Mole Removal: Effective Treatment Options
The decision to remove a mole can be motivated by a variety of factors, including aesthetic concerns, health risks, or a combination of both. Moles, also known as melanocytic nevi, are common skin growths that can appear anywhere on the body. While most moles are benign (non-cancerous), some can be precancerous or cancerous, making their removal a crucial step in maintaining skin health. Understanding the effective treatment options for mole removal is essential for those considering this procedure.
Understanding Moles
Before diving into the treatment options, it’s crucial to understand what moles are and how they can impact skin health. Moles are growths on the skin that are usually brown or black and can be flat or raised. They are formed due to a cluster of melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing pigment in the skin. Most moles appear during childhood and adolescence, but new moles can appear in adulthood as well.
Indications for Mole Removal
The decision to remove a mole is typically based on two main reasons: cosmetic concerns and health risks. From a cosmetic standpoint, moles can be considered unsightly, especially if they are located in visible areas such as the face or neck. On the other hand, some moles can pose health risks if they are precancerous or cancerous. The ABCDE rule is a useful guide for determining if a mole might be cancerous: - Asymmetry: One half of the mole does not match the other half. - Border: The edges are irregular, ragged, or blurred. - Color: The color is not uniform and may include shades of brown, black, and tan. - Diameter: The mole is larger in diameter than the eraser on an end of a pencil. - Evolving: The mole is changing in size, shape, or color.
Treatment Options for Mole Removal
There are several effective treatment options for mole removal, each with its own set of advantages and considerations. The choice of treatment depends on the size, location, and type of mole, as well as the patient’s overall health and preferences.
1. Surgical Excision
Surgical excision is a common method for removing moles. It involves numbing the area around the mole with a local anesthetic and then cutting out the mole and a small margin of skin around it. The wound is then closed with stitches. This method is particularly recommended for moles that are suspected to be cancerous, as it allows for a thorough examination of the mole tissue.
2. Shave Excision
Shave excision is another technique used for mole removal. Unlike surgical excision, it does not require stitches. The mole is shaved off with a special tool, and the area is then cauterized to stop any bleeding. This method is more superficial and is usually recommended for moles that are raised above the skin surface and are not suspected to be cancerous.
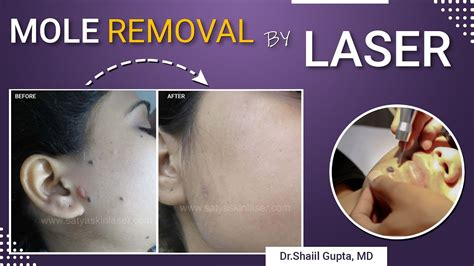
3. Laser Removal
Laser removal is a non-invasive method that uses high-energy light beams to break up the pigment in the mole. This method is best suited for small, flat moles that are not suspected to be cancerous. It may require multiple sessions and can be less effective for larger or deeper moles.
Recovery and Aftercare
Regardless of the method chosen for mole removal, proper recovery and aftercare are crucial for minimizing the risk of complications and ensuring the best possible outcome. Patients are usually advised to keep the wound area clean and dry, apply topical antibiotics as directed, and avoid heavy lifting, bending, or strenuous activities for a period of time following the procedure.
Risks and Complications
While mole removal is generally a safe procedure, there are potential risks and complications to be aware of. These can include infection, scarring, bleeding, and changes in skin sensation. In rare cases, mole removal can also lead to nerve damage. It’s essential to discuss these risks with a healthcare provider before undergoing the procedure.
Conclusion
Mole removal can be a straightforward and effective way to address aesthetic concerns or eliminate potential health risks. With various treatment options available, it’s crucial to consult with a dermatologist or a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action based on individual circumstances. By understanding the indications for mole removal, the available treatment options, and the necessary aftercare, individuals can make informed decisions about their skin health.
What are the main reasons for removing a mole?
+The main reasons for removing a mole are cosmetic concerns and health risks. Moles can be considered unsightly, and some can pose health risks if they are precancerous or cancerous.
How do I determine if a mole is cancerous?
+You can use the ABCDE rule to determine if a mole might be cancerous. The rule checks for asymmetry, border irregularity, color variation, diameter larger than the eraser on a pencil, and evolving changes in size, shape, or color.
What are the common methods for mole removal?
+The common methods for mole removal include surgical excision, shave excision, and laser removal. The choice of method depends on the size, location, and type of mole, as well as the patient’s overall health and preferences.
What is the recovery process like after mole removal?
+The recovery process after mole removal involves keeping the wound area clean and dry, applying topical antibiotics as directed, and avoiding heavy lifting, bending, or strenuous activities for a period of time. It’s essential to follow the aftercare instructions provided by the healthcare provider to minimize the risk of complications.