Strep Throat: Symptoms & Treatment
Strep throat, also known as streptococcal pharyngitis, is a highly contagious infection caused by the group A Streptococcus bacteria. It is a common illness that affects people of all ages, but it is most prevalent among children and adolescents. Strep throat can lead to severe complications if left untreated, making prompt diagnosis and treatment crucial.
Understanding Strep Throat
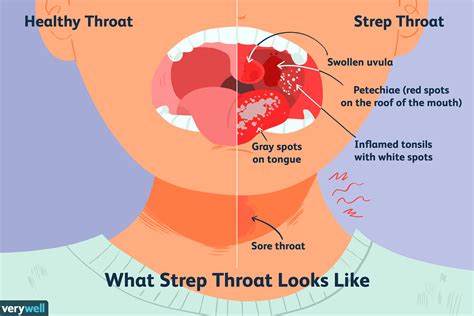
Strep throat is characterized by a severe sore throat, accompanied by a high fever, swollen lymph nodes, and white patches on the tonsils. The infection can spread through direct contact with someone who has the infection, such as sharing food or drinks, or by touching surfaces that have the bacteria on them and then touching one’s mouth or face. The incubation period for strep throat is typically two to five days, and the infected person can spread the bacteria to others during this time, even before symptoms appear.
Causes and Risk Factors
The primary cause of strep throat is the group A Streptococcus bacteria. Several factors can increase the risk of developing strep throat, including:
- Age: Children and adolescents are more susceptible to strep throat due to their developing immune systems and frequent exposure to other children who may be infected.
- Exposure: Direct contact with someone who has strep throat increases the risk of infection.
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with chronic illnesses or taking immunosuppressive medications, are more likely to develop strep throat.
- Poor Hygiene: Failure to practice good hygiene, such as not washing hands regularly, can contribute to the spread of the infection.
Symptoms of Strep Throat
The symptoms of strep throat can vary from person to person, but they often include:
- Severe Sore Throat: A sharp, stabbing pain in the throat that worsens when swallowing.
- High Fever: A temperature of 101°F (38.3°C) or higher.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: Enlarged lymph nodes in the neck, which can be tender to the touch.
- White Patches on the Tonsils: Small, white patches or streaks on the tonsils, which can indicate the presence of the bacteria.
- Headache: A severe headache that can be accompanied by fatigue and general feeling of being unwell.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Some individuals, especially children, may experience nausea and vomiting.
Diagnostic Tests for Strep Throat
A definitive diagnosis of strep throat requires a physical examination and one or more of the following diagnostic tests:
- Rapid Strep Test (RST): A quick test that involves swabbing the throat to collect a sample, which is then tested for the presence of the group A Streptococcus bacteria. The results are typically available within minutes.
- Throat Culture: A test that involves swabbing the throat to collect a sample, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. The results can take 24 to 48 hours.
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Test: A molecular test that detects the genetic material of the group A Streptococcus bacteria.
Treatment Options for Strep Throat
Treatment for strep throat typically involves antibiotics, which are effective in killing the bacteria and reducing the risk of complications. The following are common treatment options:
- Penicillin: A commonly prescribed antibiotic for strep throat, which is effective in killing the bacteria and reducing symptoms.
- Amoxicillin: A broad-spectrum antibiotic that is often prescribed for children and individuals who are allergic to penicillin.
- Azithromycin: A macrolide antibiotic that is effective in treating strep throat, especially in individuals who are allergic to penicillin.
It is essential to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed by the doctor, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication. Failure to do so can lead to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and increase the risk of complications.
Complications of Untreated Strep Throat
If left untreated, strep throat can lead to severe complications, including:
- Rheumatic Fever: A rare but potentially life-threatening condition that can occur if the infection is not treated promptly.
- Kidney Inflammation: A condition known as poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis (PSGN), which can lead to kidney damage and failure if left untreated.
- Abscesses: Pus-filled pockets that can form on the tonsils or in the throat, which can be painful and require surgical drainage.
- Sinusitis: An infection of the sinuses that can occur as a result of untreated strep throat.
Prevention and Lifestyle Changes
While it is impossible to completely prevent strep throat, there are several steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of infection:
- Practice Good Hygiene: Wash hands regularly, especially after coming into contact with someone who has strep throat.
- Avoid Close Contact: Avoid close contact with individuals who have strep throat, especially during the infectious period.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids to help soothe the throat and keep the body hydrated.
- Get Plenty of Rest: Rest and relaxation can help the body recover from the infection and reduce the risk of complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is strep throat diagnosed?
+Strep throat is diagnosed through a physical examination and one or more diagnostic tests, including a rapid strep test, throat culture, or PCR test.
What are the complications of untreated strep throat?
+Untreated strep throat can lead to severe complications, including rheumatic fever, kidney inflammation, abscesses, and sinusitis.
How can I prevent strep throat?
+While it is impossible to completely prevent strep throat, practicing good hygiene, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, staying hydrated, and getting plenty of rest can help reduce the risk of infection.
What are the symptoms of strep throat?
+The symptoms of strep throat include a severe sore throat, high fever, swollen lymph nodes, white patches on the tonsils, headache, and nausea and vomiting.
What is the treatment for strep throat?
+Treatment for strep throat typically involves antibiotics, such as penicillin, amoxicillin, or azithromycin, which are effective in killing the bacteria and reducing symptoms.
In conclusion, strep throat is a highly contagious infection that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment to prevent severe complications. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for strep throat, individuals can take steps to reduce the risk of infection and seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time.



