New Covid Variants
The emergence of new Covid variants has become a pressing concern globally, as these mutations can potentially evade existing immunity and affect the efficacy of vaccines. Understanding the dynamics of these variants, their implications, and the strategies to combat them is crucial for public health.
One of the key factors contributing to the emergence of new variants is the high rate of transmission of the virus. As Covid-19 spreads, it undergoes mutations, some of which can lead to changes in its transmissibility, severity, or ability to evade the immune system. The World Health Organization (WHO) and other global health authorities closely monitor these developments, categorizing variants based on their potential impact on public health.
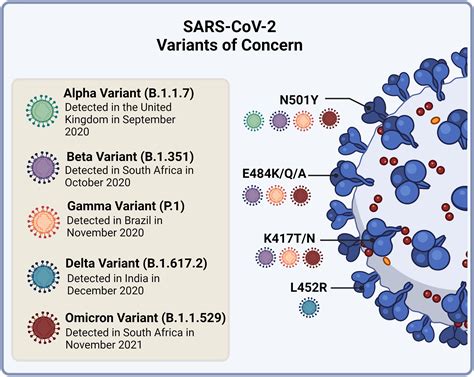
Variants of Concern
Variants of concern are those that have been shown to have significant implications for public health, either because they are more transmissible, cause more severe disease, or have the potential to evade immune responses generated by vaccines or previous infections. The most notable variants of concern include the Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, and Omicron variants, each with distinct characteristics and global distribution.
- Alpha Variant: First identified in the United Kingdom, this variant showed increased transmissibility compared to the original strain of the virus.
- Beta Variant: Detected in South Africa, it presented concerns regarding its ability to partially evade the immune system.
- Gamma Variant: Identified in Brazil, it also raised concerns about immune evasion and increased transmissibility.
- Delta Variant: Originating from India, the Delta variant was found to be significantly more transmissible than the previous variants and contributed to a surge in cases worldwide.
- Omicron Variant: First detected in South Africa, Omicron has multiple mutations that suggest a potential for increased transmissibility and immune evasion, although its severity appears to be less than that of Delta.
Impact on Vaccines and Immunity
The development of vaccines against Covid-19 has been a critical component of the global response to the pandemic. However, the emergence of new variants has raised questions about the durability and breadth of vaccine-induced immunity. Most vaccines have been shown to retain effectiveness against severe disease and hospitalization caused by the variants, albeit with slightly reduced efficacy against mild and asymptomatic infections.
It's essential to understand that while vaccine efficacy may decrease against new variants, protection against severe outcomes generally remains robust. Booster shots and updated vaccine formulations are being developed to address the evolving landscape of the virus.
Public Health Response
In response to new variants, public health strategies are evolving to include enhanced surveillance, rapid genomic sequencing to identify and track variants, and adjustments in vaccination strategies, such as booster doses and variant-specific vaccines. Additionally, non-pharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) like mask-wearing, social distancing, and travel restrictions remain crucial tools in managing outbreaks and slowing the spread of the virus.
Preparing for the Future
Preparing for future variants involves a multi-faceted approach, including continued investment in vaccine development, enhancing global surveillance and data sharing, and promoting public health measures to reduce transmission. The development of pan-coronavirus vaccines that could offer protection against a wide range of coronaviruses is also under investigation.
Steps to Combat New Variants:
- Stay Informed: Follow credible sources for updates on new variants and public health guidelines.
- Vaccination: Get vaccinated and consider booster shots as recommended by health authorities.
- Adhere to NPIs: Continue practicing mask-wearing, social distancing, and good hygiene.
- Support Global Efforts: Advocate for international cooperation in surveillance, research, and vaccine distribution.
Future Trends Projection
As we move forward, the trend suggests that Covid-19 will become endemic, meaning it will continue to circulate but potentially at lower levels as immunity builds within populations. The key to managing this endemic phase will be continued vigilance, adaptation of public health strategies, and advancements in medical and vaccination technologies.
How often will new Covid variants emerge?
+New variants will likely continue to emerge as the virus evolves. The rate at which they emerge and their potential impact will depend on various factors, including vaccination rates and public health measures.
What can individuals do to protect themselves from new variants?
+Individuals can protect themselves by getting vaccinated, following public health guidelines, practicing good hygiene, and staying informed about the latest developments and recommendations from health authorities.
In conclusion, the emergence of new Covid variants represents an ongoing challenge in the fight against the pandemic. Through continued scientific research, global cooperation, and adherence to public health strategies, we can work towards mitigating the impact of these variants and navigating the pandemic towards a more manageable endemic phase.