Vyvanse 30 Mg
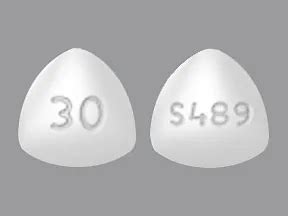
Vyvanse 30 mg is a specific dosage of the medication lisdexamfetamine, which is commonly prescribed for the treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and certain cases of binge eating disorder. To understand the implications and effects of Vyvanse 30 mg, it’s essential to delve into what the medication is, how it works, its potential benefits and side effects, and considerations for its use.
What is Vyvanse?
Vyvanse is a central nervous system stimulant prescription medication that affects chemicals in the brain and nerves that contribute to hyperactivity and impulse control. It is manufactured by Shire Pharmaceuticals, which is now part of Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited. Vyvanse is available in various dosages, including 10 mg, 20 mg, 30 mg, 40 mg, 50 mg, 60 mg, and 70 mg capsules.
Mechanism of Action
Unlike some other stimulants used to treat ADHD, Vyvanse works by using the body’s natural process to convert the medication into the active form, which then affects the brain. This unique mechanism may contribute to its prolonged duration of action and potentially reduced risk of abuse compared to immediate-release stimulants.
Usage for ADHD
For ADHD, Vyvanse is designed to help increase attention, decrease impulsivity and hyperactivity in patients. The 30 mg dose is often considered a moderate dose, suitable for individuals who have responded well to lower doses but require additional therapeutic effect. However, the starting dose for ADHD is typically 30 mg once daily in the morning, which may be adjusted based on efficacy and tolerability.
Usage for Binge Eating Disorder
Vyvanse is also approved for the treatment of moderate to severe binge eating disorder in adults. In this context, the 30 mg dose might be used after initial titration from lower doses, under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Potential Side Effects
Common side effects of Vyvanse include dry mouth, decreased appetite, insomnia (difficulty sleeping), irritability, nausea or vomiting, anxiety, constipation, and emotional volatility. More severe but less common side effects can include increased heart rate and blood pressure, psychosis (in patients with a history of psychotic disorders), and bipolar disorder (manic episodes in patients with a history of bipolar disorder). It’s crucial for patients to report any side effects to their healthcare provider to adjust the dosage or treatment plan as necessary.
Important Considerations
Dependence and Withdrawal: Long-term use of Vyvanse can lead to dependence. Abruptly stopping the medication can lead to withdrawal symptoms, so it should be tapered off under medical supervision if discontinuation is planned.
Drug Interactions: Vyvanse can interact with numerous medications, including MAOIs (monoamine oxidase inhibitors), antacids, and certain antidepressants. Patients should inform their healthcare provider about all medications they are taking.
Contraindications: Vyvanse is contraindicated in patients with advanced arteriosclerosis, symptomatic cardiovascular disease, moderate to severe hypertension, agitated states, history of drug abuse, during or within 14 days following the administration of monoamine oxidase inhibitors, and known hypersensitivity to amphetamine products.
Monitoring: Patients on Vyvanse should be monitored for changes in heart rate, blood pressure, growth (in children), and for signs of abusing the medication.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Vyvanse should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. Mothers taking Vyvanse should not breastfeed, as the drug can pass into breast milk.
Conclusion
Vyvanse 30 mg, like other dosages of the medication, is a prescription drug that should be used under the close supervision of a healthcare provider. While it can offer significant benefits for patients with ADHD and binge eating disorder, it’s crucial to be aware of its potential side effects and contraindications. Patients should work closely with their healthcare team to find the right dosage and treatment plan that balances therapeutic benefits with potential risks.
Key Points for Healthcare Providers
- Dosing: The dosage of Vyvanse should be individualized according to the therapeutic needs and response of the patient.
- Patient Education: Patients should be educated on the proper use of Vyvanse, including the risks of dependence and potential side effects.
- Regular Monitoring: Regular monitoring of heart rate and blood pressure, as well as assessment for signs of abuse or diversion, is recommended.
Future Directions
As research into ADHD and binge eating disorder continues, there may be evolving guidelines for the use of Vyvanse and other stimulant medications. Patients and healthcare providers should stay updated with the latest research and recommendations to ensure that treatment plans are optimized and aligned with the best current evidence.
Practical Advice for Patients
- Adherence: Adhere to the prescribed dosage and schedule.
- Communication: Regularly communicate with your healthcare provider about your response to the medication and any concerns.
- Lifestyle Changes: Incorporate healthy lifestyle changes, such as a balanced diet, regular exercise, and sufficient sleep, to complement the effects of the medication.
By understanding the role of Vyvanse 30 mg in treating ADHD and binge eating disorder, and by carefully managing its use, patients can experience significant improvements in their symptoms and quality of life.
What is the primary use of Vyvanse 30 mg?
+Vyvanse 30 mg is primarily used for the treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and moderate to severe binge eating disorder in adults.
How should Vyvanse be taken?
+Vyvanse should be taken orally in the morning, with or without food, as directed by a healthcare provider.
Can Vyvanse be used during pregnancy or breastfeeding?
+Vyvanse should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. It is recommended that mothers taking Vyvanse should not breastfeed.
What are common side effects of Vyvanse?
+Common side effects include dry mouth, decreased appetite, insomnia, irritability, nausea or vomiting, anxiety, constipation, and emotional volatility.
Can Vyvanse lead to dependence?
+Yes, long-term use of Vyvanse can lead to dependence, and abruptly stopping the medication can lead to withdrawal symptoms.