Pantoprazole 40 Mg Uses
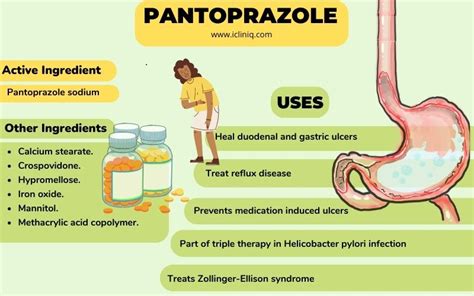
Pantoprazole, a proton pump inhibitor (PPI), is widely used for its efficacy in reducing stomach acid production. The 40 mg dosage is a commonly prescribed strength for various gastrointestinal conditions. Understanding the uses of pantoprazole 40 mg involves delving into its therapeutic applications, which are grounded in its ability to decrease the amount of acid produced by the stomach.
Introduction to Pantoprazole
Pantoprazole belongs to a class of medications known as proton pump inhibitors. It works by irreversibly inhibiting the H+/K+ ATPase (proton pump) in the gastric parietal cells. By doing so, it effectively blocks the final step of acid production, thus reducing gastric acidity. This mechanism of action underlies its utility in treating conditions characterized by excessive stomach acid.
Therapeutic Uses of Pantoprazole 40 Mg
The primary therapeutic uses of pantoprazole 40 mg include:
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): GERD is a condition where stomach acid frequently flows back into the tube connecting the mouth and stomach (esophagus). This backwash (acid reflux) can irritate the lining of the esophagus, causing discomfort. Pantoprazole 40 mg is often prescribed to reduce acid production, thereby alleviating symptoms such as heartburn and difficulty swallowing.
Erosive Esophagitis: This condition involves the erosion of the esophagus lining due to acid reflux. Pantoprazole can help heal the esophagus and prevent further erosion by reducing stomach acid.
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome: This rare disorder is characterized by one or more tumors (gastrinomas) in the pancreas or upper part of the small intestine (duodenum), leading to excessive acid production. Pantoprazole 40 mg can be used to manage the symptoms associated with excessive acid production in this condition.
Duodenal Ulcer: Duodenal ulcers are sores that develop on the inside lining of the duodenum, often due to increased stomach acid. By reducing acid production, pantoprazole 40 mg can help in healing these ulcers.
Prevention of NSAID-Induced Ulcers: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can cause stomach ulcers in some individuals. Pantoprazole 40 mg may be prescribed to prevent ulcers in patients who require long-term NSAID therapy.
Administration and Considerations
Pantoprazole 40 mg is typically administered orally, once daily, usually in the morning, before meals. It’s essential to follow the prescription instructions carefully, as the timing and dosage can influence the drug’s effectiveness. Additionally, patients should be aware of potential side effects, such as headache, diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting, although these are generally mild and temporary.
Interactions and Precautions
Pantoprazole can interact with other medications, including warfarin, atazanavir, and methotrexate, among others. It’s crucial for patients to inform their healthcare provider about all the medications they are taking. Moreover, long-term use of PPIs like pantoprazole has been associated with an increased risk of osteoporosis-related fractures and magnesium deficiency, among other potential risks.
Conclusion
Pantoprazole 40 mg is a valuable treatment option for various gastrointestinal disorders characterized by excessive acid production. Its efficacy in reducing stomach acid makes it an essential medication for managing conditions like GERD, erosive esophagitis, and duodenal ulcers. However, patients should be aware of the potential side effects, drug interactions, and precautions associated with its use to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Frequent Questions About Pantoprazole 40 Mg
What is the most common use of pantoprazole 40 mg?
+Pantoprazole 40 mg is most commonly used to treat conditions like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and erosive esophagitis by reducing stomach acid production.
Can pantoprazole 40 mg be used for ulcer prevention in patients taking NSAIDs?
+Yes, pantoprazole 40 mg can be prescribed to prevent ulcers in patients who require long-term therapy with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), as these drugs can increase the risk of developing stomach ulcers.
What are the potential long-term risks of taking pantoprazole 40 mg?
+Long-term use of pantoprazole 40 mg has been associated with an increased risk of osteoporosis-related fractures, magnesium deficiency, and potentially other risks. It’s essential to discuss these risks with a healthcare provider.