Wet Mount Test
The wet mount test, also known as the wet prep or wet preparation, is a laboratory diagnostic technique used to detect the presence of microorganisms, such as parasites, yeast, and bacteria, in a sample. This test is commonly used in medical and veterinary settings to diagnose infections, particularly those caused by protozoa, fungi, and bacteria.
Introduction to the Wet Mount Test
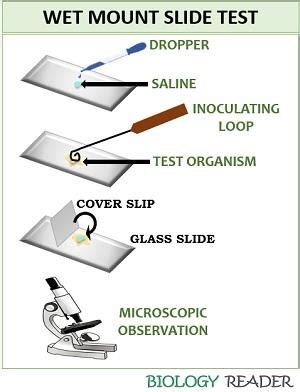
The wet mount test involves placing a small sample of tissue, fluid, or other material onto a microscope slide and adding a drop of water or a specialized solution to create a wet mount. The slide is then covered with a coverslip and examined under a microscope. This technique allows for the rapid examination of the sample and can provide valuable information about the presence and morphology of microorganisms.
Applications of the Wet Mount Test
The wet mount test has a wide range of applications in medicine and veterinary medicine. Some of the most common uses of this test include:
- Diagnosis of parasitic infections: The wet mount test is often used to diagnose parasitic infections, such as giardiasis, amoebiasis, and trichomoniasis.
- Detection of fungal infections: This test can be used to detect fungal infections, such as candidiasis and aspergillosis.
- Bacterial detection: The wet mount test can be used to detect the presence of bacteria, such as those that cause urinary tract infections or respiratory infections.
- Examination of tissue samples: The wet mount test can be used to examine tissue samples, such as skin scrapings or mucous membranes, to detect the presence of microorganisms.
Preparation and Procedure
To perform a wet mount test, the following steps are typically followed:
- Collection of the sample: A sample of tissue, fluid, or other material is collected from the patient or animal.
- Preparation of the sample: The sample is prepared for examination by adding a drop of water or a specialized solution to create a wet mount.
- Placement on a microscope slide: The sample is placed onto a microscope slide and covered with a coverslip.
- Examination under a microscope: The slide is examined under a microscope, typically using a 10x or 40x objective lens.
- Identification of microorganisms: The microorganisms present in the sample are identified based on their morphology, size, and movement.
The wet mount test is a valuable diagnostic tool that can provide rapid and accurate results. However, it requires a skilled technician or microbiologist to prepare and examine the sample, as well as to interpret the results.
Advantages and Limitations
The wet mount test has several advantages, including:
- Rapid results: The wet mount test can provide rapid results, often within minutes of preparing the sample.
- Low cost: This test is relatively inexpensive compared to other diagnostic techniques.
- Simple to perform: The wet mount test is relatively simple to perform and can be done in a laboratory or clinical setting.
However, the wet mount test also has some limitations, including:
- Limited sensitivity: The wet mount test may not detect all microorganisms present in the sample, particularly if they are present in small numbers.
- Requires skilled technician: The wet mount test requires a skilled technician or microbiologist to prepare and examine the sample, as well as to interpret the results.
- May not provide definitive diagnosis: The wet mount test may not provide a definitive diagnosis, particularly if the microorganisms present are not easily identifiable.
Future Developments and Trends
The wet mount test is a well-established diagnostic technique that has been used for many years. However, there are several future developments and trends that may impact the use of this test, including:
- Advances in microscopy: Advances in microscopy, such as the development of new types of microscopes or imaging techniques, may improve the sensitivity and accuracy of the wet mount test.
- New diagnostic techniques: The development of new diagnostic techniques, such as molecular diagnostics or point-of-care tests, may provide alternative or complementary methods for detecting microorganisms.
- Increased use of automation: The increased use of automation in laboratories and clinical settings may improve the efficiency and accuracy of the wet mount test.
What is the wet mount test used for?
+The wet mount test is used to detect the presence of microorganisms, such as parasites, yeast, and bacteria, in a sample.
How is the wet mount test performed?
+The wet mount test involves placing a small sample of tissue, fluid, or other material onto a microscope slide and adding a drop of water or a specialized solution to create a wet mount. The slide is then covered with a coverslip and examined under a microscope.
What are the advantages and limitations of the wet mount test?
+The advantages of the wet mount test include rapid results, low cost, and simplicity. However, the test also has limitations, including limited sensitivity, the need for a skilled technician, and the potential for not providing a definitive diagnosis.
In conclusion, the wet mount test is a valuable diagnostic technique that can provide rapid and accurate results. While it has several advantages, it also has limitations that must be considered. As diagnostic techniques continue to evolve, it is likely that the wet mount test will remain an important tool in the diagnosis of microorganism-related infections.