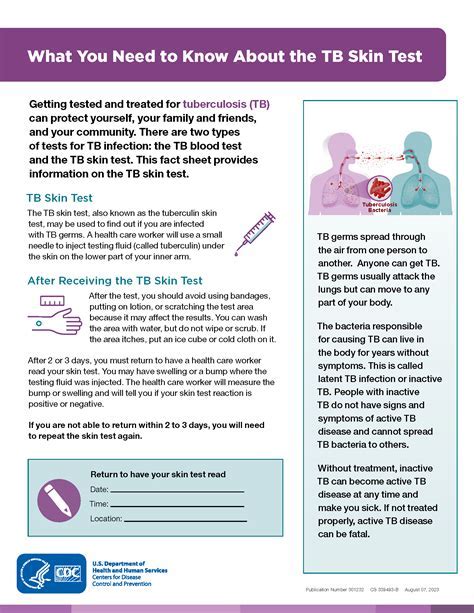
The TB skin test, also known as the Mantoux test, is a widely used method for detecting tuberculosis (TB) infection. It involves injecting a small amount of tuberculin into the skin, and after 48-72 hours, the skin is examined for any reaction. While the TB skin test is generally considered safe, it can cause some side effects, ranging from mild to severe.
Common Side Effects:
- Redness and Swelling: The most common side effect of the TB skin test is redness and swelling at the injection site. This reaction is usually mild and temporary, resolving on its own within a few days.
- Itching and Discomfort: Some people may experience itching or discomfort at the injection site, which can be alleviated with over-the-counter antihistamines or topical creams.
- Blisters or Bumps: In some cases, the TB skin test can cause blisters or bumps to form at the injection site. These typically resolve on their own within a week.
- Fever: A low-grade fever is a possible side effect of the TB skin test, usually resolving within 24-48 hours.
Less Common Side Effects:
- Allergic Reactions: Rarely, people may experience an allergic reaction to the tuberculin, which can cause symptoms such as hives, itching, and difficulty breathing.
- Infection: As with any injection, there is a small risk of infection at the injection site. This can be treated with antibiotics.
- Keloid Formation: In some cases, the TB skin test can cause keloid formation, which is a type of raised scar tissue.
- Desensitization: Repeated TB skin tests can lead to desensitization, making it more difficult to interpret the results.
Severe Side Effects:
- Anaphylaxis: Although extremely rare, anaphylaxis is a life-threatening allergic reaction that can occur in response to the TB skin test. Symptoms include difficulty breathing, rapid heartbeat, and a drop in blood pressure.
- Steven-Johnson Syndrome: This is a rare but serious disorder that can occur in response to the TB skin test, characterized by a severe skin rash, blisters, and mucous membrane lesions.
Who is at Risk for Side Effects?
Certain individuals may be more prone to side effects from the TB skin test, including:
- People with Weakened Immune Systems: Those with compromised immune systems, such as HIV/AIDS patients or individuals undergoing chemotherapy, may be more susceptible to side effects.
- Pregnant Women: Pregnant women should consult their healthcare provider before undergoing a TB skin test, as the risks and benefits need to be carefully weighed.
- People with Allergies: Individuals with a history of allergies, particularly to tuberculin, may be more likely to experience side effects.
What to Do if You Experience Side Effects:
If you experience any side effects after a TB skin test, it is essential to contact your healthcare provider. They can provide guidance on how to manage mild side effects and determine if further evaluation or treatment is necessary.
In conclusion, while the TB skin test is generally a safe and effective method for detecting TB infection, it can cause side effects. Being aware of the potential side effects and taking steps to manage them can help ensure a smooth and successful testing experience.
What are the common side effects of the TB skin test?
+Common side effects of the TB skin test include redness and swelling, itching and discomfort, blisters or bumps, and fever.
Can the TB skin test cause severe side effects?
+Yes, although rare, the TB skin test can cause severe side effects, including anaphylaxis and Steven-Johnson syndrome.
What should I do if I experience side effects from the TB skin test?
+If you experience any side effects, contact your healthcare provider for guidance on managing mild side effects and determining if further evaluation or treatment is necessary.
Remember, if you have any concerns or questions about the TB skin test or its side effects, consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice and guidance.