What Are Normal Glucose Levels? After Eating Guide
Understanding normal glucose levels is crucial for maintaining good health, especially for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. Glucose, a simple sugar, is the primary source of energy for the body’s cells. It is obtained from the food we eat and is regulated by insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas. The level of glucose in the blood can fluctuate significantly throughout the day, depending on when and what you eat, your physical activity level, and other factors.
Fasting Glucose Levels
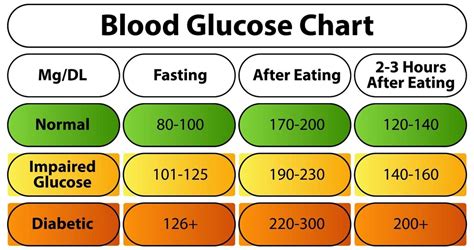
Fasting glucose levels, measured after an overnight fast of at least 8 hours, provide a baseline indication of blood glucose control. Normal fasting blood glucose levels are typically between 70 and 99 mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter). Levels within this range suggest that the body is effectively regulating blood glucose during periods without food intake.
Postprandial (After Eating) Glucose Levels
Postprandial glucose levels refer to the blood glucose concentrations measured after eating. These levels can rise significantly after a meal, especially if the meal contains a high amount of carbohydrates, which are broken down into glucose during digestion. In individuals without diabetes, the body’s insulin response helps to manage these spikes, keeping blood glucose levels within a relatively normal range.
For people without diabetes, a normal postprandial glucose level is usually less than 140 mg/dL two hours after eating. However, this can vary depending on the type and quantity of food consumed, as well as individual factors such as physical activity and overall health.
Guidelines for Postprandial Glucose Levels
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) provides guidelines for blood glucose targets, which can also serve as a reference for non-diabetic individuals aiming to maintain optimal glucose levels:
- Before meals: 70 to 130 mg/dL
- After meals (1-2 hours): Less than 180 mg/dL
It’s essential to note that these are general guidelines. The ideal blood glucose range can vary from person to person, depending on factors like age, health status, and the presence of other medical conditions.
Factors Influencing Postprandial Glucose Levels
Several factors can influence postprandial glucose levels, including:
- Type of Carbohydrates: Consuming carbohydrates with a high glycemic index (GI) can lead to quicker and more significant increases in blood glucose levels compared to low GI foods, which cause a more gradual rise in glucose levels.
- Meal Size and Frequency: Larger meals can cause greater spikes in blood glucose, while eating smaller, more frequent meals may help maintain more stable glucose levels.
- Physical Activity: Regular physical activity can improve the body’s sensitivity to insulin, helping to lower postprandial glucose levels.
- Stress Levels: High stress levels can increase cortisol production, which can contribute to higher blood glucose levels.
Managing Postprandial Glucose Levels
Maintaining normal postprandial glucose levels is crucial for overall health and can be achieved through a combination of dietary modifications, regular physical activity, and, if necessary, medication as prescribed by a healthcare provider. Here are some strategies for managing postprandial glucose levels:
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Focus on whole foods, including vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Avoid or limit foods with added sugars, saturated fats, and refined carbohydrates.
- Choose Low Glycemic Index Foods: Foods with a low GI can help prevent sharp spikes in blood glucose levels.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water can help regulate blood glucose levels and improve overall insulin sensitivity.
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity, especially after meals, can help lower postprandial glucose levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Monitor Blood Glucose: Regularly checking blood glucose levels can provide valuable insights into how different foods and activities affect glucose levels, helping individuals make informed decisions about their diet and lifestyle.
Conclusion
Normal glucose levels are a critical aspect of maintaining optimal health. Understanding how glucose levels fluctuate throughout the day, especially in response to eating, can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their diet and lifestyle. By adopting healthy habits, individuals can better manage their glucose levels, reducing the risk of chronic diseases like diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Consulting with a healthcare provider is essential for developing a personalized plan to achieve and maintain normal glucose levels.
What are considered normal blood glucose levels after eating?
+Normal postprandial glucose levels are typically considered to be less than 140 mg/dL two hours after eating for individuals without diabetes. However, this can vary depending on the type and quantity of food consumed, as well as individual factors.
How can I manage my postprandial glucose levels effectively?
+Effective management of postprandial glucose levels involves a combination of dietary modifications, such as eating a balanced diet focusing on whole foods, choosing low glycemic index foods, staying hydrated, exercising regularly, and if necessary, taking medication as prescribed by a healthcare provider.
Why is it important to monitor blood glucose levels regularly?
+Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels provides valuable insights into how different foods, activities, and other factors affect glucose levels. This information can help individuals make informed decisions about their diet and lifestyle, enabling them to maintain optimal glucose levels and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.



