Types Of Abortion
Abortion, a complex and multifaceted topic, encompasses various methods and types, each with its own set of considerations, implications, and ethical debates. The discussion around abortion is deeply personal, touching on health, rights, and societal norms. Understanding the different types of abortion is crucial for informed decision-making and for fostering a nuanced dialogue about this sensitive subject.
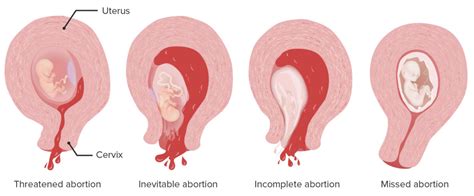
1. Spontaneous Abortion (Miscarriage)
Spontaneous abortion, commonly referred to as a miscarriage, occurs when a pregnancy ends on its own, typically before the 20th week. This can happen due to various reasons such as chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus, uterine abnormalities, hormonal problems, or other health issues. Miscarriages are often a natural process but can be emotionally challenging for those who experience them.
2. Induced Abortion
Induced abortion refers to the intentional termination of a pregnancy. This can be performed for several reasons, including health risks to the mother, severe fetal anomalies, or personal and social reasons. Induced abortions can be further categorized based on the methods used and the gestational age of the pregnancy.
Surgical Abortion
- Vacuum Aspiration: A common method used in the first trimester, where the contents of the uterus are gently suctioned out.
- Dilation and Evacuation (D&E): Typically used later in pregnancy, this involves dilating the cervix and removing the fetus and placenta with surgical instruments.
- Dilation and Curettage (D&C): This method involves dilating the cervix and using a curette to remove tissue from the uterus.
Medical Abortion
- Abortion Pill (Mifepristone and Misoprostol): Used early in pregnancy, these medications work together to induce a miscarriage-like process. Mifepristone blocks the hormone progesterone, which is necessary to maintain a pregnancy, while misoprostol causes the uterus to contract and expel its contents.
3. Therapeutic Abortion
Therapeutic abortion refers to the termination of a pregnancy for medical reasons, such as when the continuation of the pregnancy would endanger the life of the mother or when the fetus has severe anomalies incompatible with life. This type of abortion is performed to protect the physical or mental health of the mother.
4. Elective Abortion
Elective abortion is chosen by the woman for personal, social, or economic reasons. The decision is not necessarily due to health concerns but can be influenced by a variety of factors, including the woman’s age, relationship status, financial situation, and personal goals.
5. Surgical Abortion Methods by Trimester
- First Trimester (Up to 12 weeks): Vacuum aspiration and medical abortion are commonly used.
- Second Trimester (13-26 weeks): Dilation and evacuation (D&E) is a typical method.
- Third Trimester (After 26 weeks): Abortions in the third trimester are less common and often performed due to severe fetal anomalies or significant risks to the mother’s health. Methods can include induced labor or D&E.
Considerations and Access
Access to safe abortion services is a critical aspect of reproductive health. In many parts of the world, restrictive laws and lack of access to healthcare can lead to unsafe abortions, significantly increasing the risk of complications and death. The World Health Organization (WHO) and other global health entities advocate for safe, legal abortion services as part of comprehensive reproductive health care.
Ethical and Social Perspectives
The ethical and social considerations surrounding abortion are deeply divisive. Some argue that abortion is a fundamental right, essential for women’s autonomy and health, while others believe it is morally equivalent to taking a life. These perspectives are influenced by cultural, religious, and personal beliefs, contributing to the ongoing debate about abortion.
Conclusion
The types of abortion reflect the complexity and diversity of human experiences and circumstances. Understanding these differences is essential for fostering empathy and for developing policies and healthcare services that respect the autonomy and dignity of all individuals involved. As societal attitudes and medical technologies evolve, the discussion around abortion will continue, highlighting the need for compassion, accurate information, and support for those navigating these personal and often challenging decisions.
What is the difference between a spontaneous and induced abortion?
+A spontaneous abortion refers to a miscarriage, which is when a pregnancy ends on its own. An induced abortion, on the other hand, is the intentional termination of a pregnancy through medical or surgical means.
At what stages of pregnancy can different types of abortion be performed?
+Abortion methods vary by gestational age. Vacuum aspiration and medical abortion are commonly used in the first trimester. Dilation and evacuation (D&E) is typically used in the second trimester. Abortions in the third trimester are less common and often due to severe health concerns or fetal anomalies.
What are the ethical considerations surrounding abortion?
+The ethical considerations surrounding abortion are complex and divisive. They involve debates about autonomy, the right to life, and the moral status of the fetus, as well as considerations of health, dignity, and societal norms.