What Is Normal Blood Sugar? Levels Chart Explained
Understanding blood sugar levels is crucial for maintaining good health, particularly for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. Blood sugar, also known as glucose, is the primary source of energy for the body’s cells. The level of glucose in the blood is tightly regulated by the body’s internal mechanisms, primarily through the actions of insulin and glucagon, hormones produced by the pancreas.
What are Normal Blood Sugar Levels?
Normal blood sugar levels vary throughout the day, depending on when you last ate and what you consumed. Generally, for individuals without diabetes, normal blood sugar levels are as follows:
- Fasting blood sugar levels are typically between 70 to 99 mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter). Fasting means that you haven’t eaten for at least 8 hours.
- After eating (postprandial), blood sugar levels should be less than 140 mg/dL. This measurement is usually taken 2 hours after eating.
For people with diabetes, the American Diabetes Association recommends the following targets for blood glucose levels:
- Before meals, levels should be between 70 and 130 mg/dL.
- After meals (1-2 hours after eating), levels should be less than 180 mg/dL.
Why is it Important to Maintain Normal Blood Sugar Levels?
Maintaining blood sugar levels within the normal range is crucial for several reasons:
- Prevents Diabetes Complications: High blood sugar levels over time can lead to complications such as heart disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, and vision problems.
- Maintains Energy: Glucose is the body’s primary energy source. Proper levels ensure that your body functions optimally.
- Supports Weight Management: Avoiding high blood sugar spikes can help in managing weight, as it prevents excessive insulin release, which can lead to fat storage.
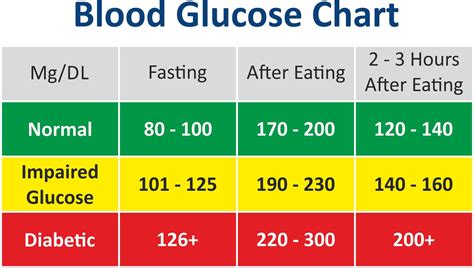
Blood Sugar Levels Chart
The following chart is a simplified guide to understanding blood sugar levels:
| Time/Condition | Normal Range | Prediabetes | Diabetes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fasting | 70-99 mg/dL | 100-125 mg/dL | 126 mg/dL or higher |
| 1 hour after eating | <140 mg/dL | 140-199 mg/dL | 200 mg/dL or higher |
| 2 hours after eating | <140 mg/dL | 140-199 mg/dL | 200 mg/dL or higher |
How to Maintain Normal Blood Sugar Levels
Maintaining normal blood sugar levels involves a combination of a healthy diet, regular physical activity, and, if necessary, medication. Here are some tips:
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water can help keep your blood sugar levels stable.
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity can help lower your blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Monitor Your Levels: Regularly checking your blood sugar can help you understand how different foods and activities affect your levels.
- Manage Stress: Stress can raise your blood sugar levels. Engage in stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing blood sugar levels is crucial for everyone, but especially for those with diabetes or at risk of developing it. By maintaining healthy habits and staying informed about your blood sugar levels, you can prevent complications and ensure a healthier life. If you have specific concerns about your blood sugar levels or Diabetes management, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional.
What are the symptoms of high blood sugar levels?
+Symptoms of high blood sugar include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurred vision, cuts or wounds that are slow to heal, and tingling or numbness in the hands and feet. If you’re experiencing these symptoms, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider.
How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of checking blood sugar levels depends on the type of diabetes you have and your treatment plan. Generally, people with type 1 diabetes or those using insulin may need to check more frequently, up to 4-6 times a day, while those with type 2 diabetes might check less often, perhaps 1-3 times a day.
Can diet and exercise alone control blood sugar levels?
+For some people, especially those with prediabetes or type 2 diabetes, losing weight, following a healthy diet, and engaging in regular physical activity can help control blood sugar levels. However, this isn’t true for everyone, particularly those with type 1 diabetes, who will always require insulin therapy. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine the best management plan for your specific situation.