Tubal Ligation Guide: Permanent Birth Control Options
Understanding the complexities of family planning and birth control is crucial for individuals and couples seeking to make informed decisions about their reproductive health. One of the most effective and permanent forms of birth control is tubal ligation, a surgical procedure that has been a cornerstone in family planning for decades. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of tubal ligation, its procedure, benefits, risks, and what to expect post-surgery, helping individuals make an educated decision about this significant step in their reproductive journey.
Introduction to Tubal Ligation
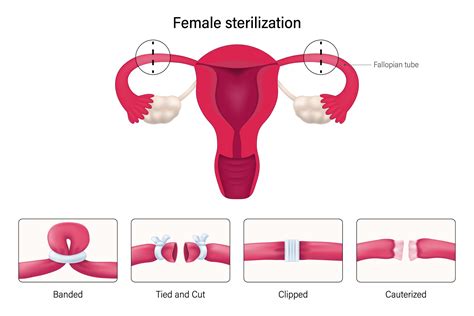
Tubal ligation, often referred to as “getting your tubes tied,” is a surgical procedure designed to prevent pregnancy by blocking the fallopian tubes. These tubes are the pathways through which egg cells travel from the ovaries to the uterus. By blocking them, sperm cannot fertilize an egg, thereby preventing pregnancy. This procedure is considered permanent and is typically recommended for women who are certain they do not wish to have any more children.
How Tubal Ligation Works
The procedure of tubal ligation involves a surgeon cutting, tying, or blocking the fallopian tubes. There are several methods through which this can be achieved, including:
- Open Surgery: This traditional method involves making a small incision in the abdomen to access the fallopian tubes.
- Laparoscopic Surgery: A minimally invasive technique where a laparoscope (a thin, lighted tube with a camera) and surgical instruments are inserted through small incisions in the abdomen.
- Essure Procedure: Although no longer available in the US due to safety concerns, this method involved inserting small metal coils into the fallopian tubes through the vagina and uterus, which then prompted the formation of scar tissue to block the tubes.
Benefits of Tubal Ligation
The benefits of tubal ligation are multifaceted, making it an attractive option for many:
- High Efficacy: Tubal ligation is nearly 100% effective in preventing pregnancy, offering a reliable form of permanent birth control.
- Low Maintenance: Once the procedure is complete, there’s no need for ongoing birth control management, such as taking daily pills or replacing contraceptive devices.
- Reversal is Possible but Challenging: While tubal ligation is considered permanent, reversal is possible under certain circumstances, though it’s a more complex and less successful procedure than the initial ligation.
Risks and Potential Complications
Like any surgical procedure, tubal ligation carries risks and potential complications:
- Surgical Risks: These can include infection, bleeding, and adverse reactions to anesthesia.
- Failure: Although rare, there’s a small chance that the procedure might not be 100% effective, leading to an unexpected pregnancy.
- Regret: Some individuals may experience regret over their decision, especially if their personal circumstances change.
- Increased Risk of Ectopic Pregnancy: If a pregnancy were to occur after tubal ligation, it’s more likely to be ectopic (where the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus), which is a medical emergency.
What to Expect
Understanding what to expect both during and after the procedure can help alleviate anxiety and prepare individuals for the recovery process:
- Preparation: This typically involves discussing the procedure with a healthcare provider, undergoing any necessary pre-operative tests, and arranging for post-operative care and recovery support.
- The Procedure: Depending on the method chosen, the procedure can take anywhere from 30 minutes to a couple of hours and may require a hospital stay or can be performed on an outpatient basis.
- Recovery: Recovery times vary, but most women can return to their normal activities within a few days to a week after the procedure. It’s essential to follow the healthcare provider’s instructions for a smooth recovery.
Decision-Making Process
Deciding on tubal ligation as a form of permanent birth control involves careful consideration and consultation with healthcare professionals. It’s crucial to weigh the benefits against the risks and to have a clear understanding of what the procedure entails and its implications. Questions to consider include:
- Are you certain you do not want more children? This is the most critical factor, as tubal ligation is designed to be permanent.
- Have you explored other birth control options? Understanding the range of birth control methods available can help in making an informed decision.
- What are your health considerations? Certain health conditions or previous surgeries might affect the feasibility or safety of the procedure.
Conclusion
Tubal ligation is a significant decision that offers a permanent solution for birth control. While it’s highly effective, the procedure is not without its risks and should be considered carefully. By understanding the ins and outs of tubal ligation, individuals can make informed decisions about their reproductive health and future. Always consult with a healthcare provider to discuss the specifics of the procedure and determine if it’s the right choice for your unique circumstances.
Is tubal ligation reversible?
+Tubal ligation is considered a permanent form of birth control. However, reversal is possible but challenging and not always successful. The success of reversal procedures depends on various factors, including the method used for the initial ligation, the length of the remaining fallopian tube segments, and the woman’s age.
How effective is tubal ligation in preventing pregnancy?
+Tubal ligation is nearly 100% effective in preventing pregnancy. It is one of the most reliable forms of birth control available, with failure rates being less than 1%.
What are the potential risks and complications of tubal ligation?
+Potential risks and complications include infection, bleeding, adverse reactions to anesthesia, and an increased risk of ectopic pregnancy if a pregnancy were to occur after the procedure. Additionally, some individuals may experience regret over their decision.