Normal Blood Sugar: Stay Healthy With Target Ranges
Understanding normal blood sugar levels is crucial for maintaining overall health, as both high and low blood sugar can lead to significant health complications. The body’s primary source of energy is glucose, a simple sugar found in the food we eat. The level of glucose in the blood is tightly regulated by insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, and other hormones. In this article, we will delve into what constitutes normal blood sugar levels, how to measure and manage them, and the implications of deviating from these target ranges.
What are Normal Blood Sugar Levels?
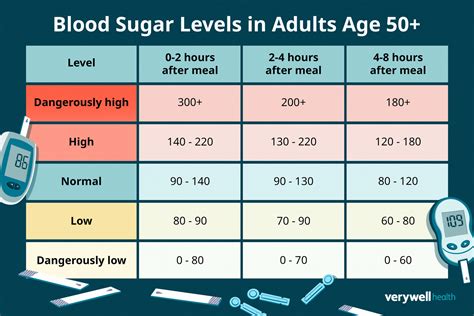
Normal blood sugar levels vary throughout the day, depending on when you last ate and what you ate. Generally, a normal fasting blood glucose level is between 70 and 99 mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter). After eating, blood glucose levels typically rise and may peak at around 120-140 mg/dL about 1-2 hours after a meal, before returning to the pre-meal levels due to insulin action.
Measuring Blood Sugar Levels
Blood glucose levels are measured using a small device called a glucometer, which requires a small drop of blood obtained by pricking the skin with a lancet. The blood is then placed on a test strip inserted into the glucometer, which gives a reading of the blood glucose level in mg/dL. Continuous glucose monitoring systems (CGMS) are also available, which involve wearing a small sensor under the skin to track glucose levels throughout the day.
Factors Influencing Blood Sugar Levels
Several factors can influence blood sugar levels, including diet, physical activity, stress levels, certain medications, and the presence of underlying health conditions such as diabetes. Foods that are high in simple sugars and low in fiber can cause spikes in blood sugar, while regular physical activity can help improve insulin sensitivity, reducing blood sugar levels.
Health Implications of High and Low Blood Sugar
Both high (hyperglycemia) and low (hypoglycemia) blood sugar levels can have serious health implications. Hyperglycemia can lead to diabetes, damage nerves, and increase the risk of heart disease and stroke over time. Hypoglycemia can cause confusion, dizziness, and in severe cases, loss of consciousness or even death.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels
Managing blood sugar levels involves a combination of diet, exercise, and, for those with diabetes, medication. Eating a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help keep blood sugar levels stable. Regular physical activity, such as walking or more intense exercise, also plays a crucial role. For those with diabetes, following a treatment plan as prescribed by a healthcare provider is essential.
Strategies for Healthy Blood Sugar Levels
- Eat Regular Meals: Skipping meals can lead to low blood sugar, while eating too much can cause high blood sugar. Aim for balanced meals and snacks.
- Choose Low Glycemic Index Foods: Foods with a low glycemic index (GI) release glucose more slowly into the bloodstream, helping to keep blood sugar levels stable.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water can help the kidneys remove excess sugar from the blood.
- Limit Sugary Drinks: Beverages high in sugar can cause spikes in blood sugar.
- Monitor and Manage Stress: High levels of stress can increase blood sugar levels. Engaging in stress-reducing activities like yoga or meditation can help.
Conclusion
Maintaining normal blood sugar levels is vital for overall health and can be achieved through a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and for some, adhering to a prescribed treatment plan. Understanding the factors that influence blood sugar and taking proactive steps to manage them can help prevent the complications associated with abnormal blood sugar levels.
What are the normal ranges for blood sugar levels after eating?
+After eating, blood glucose levels may peak at around 120-140 mg/dL about 1-2 hours later, before returning to pre-meal levels due to insulin action. However, for individuals with diabetes, these target ranges may vary based on the type of diabetes and the individual's specific treatment plan.
How does exercise affect blood sugar levels?
+Exercise can help improve insulin sensitivity, lowering blood sugar levels. Regular physical activity can also reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. It's important for those with diabetes to consult with their healthcare provider to develop an exercise plan that works with their treatment strategy.
What are the symptoms of high and low blood sugar?
+High blood sugar (hyperglycemia) symptoms can include increased thirst and urination, blurred vision, and headaches. Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) can cause shakiness, dizziness, sweating, hunger, irritability, confusion, or even loss of consciousness in severe cases. It's crucial to recognize these symptoms to take appropriate action.
In summary, maintaining normal blood sugar levels is a multifaceted endeavor that involves awareness, proactive lifestyle choices, and, for some, adherence to a treatment plan. By understanding the factors that influence blood sugar levels and taking steps to manage them, individuals can mitigate the risk of complications and stay healthy.



