Right Heart Catheterization
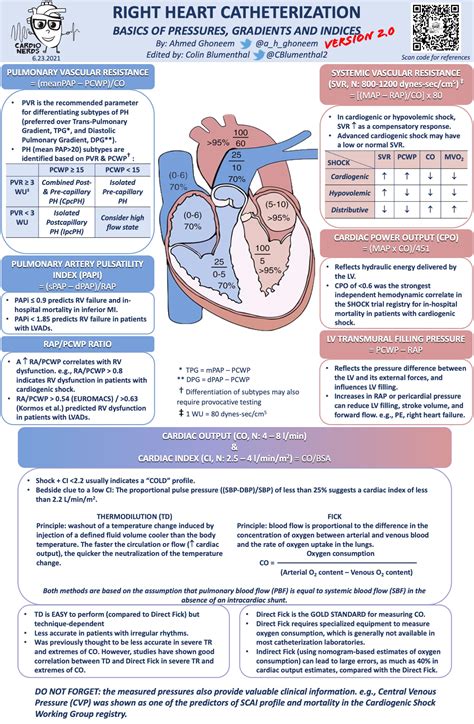
The right heart catheterization, also known as pulmonary artery catheterization, is a medical procedure that involves inserting a catheter into the right side of the heart to measure the pressure and oxygen levels in the heart and lungs. This procedure is used to diagnose and monitor various heart and lung conditions, such as heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, and cardiomyopathy.
History of Right Heart Catheterization
The concept of right heart catheterization dates back to the 18th century, when physician Stephen Hales first measured blood pressure in animals. However, it wasn’t until the 1940s and 1950s that the procedure began to gain popularity as a diagnostic tool. The development of the Swan-Ganz catheter in the 1970s revolutionized the field, allowing for more accurate and reliable measurements.
Indications for Right Heart Catheterization
Right heart catheterization is indicated in various clinical scenarios, including:
- Heart failure: To assess cardiac output, pulmonary artery pressure, and left ventricular filling pressure.
- Pulmonary hypertension: To measure pulmonary artery pressure and resistance.
- Cardiomyopathy: To evaluate left and right ventricular function.
- Cor pulmonale: To assess right ventricular function and pulmonary artery pressure.
- Congenital heart disease: To evaluate cardiac anatomy and function.
Procedure Overview
The right heart catheterization procedure involves the following steps:
- Preparation: The patient is prepared for the procedure by administering local anesthesia and sedation.
- Catheter insertion: A catheter is inserted through a vein in the neck or arm and guided to the right atrium.
- Pressure measurements: The catheter is advanced to the right ventricle and pulmonary artery, where pressure measurements are taken.
- Oxygen saturation: Oxygen saturation is measured in the pulmonary artery and other chambers of the heart.
- Blood sampling: Blood samples are taken from the pulmonary artery and other chambers to measure oxygen levels and other parameters.
- Catheter removal: The catheter is removed, and the insertion site is closed.
Technical Breakdown
The right heart catheterization procedure involves several technical aspects, including:
- Catheter design: The Swan-Ganz catheter is a balloon-tipped catheter that allows for accurate measurements of pressure and oxygen levels.
- Guidewire: A guidewire is used to guide the catheter to the desired location.
- Fluoroscopy: Fluoroscopy is used to visualize the catheter and guide it to the correct position.
- Pressure transducers: Pressure transducers are used to measure pressure in the heart and lungs.
Comparative Analysis
Right heart catheterization is compared to other diagnostic procedures, such as:
- Echocardiography: Echocardiography is a non-invasive procedure that uses ultrasound to visualize the heart.
- Cardiac MRI: Cardiac MRI is a non-invasive procedure that uses magnetic resonance imaging to visualize the heart.
- Cardiac CT: Cardiac CT is a non-invasive procedure that uses computed tomography to visualize the heart.
Myth vs. Reality
There are several myths and misconceptions surrounding right heart catheterization, including:
- Myth: Right heart catheterization is a painful procedure.
- Reality: The procedure is typically well-tolerated, and local anesthesia and sedation are used to minimize discomfort.
- Myth: Right heart catheterization is only used for heart failure.
- Reality: The procedure is used to diagnose and monitor a wide range of heart and lung conditions.
FAQ Section
What are the risks and complications of right heart catheterization?
+The risks and complications of right heart catheterization include bleeding, infection, and damage to the heart or lungs. However, these risks are rare and can be minimized with proper technique and patient selection.
How long does the right heart catheterization procedure take?
+The procedure typically takes 30-60 minutes to complete, depending on the complexity of the procedure and the patient's condition.
What are the benefits of right heart catheterization?
+The benefits of right heart catheterization include accurate diagnosis and monitoring of heart and lung conditions, as well as the ability to guide treatment and improve patient outcomes.
Future Trends Projection
The future of right heart catheterization is expected to involve advances in technology, including:
- Miniaturization: The development of smaller and more advanced catheters that can provide more accurate measurements.
- Imaging: The use of advanced imaging techniques, such as MRI and CT, to guide the procedure and provide more detailed information.
- Robotics: The use of robotic systems to perform the procedure, which can improve accuracy and reduce complications.
Conclusion
Right heart catheterization is a valuable diagnostic tool that provides accurate and reliable measurements of pressure and oxygen levels in the heart and lungs. The procedure is used to diagnose and monitor a wide range of heart and lung conditions and is an essential part of cardiovascular medicine. As technology continues to evolve, right heart catheterization is expected to play an increasingly important role in the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular disease.