Newborn Vital Signs: Monitor Health Easily
Monitoring a newborn’s vital signs is a crucial aspect of ensuring their health and wellbeing. Immediately after birth, healthcare providers assess a newborn’s overall condition using the Apgar score, which evaluates heart rate, muscle tone, reflexes, breathing effort, and skin color. This initial assessment provides valuable insights into the newborn’s transition to life outside the womb. However, ongoing monitoring of vital signs is essential for detecting any potential issues early on.
Understanding Newborn Vital Signs
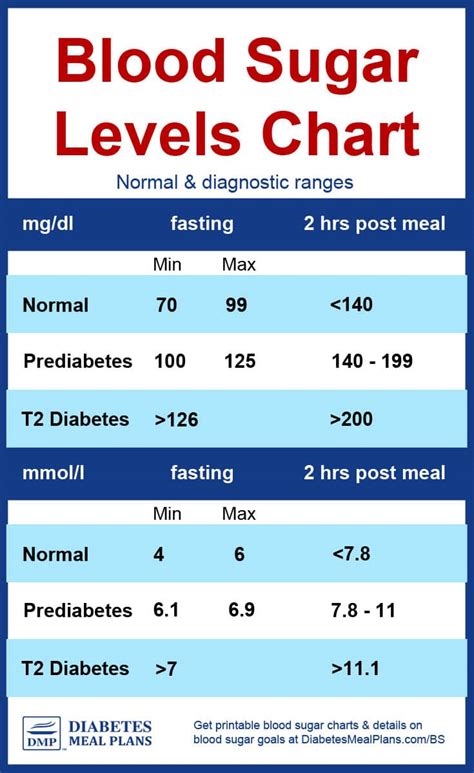
Newborn vital signs include heart rate, respiratory rate, blood pressure, temperature, and oxygen saturation. Each of these signs provides critical information about the newborn’s cardiovascular, respiratory, and overall physiological health.
- Heart Rate: Newborns have a higher heart rate compared to adults, typically ranging from 100 to 160 beats per minute. Monitoring heart rate helps in assessing the newborn’s cardiovascular health and detecting any signs of distress or infection.
- Respiratory Rate: The normal respiratory rate for newborns is between 30 to 60 breaths per minute. This rate is higher than in adults due to the smaller lung capacity and higher metabolic rate of newborns. Monitoring breathing rate is crucial for identifying respiratory issues.
- Blood Pressure: While not as commonly monitored in newborns as other vital signs, blood pressure is critical in certain situations, such as in premature infants or those with suspected cardiovascular issues. Normal blood pressure values in newborns vary based on age, weight, and gestation.
- Temperature: Maintaining a stable body temperature is vital for newborns, as they can quickly lose heat due to their high surface area to volume ratio. The normal temperature range is between 97.7°F and 99.5°F (36.5°C to 37.5°C).
- Oxygen Saturation: This measures the percentage of hemoglobin binding sites in the bloodstream occupied by oxygen. Normal oxygen saturation levels for newborns are typically above 95%.
Methods of Monitoring
Healthcare providers use various methods to monitor these vital signs, ranging from simple observations to the use of sophisticated medical devices.
- Heart Rate and Respiratory Rate: These can often be assessed through observation or by listening with a stethoscope.
- Blood Pressure: Automated blood pressure monitors or Doppler devices are used, especially in critical care situations.
- Temperature: Digital thermometers or temperature probes are common tools.
- Oxygen Saturation: Pulse oximetry, a non-invasive method using a probe typically placed on the newborn’s foot or hand, is widely used.
Importance of Continuous Monitoring
Continuous monitoring of newborn vital signs is critical, especially in the first few days of life and in newborns admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU). This ongoing assessment allows healthcare providers to:
- Detect Issues Early: Prompt identification of abnormalities in vital signs can lead to early intervention, potentially preventing severe complications.
- Adjust Care Plans: Monitoring vital signs helps in tailoring the care plan to the individual needs of the newborn, ensuring that they receive the most appropriate treatment.
- Reassure Parents: For newborns without complications, regular monitoring can provide reassurance to parents about their baby’s health, helping to reduce anxiety and promote bonding.
Role of Parents in Monitoring
While healthcare providers are responsible for the medical monitoring of newborns, parents play a vital role in observing their baby’s overall condition and reporting any concerns.
- Observing Behavior: Changes in feeding patterns, sleep, or behavior can be indicators of underlying issues.
- Reporting Concerns: Parents should communicate any concerns they have about their newborn’s health to their healthcare provider promptly.
Emerging Trends and Technologies
The field of neonatal care is evolving, with advancements in technology aimed at improving the monitoring and care of newborns. For example:
- Wearable Devices: Some hospitals are beginning to use wearable devices that can continuously monitor a newborn’s vital signs, providing real-time data to healthcare providers.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI algorithms can analyze data from vital sign monitors to predict potential issues before they become critical, allowing for preemptive care.
Conclusion
Monitoring newborn vital signs is a foundational aspect of neonatal care, enabling healthcare providers to ensure the health and wellbeing of newborns. Through a combination of traditional monitoring methods and emerging technologies, the care provided to newborns continues to improve. As with any aspect of healthcare, ongoing research and innovation are key to advancing our understanding and capabilities in this critical area.
What are the normal vital sign ranges for a newborn?
+Newborn vital signs include heart rate (100-160 beats per minute), respiratory rate (30-60 breaths per minute), blood pressure (varies by age, weight, and gestation), temperature (97.7°F to 99.5°F or 36.5°C to 37.5°C), and oxygen saturation (above 95%).
Why is continuous monitoring of newborn vital signs important?
+Continuous monitoring allows for the early detection of issues, adjustment of care plans, and reassurance for parents. It is especially critical in the first few days of life and for newborns in the NICU.
What role do parents play in monitoring their newborn’s health?
+Parents should observe their newborn’s behavior, including feeding patterns, sleep, and overall condition, and report any concerns to their healthcare provider. This collaboration is vital for ensuring the newborn receives appropriate care.