Pronation Of Foot Explained: Causes & Fixes
The human foot is a complex and fascinating structure, comprising 26 bones, 33 joints, and over 100 muscles, tendons, and ligaments. One of the most critical aspects of foot mechanics is pronation, which plays a vital role in our overall mobility and comfort. In this article, we will delve into the world of foot pronation, exploring its causes, effects, and most importantly, the fixes.
Understanding Pronation
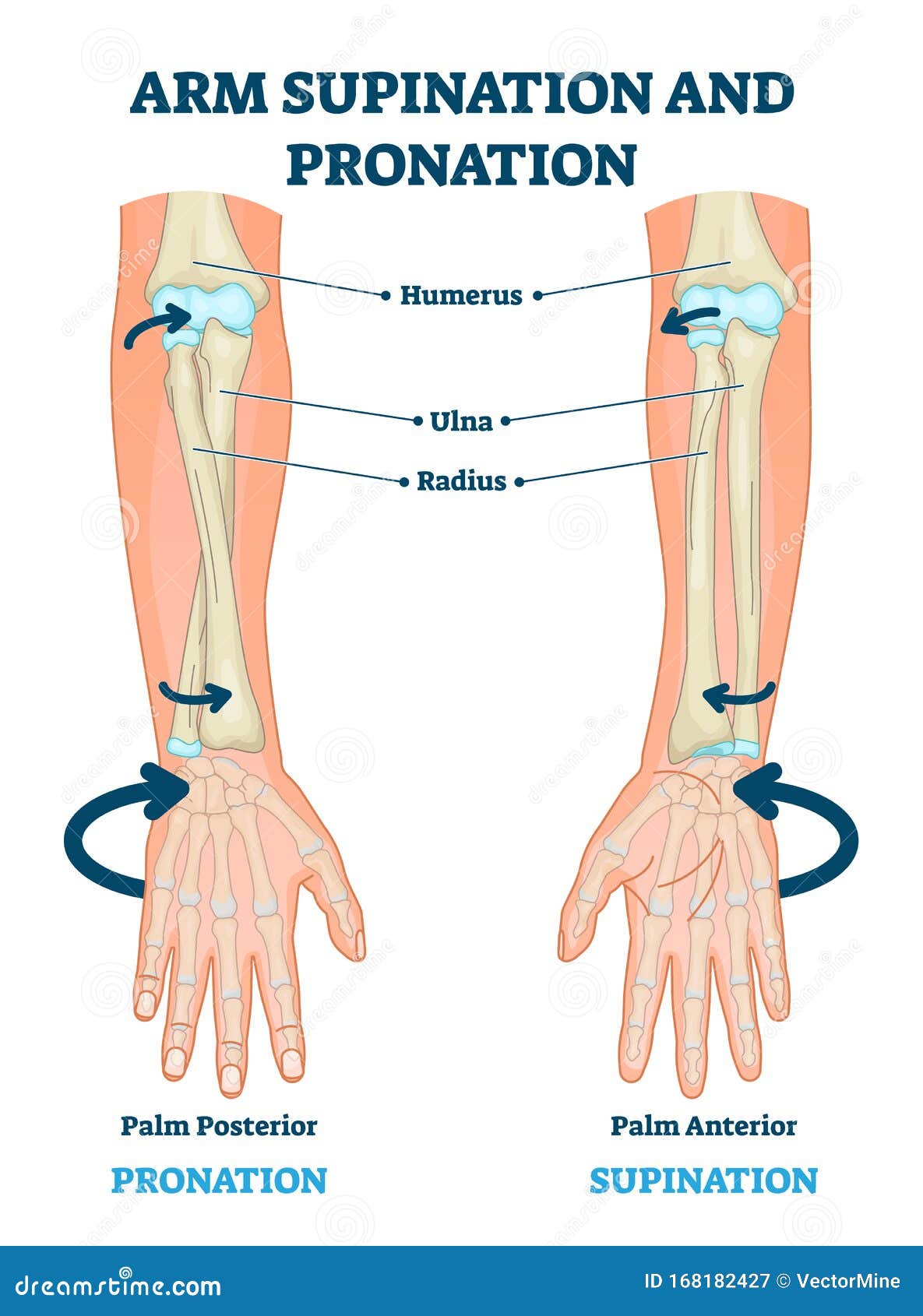
Pronation refers to the natural movement of the foot as it rolls inward and downward after heel strike, allowing the foot to adapt to the surface and distribute pressure evenly. This movement is essential for shock absorption, balance, and propulsion. However, excessive or abnormal pronation can lead to a range of issues, from mild discomfort to debilitating pain and injuries.
Types of Pronation
There are three main types of pronation: neutral, overpronation, and underpronation (supination).
- Neutral Pronation: This is the ideal type of pronation, where the foot rolls inward slightly, allowing for efficient transfer of force from the heel to the toes.
- Overpronation: This occurs when the foot rolls inward excessively, causing the arch to collapse and the ankle to rotate inward. Overpronation can lead to issues such as flat feet, plantar fasciitis, and shin splints.
- Underpronation (Supination): This is the opposite of overpronation, where the foot rolls outward, causing the arch to become rigid and the ankle to rotate outward. Underpronation can lead to issues such as high arches, ankle instability, and stress fractures.
Causes of Abnormal Pronation
Abnormal pronation can be caused by a range of factors, including:
- Genetic Predisposition: Some people may be born with a tendency towards overpronation or underpronation due to their foot shape or structure.
- Muscle Imbalances: Weak or tight muscles in the foot, ankle, or leg can disrupt the normal pronation mechanism.
- Poor Footwear: Wearing shoes that do not provide adequate support or cushioning can contribute to abnormal pronation.
- Injury or Trauma: Injuries such as ankle sprains or fractures can affect the foot’s natural pronation pattern.
- Biomechanical Issues: Abnormalities in the way the foot or leg moves, such as issues with the knee or hip, can also contribute to abnormal pronation.
Fixes for Abnormal Pronation
Fortunately, there are several fixes for abnormal pronation, including:
Orthotics and Shoe Modifications
- Custom Orthotics: These are specially designed shoe inserts that can help correct abnormal pronation by providing additional support and cushioning.
- Motion Control Shoes: These shoes are designed to limit excessive pronation and provide extra support for the foot.
- Shoe Modifications: Adding arch supports or heel cups to existing shoes can also help correct abnormal pronation.
Exercises and Stretching
- Foot Strengthening Exercises: Exercises such as toe curls and heel raises can help strengthen the muscles in the foot and ankle, improving pronation.
- Calf Stretching: Stretching the calf muscles can help reduce tension in the foot and ankle, improving pronation.
- Ankle Mobilization: Exercises that promote ankle mobility, such as ankle circles and toe spreads, can also help improve pronation.
Physical Therapy and Gait Analysis
- Gait Analysis: A professional gait analysis can help identify abnormalities in the way you walk or run, allowing for targeted interventions to correct pronation.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can provide personalized exercises and stretches to help correct abnormal pronation and improve overall foot function.
Conclusion
Pronation is a complex and multifaceted aspect of foot mechanics, and abnormal pronation can have significant effects on our comfort and mobility. By understanding the causes and fixes for abnormal pronation, we can take steps to prevent and treat related issues, improving our overall quality of life. Whether through orthotics, exercises, or physical therapy, there are many effective solutions available to help correct abnormal pronation and promote healthy, happy feet.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between overpronation and underpronation?
+Overpronation occurs when the foot rolls inward excessively, causing the arch to collapse and the ankle to rotate inward. Underpronation (supination) is the opposite, where the foot rolls outward, causing the arch to become rigid and the ankle to rotate outward.
Can abnormal pronation be caused by genetic factors?
+Yes, genetic predisposition can play a role in abnormal pronation. Some people may be born with a tendency towards overpronation or underpronation due to their foot shape or structure.
What are some effective fixes for abnormal pronation?
+Effective fixes for abnormal pronation include orthotics and shoe modifications, exercises and stretching, and physical therapy and gait analysis. Custom orthotics, motion control shoes, and shoe modifications can provide additional support and cushioning, while exercises such as foot strengthening and calf stretching can help improve pronation.