Pronation Of The Foot
Pronation of the foot is a complex and multifaceted topic that has garnered significant attention in the realms of orthopedics, podiatry, and sports medicine. At its core, pronation refers to the natural movement of the foot as it rolls inward and flattens during the weight-bearing phase of walking or running. This movement is a critical component of the gait cycle, as it allows the foot to adapt to uneven surfaces, absorb shock, and facilitate propulsion.
Understanding Pronation: A Biomechanical Perspective
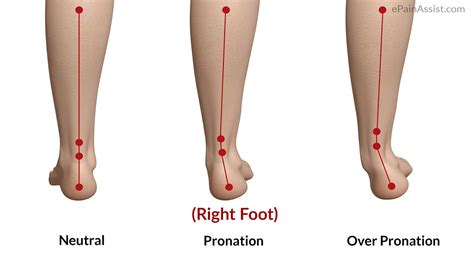
From a biomechanical standpoint, pronation is characterized by the inward rotation of the talus, the calcaneus, and the navicular bone. As the foot pronates, the arch of the foot collapses, and the medial aspect of the foot (the side closest to the midline of the body) makes contact with the ground. This movement is facilitated by the contraction of the peroneal muscles, which run along the lateral aspect of the lower leg.
Pronation is often misunderstood as being synonymous with “flat feet” or “low arches.” However, pronation is a normal and necessary movement that occurs in all feet, regardless of arch height. In fact, excessive pronation (also known as overpronation) can be just as problematic as insufficient pronation (also known as underpronation or supination).
The Consequences of Abnormal Pronation
Abnormal pronation patterns can have far-reaching consequences for the foot, ankle, and lower leg. Overpronation, for example, can lead to a range of issues, including:
- Plantar fasciitis: inflammation of the plantar fascia, a band of tissue that runs along the bottom of the foot
- Achilles tendonitis: inflammation of the Achilles tendon, which connects the calf muscles to the heel bone
- Shin splints: pain and inflammation in the lower leg, often caused by overuse or poor foot mechanics
- Knee pain: abnormal pronation patterns can place excessive stress on the knee joint, leading to pain and degenerative conditions such as osteoarthritis
On the other hand, underpronation (or supination) can also lead to problems, including:
- Ankle instability: insufficient pronation can cause the ankle joint to become unstable, leading to chronic pain and instability
- Peroneal tendonitis: inflammation of the peroneal tendons, which can cause pain and weakness in the ankle and foot
- Lateral ankle pain: pain and inflammation on the outside of the ankle, often caused by repetitive strain or poor foot mechanics
Addressing Abnormal Pronation: Treatment Options and Strategies
Fortunately, abnormal pronation patterns can be addressed through a range of treatment options and strategies. These may include:
- Orthotics and shoe modifications: custom orthotics or shoe inserts can help to redistribute pressure and stabilize the foot, reducing the risk of overpronation or underpronation
- Physical therapy: targeted exercises and stretches can help to strengthen the muscles of the foot and ankle, improving foot mechanics and reducing pain
- Footwear selection: choosing shoes that provide adequate support and stability can help to reduce the risk of abnormal pronation patterns
- Gait retraining: working with a physical therapist or healthcare professional to retrain the gait pattern can help to improve foot mechanics and reduce the risk of injury
The Role of Technology in Assessing and Addressing Pronation
In recent years, advances in technology have enabled healthcare professionals to assess and address pronation patterns with greater accuracy and precision. Some of the technologies used to assess pronation include:
- Gait analysis software: computerized systems that use cameras and sensors to track the movement of the foot and ankle during walking or running
- 3D scanning: technology that uses lasers or structured light to create a detailed, three-dimensional model of the foot
- Pressure plate analysis: systems that use sensors to measure the distribution of pressure across the foot during weight-bearing activities
These technologies can provide valuable insights into pronation patterns, enabling healthcare professionals to develop targeted treatment plans and interventions.
Conclusion
Pronation of the foot is a complex and multifaceted topic that plays a critical role in maintaining proper foot mechanics and preventing injury. By understanding the biomechanics of pronation, recognizing the consequences of abnormal pronation patterns, and utilizing advanced technologies and treatment strategies, individuals can take steps to promote healthy foot function and reduce the risk of pain and injury.
What is the difference between pronation and supination?
+Pronation refers to the inward movement of the foot as it rolls inward and flattens during weight-bearing activities. Supination, on the other hand, refers to the outward movement of the foot as it rolls outward and becomes more rigid. Both pronation and supination are normal movements that occur during the gait cycle, but excessive or insufficient movement in either direction can lead to problems.
Can pronation be improved through exercise and stretching?
+Yes, certain exercises and stretches can help to improve pronation patterns. These may include exercises that strengthen the muscles of the foot and ankle, such as toe curls and heel raises, as well as stretches that target the calf and peroneal muscles. However, it is essential to work with a healthcare professional to develop a personalized exercise program that addresses specific foot mechanics and needs.
What are the benefits of using orthotics or shoe inserts to address pronation?
+Orthotics or shoe inserts can help to redistribute pressure and stabilize the foot, reducing the risk of overpronation or underpronation. By providing additional support and stability, these devices can help to alleviate pain and inflammation, improve foot mechanics, and reduce the risk of injury. However, it is essential to work with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of treatment and to ensure that any orthotics or shoe inserts are properly fitted and customized to meet individual needs.