Normal Blood Sugar Range
Maintaining a normal blood sugar range is crucial for overall health and well-being. Blood sugar, also known as glucose, is the primary source of energy for the body’s cells. When we eat, our body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. The pancreas, a small organ located behind the stomach, releases insulin to help regulate blood sugar levels. Insulin acts as a key, allowing glucose to enter the cells and provide them with the necessary energy.
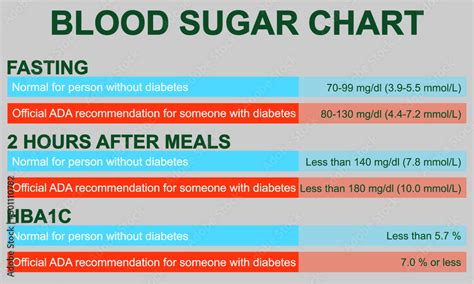
The normal blood sugar range varies throughout the day, depending on factors such as the time of day, the type and quantity of food consumed, and the individual’s physical activity level. Generally, a normal blood sugar range is considered to be between 70 and 140 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). However, it’s essential to note that these values can fluctuate depending on the individual and their specific circumstances.
For people without diabetes, the normal blood sugar range is typically as follows:
- Fasting blood sugar: 70-100 mg/dL (after an overnight fast of at least 8 hours)
- After meals: Less than 140 mg/dL (1-2 hours after eating)
- Before meals: 70-130 mg/dL
It’s also important to understand that blood sugar levels can be affected by various factors, such as:
- Food intake: Consuming high-carbohydrate or high-sugar foods can cause blood sugar levels to rise.
- Physical activity: Regular exercise can help lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Stress: Stress can cause blood sugar levels to increase due to the release of stress hormones like cortisol.
- Sleep: Poor sleep quality and duration can disrupt blood sugar regulation.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as steroids and certain psychiatric medications, can affect blood sugar levels.
Monitoring blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes, as it helps them manage their condition and prevent complications. There are several ways to monitor blood sugar levels, including:
- Fingerstick testing: This involves pricking the finger with a lancet to collect a small blood sample, which is then placed on a test strip and read with a glucose meter.
- Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM): This involves wearing a small device that tracks blood sugar levels throughout the day and night.
- Urine testing: This involves testing urine for ketones, which can indicate high blood sugar levels.
Maintaining a normal blood sugar range is essential for preventing long-term complications, such as:
- Nerve damage: High blood sugar levels can damage the nerves, leading to numbness, tingling, and pain.
- Kidney damage: High blood sugar levels can damage the kidneys, leading to kidney failure.
- Eye damage: High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to vision problems and even blindness.
- Heart disease: High blood sugar levels can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.
In addition to monitoring blood sugar levels, there are several lifestyle changes that can help maintain a normal blood sugar range, including:
- Eating a healthy diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods, such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Exercising regularly: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week.
- Staying hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Getting enough sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night to help regulate blood sugar levels.
In conclusion, maintaining a normal blood sugar range is crucial for overall health and well-being. By understanding the factors that affect blood sugar levels and making lifestyle changes to manage them, individuals can reduce their risk of long-term complications and maintain optimal health.
What is the normal blood sugar range for people without diabetes?
+The normal blood sugar range for people without diabetes is typically between 70 and 140 mg/dL. However, this can vary depending on the individual and their specific circumstances.
How can I maintain a normal blood sugar range?
+To maintain a normal blood sugar range, focus on eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, staying hydrated, and getting enough sleep. It's also essential to monitor your blood sugar levels regularly and make lifestyle changes as needed.
What are the risks of high blood sugar levels?
+High blood sugar levels can increase the risk of long-term complications, such as nerve damage, kidney damage, eye damage, and heart disease. It's essential to maintain a normal blood sugar range to prevent these complications.
By following these guidelines and making lifestyle changes to maintain a normal blood sugar range, individuals can reduce their risk of long-term complications and maintain optimal health. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice on managing blood sugar levels.


