Tubal Ligation Procedure: Your Comprehensive Overview

The decision to undergo a tubal ligation procedure, also known as “getting your tubes tied,” is a significant one, often made after careful consideration of various factors, including family size, health, and personal preferences. This surgical method of sterilization is designed to provide a permanent solution to birth control, making it an attractive option for women who have completed their families or have decided against future pregnancies. Understanding the intricacies of the procedure, its benefits, potential risks, and the aftermath is crucial for anyone contemplating this path.
What is Tubal Ligation?
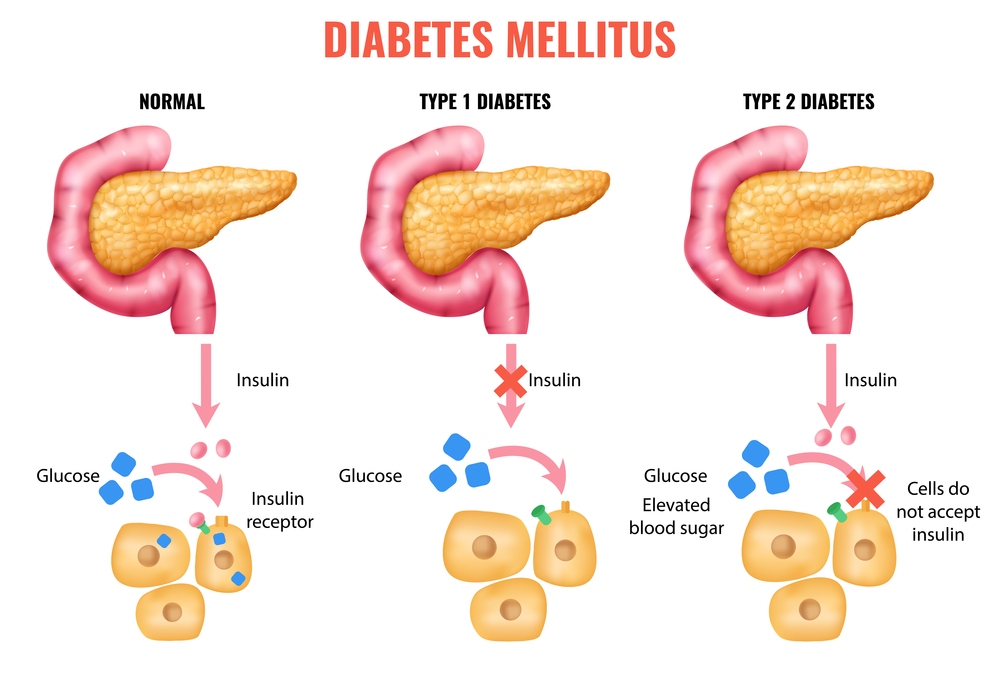
Tubal ligation is a surgical procedure that involves cutting or blocking the fallopian tubes to prevent egg cells from being fertilized, thereby preventing pregnancy. The fallopian tubes are the pathways through which the egg cells travel from the ovaries to the uterus. By interrupting this pathway, the procedure ensures that sperm cannot reach the egg for fertilization. This method is considered permanent, although it is possible to reverse it in some cases, the success of which can vary and is not guaranteed.
Why Choose Tubal Ligation?
There are several reasons why a woman might choose to undergo a tubal ligation. For many, the primary motivation is the desire for a permanent form of birth control. Unlike other contraceptive methods that may have failure rates or require consistent use, tubal ligation provides a sense of security and freedom from the worry of unplanned pregnancies. Additionally, some women may choose this option due to health concerns related to pregnancy or childbirth, or as part of a family planning strategy after having the desired number of children.
The Procedure: What to Expect
The tubal ligation procedure can be performed in various ways, depending on the technique preferred by the surgeon and the individual’s health status. The most common methods include:
- Laparoscopic Tubal Ligation: This is a minimally invasive procedure where a laparoscope (a thin, lighted tube with a camera) and surgical instruments are inserted through small incisions in the abdomen. The surgeon then cuts, blocks, or clips the fallopian tubes to prevent egg release.
- Open Tubal Ligation: Although less common due to its more invasive nature, this method involves making a small incision in the abdomen to access the fallopian tubes.
- Postpartum Tubal Ligation: This can be performed shortly after childbirth, either vaginally or through a small abdominal incision, depending on whether a cesarean section was performed.
Each method has its advantages and potential risks, which should be discussed thoroughly with a healthcare provider to determine the best approach for an individual’s specific situation.
Recovery and Aftercare
The recovery process for tubal ligation varies depending on the surgical technique used. For laparoscopic procedures, most women can return home the same day and resume their normal activities within a few days. The recovery time for open tubal ligation or postpartum procedures might be slightly longer. It is common to experience mild discomfort, such as abdominal cramps or shoulder pain, which can be managed with pain medication.
Following the procedure, it is essential to follow the post-operative instructions provided by the healthcare provider, which may include avoiding heavy lifting, sexual intercourse, and strenuous activities for a specified period. Additionally, attending follow-up appointments is crucial to ensure proper healing and to address any concerns or complications that may arise.
Risks and Complications
As with any surgical procedure, there are potential risks and complications associated with tubal ligation. These may include:
- Bleeding or Hematoma: Excessive bleeding during or after the surgery.
- Infection: Bacterial infection at the site of the incision.
- Damage to Surrounding Organs: Although rare, there is a risk of unintentional damage to organs like the bowel, bladder, or blood vessels.
- Ectopic Pregnancy: A rare but serious complication where a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, which can be life-threatening.
It is vital to discuss these risks with a healthcare provider and understand the measures that can be taken to minimize them.
Emotional and Psychological Considerations
The decision to undergo tubal ligation is not only medical but also deeply personal and emotional. It’s a choice that can have profound implications on a woman’s emotional well-being, relationships, and overall quality of life. Some women may experience a sense of relief and empowerment following the procedure, while others may face emotional challenges, including regret or grief related to the permanence of their decision.
Support from family, friends, and possibly professional counseling can play a significant role in navigating these emotions and making the transition smoother.
Conclusion
Tubal ligation is a significant and permanent decision that requires careful consideration of its implications. While it offers a reliable means of birth control, it is essential to weigh the benefits against the potential risks and to ensure that this choice aligns with one’s personal, emotional, and health circumstances. Through a comprehensive understanding of the procedure, its aftermath, and by engaging in open and informed discussions with healthcare providers, women can make empowered decisions regarding their reproductive health.
FAQ Section
Is tubal ligation reversible?
+Tubal ligation is considered a permanent form of birth control, but reversal is possible in some cases. The success of reversal depends on various factors, including the method of tubal ligation used, the length of the remaining fallopian tube segments, and the overall health of the woman. It’s a complex procedure with no guarantee of success, and it’s essential to discuss this with a healthcare provider.
How effective is tubal ligation as a form of birth control?
+Tubal ligation is highly effective, with a failure rate of less than 1%. However, as with any form of birth control, there is a small chance of ectopic pregnancy, although rare, if a pregnancy were to occur.
Will tubal ligation affect my menstrual cycle or hormone levels?
+Tubal ligation does not affect hormone production or menstrual cycles. The ovaries continue to produce eggs and hormones, but the eggs are simply absorbed by the body instead of being released into the fallopian tubes. Some women may experience changes in their menstrual cycles due to other factors, but these changes are not typically a direct result of the tubal ligation procedure.
Can I still get pregnant after a tubal ligation?
+Although tubal ligation is a highly effective form of birth control, there is a small chance of pregnancy, particularly in the first year after the procedure. If pregnancy does occur, it is more likely to be an ectopic pregnancy, which is a serious condition requiring immediate medical attention. It’s essential to follow post-procedure instructions carefully and attend all recommended follow-up appointments to ensure the procedure’s success.
How long does it take to recover from a tubal ligation procedure?
+Recovery time from tubal ligation can vary depending on the method used. For laparoscopic procedures, most women can resume their normal activities within a few days. Open tubal ligation or postpartum procedures may require a slightly longer recovery period. It’s crucial to follow the healthcare provider’s post-operative instructions to ensure a smooth and safe recovery.