What An A1c Blood Test
The A1c blood test, also known as the hemoglobin A1c or HbA1c test, is a crucial diagnostic tool used to measure the average level of glucose (sugar) in the blood over the past 2 to 3 months. It’s a widely used test to assess blood sugar control in people with diabetes, as well as to screen for and diagnose diabetes and prediabetes.
How the A1c Test Works
The A1c test measures the percentage of glucose that has attached to the hemoglobin in red blood cells. Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen to different parts of the body. When glucose is present in the blood, some of it binds to the hemoglobin, forming a compound called glycated hemoglobin or hemoglobin A1c. The more glucose in the blood, the more hemoglobin gets glycated.
The lifespan of a red blood cell is approximately 120 days, which is why the A1c test can provide a picture of blood sugar control over the past 2 to 3 months. By measuring the percentage of glycated hemoglobin, healthcare providers can get an idea of how well diabetes is being managed or if someone is at risk of developing diabetes.
Why is the A1c Test Important?
The A1c test is an essential tool for several reasons:
- Diagnosis: The A1c test is used to diagnose diabetes and prediabetes. A result of 6.5% or higher indicates diabetes, while a result between 5.7% and 6.4% indicates prediabetes.
- Monitoring: For people with diabetes, the A1c test helps healthcare providers assess how well the condition is being managed. It provides a snapshot of blood sugar control over time, allowing for adjustments to treatment plans as needed.
- Risk Assessment: The A1c test can help identify people at risk of developing diabetes or cardiovascular disease.
- Treatment Planning: The results of the A1c test can inform treatment decisions, such as adjusting medication, diet, or exercise plans.
Interpreting A1c Results
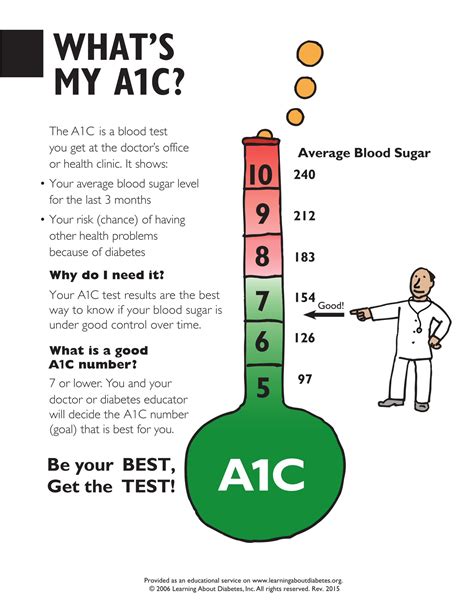
A1c results are typically reported as a percentage, which represents the average percentage of glucose attached to hemoglobin over the past 2 to 3 months. Here’s a general guide to interpreting A1c results:
- Below 5.7%: Normal
- 5.7% to 6.4%: Prediabetes
- 6.5% or higher: Diabetes
- 6.5% to 7%: Good control (for people with diabetes)
- 7% to 8%: Fair control (for people with diabetes)
- Above 8%: Poor control (for people with diabetes)
Keep in mind that A1c results can be influenced by various factors, such as age, ethnicity, and certain medical conditions. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider to understand the results and develop a personalized plan for managing blood sugar control.
It's essential to note that the A1c test is just one tool used to diagnose and manage diabetes. Healthcare providers may use other tests, such as fasting plasma glucose or oral glucose tolerance tests, to confirm diagnoses or monitor blood sugar control.
Limitations and Considerations
While the A1c test is a valuable tool, it has some limitations and considerations:
- Red blood cell lifespan: The A1c test assumes a normal red blood cell lifespan. Certain conditions, such as anemia or blood transfusions, can affect red blood cell lifespan and skew A1c results.
- Hemoglobin variants: Some people have abnormal hemoglobin variants, which can affect A1c test results.
- Pregnancy: A1c results may be lower during pregnancy due to changes in red blood cell turnover.
What is a normal A1c level?
+A normal A1c level is below 5.7%. This indicates that blood sugar levels have been within a healthy range over the past 2 to 3 months.
Can I take the A1c test at home?
+Yes, there are at-home A1c testing kits available. However, it's essential to follow the manufacturer's instructions and consult with a healthcare provider to ensure accurate results and proper interpretation.
How often should I get an A1c test?
+The frequency of A1c testing depends on individual circumstances. People with diabetes typically get an A1c test every 3 to 6 months, while those at risk of developing diabetes may get tested annually.
In conclusion, the A1c blood test is a powerful tool for assessing blood sugar control and diagnosing diabetes and prediabetes. By understanding the test’s purpose, limitations, and results, individuals can take a proactive approach to managing their blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications.