Tulare Lake California
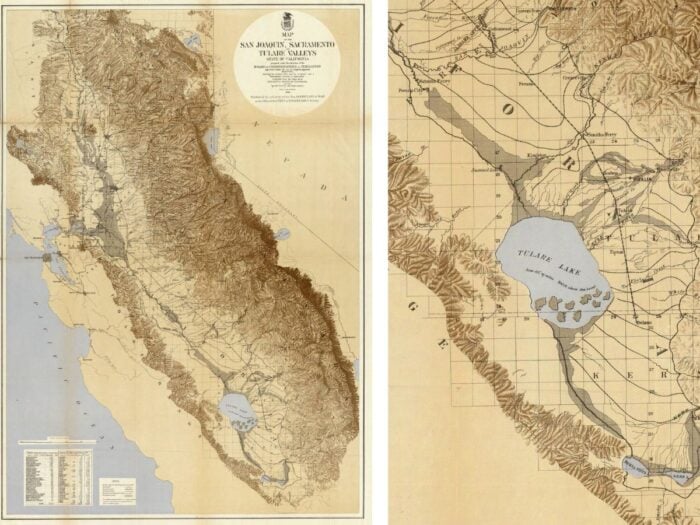
Tulare Lake, once the largest freshwater lake west of the Mississippi River, played a pivotal role in the ecological and agricultural history of California. Located in the San Joaquin Valley, the lake’s significance stretches back thousands of years, serving as a habitat for numerous species and a source of sustenance for indigenous peoples. However, its story is also one of dramatic change, influenced by human activities that have reshaped its very existence.
Historically, Tulare Lake covered an expansive area, fluctuating with the seasons and the water levels. It was part of an intricate network of rivers, sloughs, and wetlands that provided a rich environment for wildlife. The lake’s basin was home to several Native American tribes, including the Yokuts, who relied on its resources for fishing, hunting, and gathering. The area’s natural abundance made it an ideal place for these communities to thrive, with the lake and its surrounding wetlands offering a variety of fish, birds, and other wildlife that were essential to their diet and culture.
The arrival of European settlers marked the beginning of significant changes for Tulare Lake. The construction of dams, canals, and other water diversion structures, aimed at controlling flooding and irrigating agricultural lands, gradually altered the lake’s hydrology. The rerouting of rivers that once fed the lake, such as the Kern, Kings, and San Joaquin rivers, led to a substantial decrease in water inflow. By the early 20th century, these alterations, combined with droughts and increased agricultural demand for water, resulted in the lake’s drastic shrinkage. Eventually, Tulare Lake disappeared from the landscape, leaving behind a dry lake bed that has occasionally seen temporary flooding, especially during periods of high rainfall or when water from agricultural runoff collects in the area.
The disappearance of Tulare Lake has had profound environmental and socio-economic impacts. The loss of such a vast wetland ecosystem has led to a significant decline in biodiversity. Many species that once called the lake and its surrounding areas home, such as certain fish species, birds, and other wildlife, have seen their populations diminish or have been forced to adapt to new habitats. Additionally, the indigenous communities that traditionally relied on the lake’s resources have faced challenges in preserving their cultural practices and way of life, further highlighting the lake’s significance beyond its ecological role.
Despite its current state, there are ongoing efforts to restore parts of the Tulare Lake ecosystem. These initiatives aim to revive some of the lake’s original functions, such as providing habitat for wildlife and helping to manage floodwaters. Restoring wetlands and improving water quality are crucial components of these projects, which also involve educating the public about the historical and ecological importance of Tulare Lake. Furthermore, the issue of water management in the region remains complex, with ongoing debates about how to balance the needs of agriculture, urban areas, and environmental conservation.
The story of Tulare Lake serves as a reminder of the dynamic and often fragile relationship between human activities and natural environments. It highlights the importance of considering long-term consequences and adopting sustainable practices that preserve ecological balance. As California continues to grapple with issues of water management, environmental conservation, and the impacts of climate change, the legacy of Tulare Lake offers valuable lessons for the future, underscoring the need for careful planning and responsible stewardship of the state’s natural resources.
In exploring the history and significance of Tulare Lake, it becomes clear that its impact extends beyond the local level, offering insights into broader themes of environmental management, cultural preservation, and the challenges of balancing human needs with ecological sustainability. The once vast and thriving ecosystem of Tulare Lake stands as a poignant example of how human actions can shape, and sometimes irreparably alter, the natural world, emphasizing the importance of learning from the past to inform a more sustainable future.
What was the primary cause of Tulare Lake's disappearance?
+The primary cause of Tulare Lake's disappearance was the alteration of its water inflow due to the construction of dams, canals, and other water diversion structures aimed at controlling flooding and irrigating agricultural lands.
What ecological impacts resulted from the loss of Tulare Lake?
+The loss of Tulare Lake led to a significant decline in biodiversity, as many species that relied on the lake and its surrounding wetlands for habitat saw their populations diminish or were forced to adapt to new environments.
Are there any current efforts to restore Tulare Lake or its ecosystem?
+Yes, there are ongoing efforts to restore parts of the Tulare Lake ecosystem, focusing on reviving some of the lake's original functions, such as providing habitat for wildlife and managing floodwaters, through the restoration of wetlands and improvement of water quality.
The history and legacy of Tulare Lake offer a complex narrative of environmental change, cultural impact, and the ongoing challenges of sustainable resource management. As discussions around water conservation, environmental restoration, and the preservation of natural habitats continue, the story of Tulare Lake stands as a critical reminder of the importance of understanding and learning from the past to guide future decisions and actions.