Thyroid Health Guide: Accurate Diagnosis
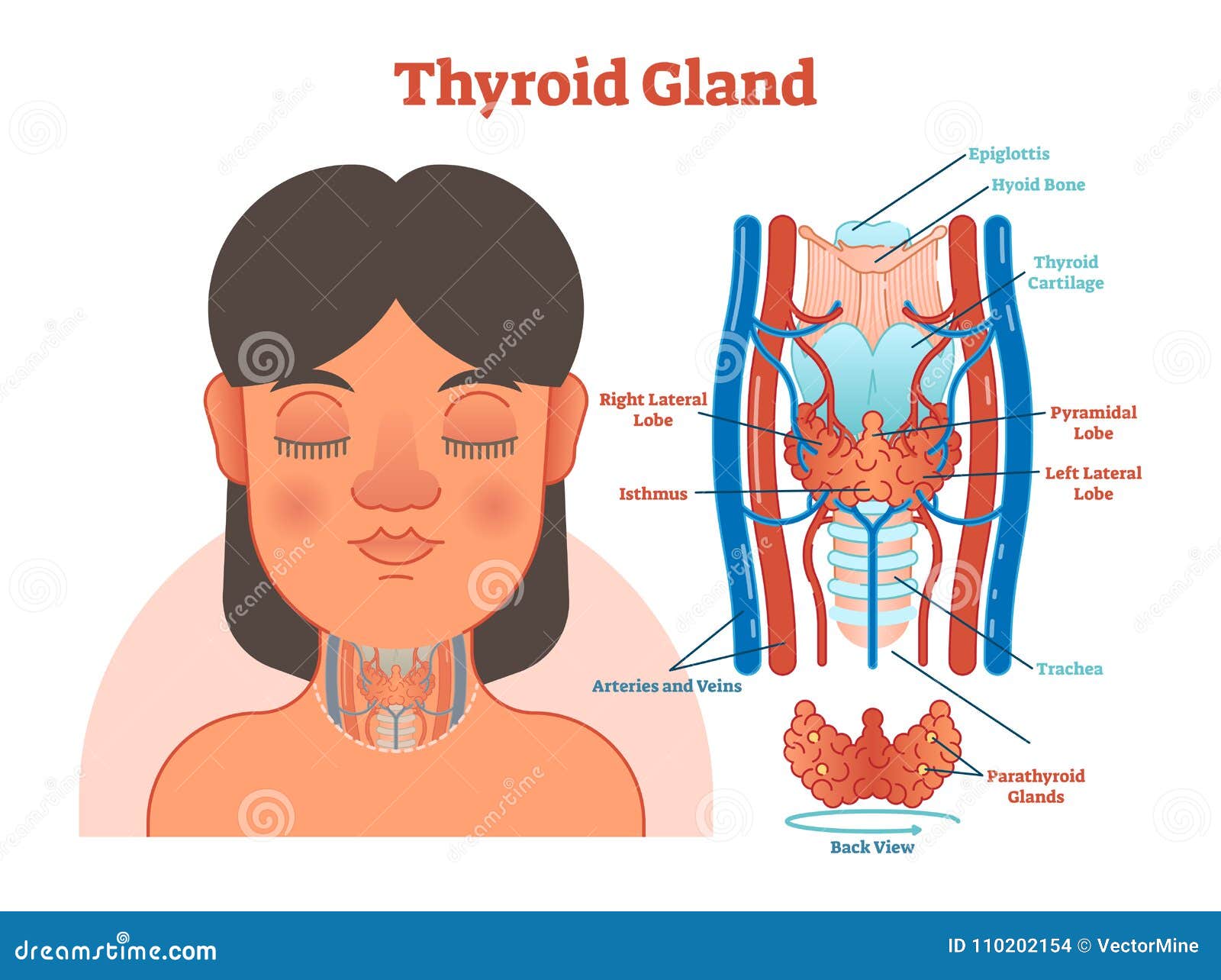
Thyroid health is a complex and multifaceted aspect of human wellness, with the thyroid gland playing a critical role in regulating metabolism, energy production, and overall bodily function. Despite its importance, thyroid disorders are common, affecting millions of people worldwide. The key to effective management and treatment of thyroid conditions lies in accurate diagnosis, which can be a challenging and nuanced process. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of thyroid health, exploring the intricacies of diagnosis, the latest advancements in diagnostic techniques, and the importance of personalized care.
Understanding Thyroid Disorders
Thyroid disorders can be broadly categorized into two main types: hypothyroidism, where the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones, and hyperthyroidism, where the gland produces excessive amounts of these hormones. Both conditions can have significant impacts on health, ranging from mild symptoms such as fatigue and weight changes to more severe complications like heart problems and reproductive issues. The causes of thyroid disorders are varied, including autoimmune diseases like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease, iodine deficiency, and certain medications.
The Diagnostic Process
Accurate diagnosis of thyroid disorders typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and sometimes imaging studies. The process begins with a thorough medical history and physical examination, during which a healthcare provider will look for signs and symptoms suggestive of thyroid dysfunction, such as changes in skin texture, hair loss, and eye bulging.
Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests are crucial for confirming the diagnosis and assessing the severity of thyroid dysfunction. The most commonly used tests include:
- Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Test: This is often the first line of testing. TSH is a hormone produced by the pituitary gland that regulates the production of thyroid hormones. Abnormal TSH levels can indicate thyroid dysfunction.
- Free Thyroxine (FT4) and Free Triiodothyronine (FT3) Tests: These tests measure the levels of circulating thyroid hormones in the blood, providing insight into the thyroid gland’s functional status.
- Thyroid Antibody Tests: These can help diagnose autoimmune thyroid diseases by detecting the presence of specific antibodies.
Imaging Studies
In some cases, imaging studies such as ultrasound, radioactive iodine uptake test, or thyroid scan may be recommended to evaluate the structure and function of the thyroid gland, especially when nodules or goiter (enlargement of the thyroid gland) are suspected.
The Role of Technology in Thyroid Diagnosis
Advancements in technology have significantly improved the accuracy and efficiency of thyroid diagnosis. For instance, high-resolution ultrasound machines can provide detailed images of the thyroid gland, helping in the detection of small nodules or irregularities that might not be palpable during a physical examination. Furthermore, fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) under ultrasound guidance allows for the sampling of thyroid tissue for cytological examination, which is critical for distinguishing between benign and malignant nodules.
Personalized Medicine in Thyroid Care
The concept of personalized medicine is gaining traction in the field of thyroid health, emphasizing the need for tailored diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. Each individual’s thyroid condition is unique, influenced by genetic predispositions, environmental factors, and lifestyle choices. Therefore, a one-size-fits-all approach to diagnosis and treatment is often inadequate. By integrating genetic testing, advanced imaging, and comprehensive clinical evaluations, healthcare providers can offer more precise and effective care plans that address the specific needs of each patient.
Lifestyle and Thyroid Health
While medical diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing thyroid disorders, lifestyle plays a significant role in overall thyroid health. Dietary factors, such as maintaining adequate iodine intake and avoiding goitrogens (substances that can interfere with thyroid function), are important. Regular exercise, stress management through techniques like yoga or meditation, and ensuring sufficient sleep can also contribute to better thyroid health and overall well-being.
Future Directions in Thyroid Diagnosis
The field of thyroid diagnosis is evolving, with ongoing research into new biomarkers, improved imaging techniques, and the potential of artificial intelligence (AI) in enhancing diagnostic accuracy. The development of more sensitive and specific tests for early detection of thyroid disorders, before they lead to significant health issues, is a key area of focus. Additionally, the integration of genetic and molecular diagnostics promises to revolutionize the approach to thyroid health, enabling earlier intervention and more targeted treatments.
Conclusion
Accurate diagnosis is the cornerstone of effective thyroid care, requiring a multifaceted approach that combines clinical acumen, advanced laboratory tests, and personalized consideration of each patient’s unique circumstances. As our understanding of thyroid health and disease continues to grow, so too do the possibilities for improving diagnostic precision and therapeutic efficacy. By embracing advancements in technology, adopting personalized medicine principles, and recognizing the interplay between lifestyle and thyroid function, we can strive towards better health outcomes for individuals affected by thyroid disorders.
What are the common symptoms of hypothyroidism?
+Common symptoms of hypothyroidism include fatigue, weight gain, dry skin, hair loss, cold intolerance, and depression. These symptoms can vary in severity and may develop gradually over time.
How is hyperthyroidism typically treated?
+Treatment for hyperthyroidism depends on the cause and severity of the condition but often involves antithyroid medications to reduce hormone production, radioactive iodine to destroy part of the thyroid gland, or surgery to remove part or all of the gland.
Can thyroid disorders be prevented?
+While many thyroid disorders cannot be prevented, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet with adequate iodine, regular physical activity, and avoidance of smoking, can help support overall thyroid health.



