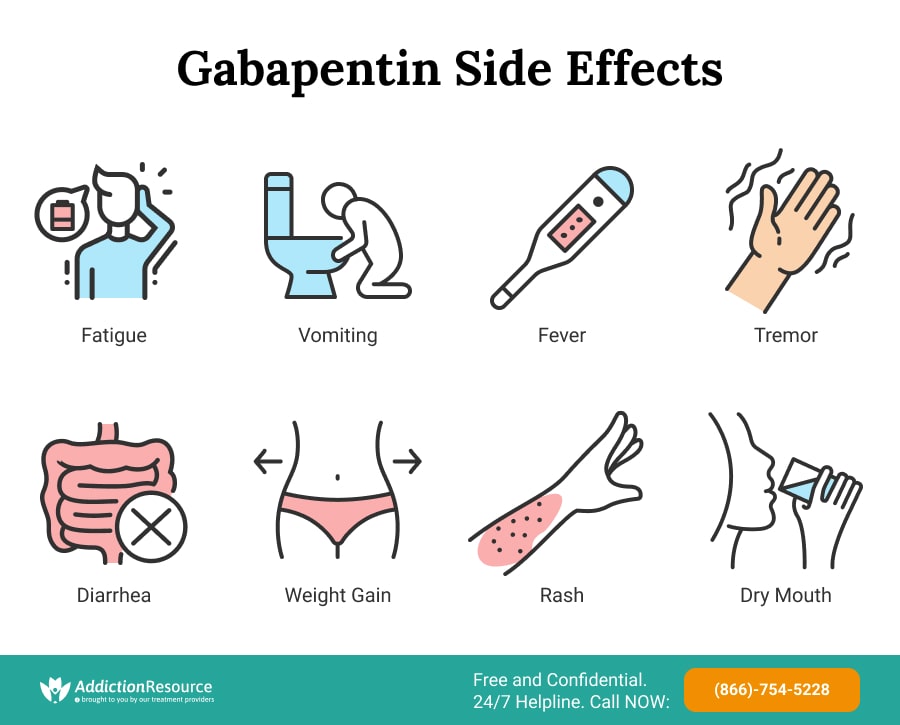
Side Effects
While metronidazole is generally well-tolerated, it can cause several side effects, including:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal cramps
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Metallic taste
- Darkening of urine
Rare but serious side effects include seizures, peripheral neuropathy (numbness or weakness in hands and feet), and anaphylaxis.
Interactions
Metronidazole can interact with several medications, including:
- Alcohol: Concurrent use can lead to a disulfiram-like reaction (nausea, vomiting, flushing).
- Warfarin: Can increase the risk of bleeding by enhancing the anticoagulant effect.
- Lithium: May increase lithium levels, leading to toxicity.
- Phenytoin: Can increase phenytoin levels, potentially leading to toxicity.
Contraindications
Metronidazole is contraindicated in patients with:
- Known hypersensitivity to metronidazole or other nitroimidazole derivatives.
- First trimester of pregnancy due to potential risks to the fetus.
- Breastfeeding, as it can be secreted in breast milk, although the American Academy of Pediatrics states that it is usually compatible with nursing.
Conclusion
Metronidazole 500 mg is an effective and widely used antibiotic and antiprotozoal medication. Its broad spectrum of activity makes it a valuable treatment option for various infections. However, like all medications, it should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional, considering its potential side effects, interactions, and contraindications to ensure safe and effective treatment.
What is the typical dosage of metronidazole for treating bacterial vaginosis?
+The typical dosage for bacterial vaginosis is 500 mg twice daily for 7 days.
Can metronidazole interact with alcohol?
+Yes, taking metronidazole with alcohol can lead to a disulfiram-like reaction, which includes symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and flushing.
Is metronidazole safe during pregnancy?
+Metronidazole should be used with caution during pregnancy, and it is contraindicated in the first trimester due to potential risks to the fetus. Its use in later trimesters should be under strict medical supervision.
What are common side effects of metronidazole?
+Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, abdominal cramps, headache, and a metallic taste.
Can metronidazole treat all types of infections?
+No, metronidazole is specifically used for treating infections caused by susceptible bacteria and protozoa. It is not effective against all types of infections and should only be used as directed by a healthcare provider.