What Is 3Rd Degree Av Block Treatment? Expert Guide
Third-degree atrioventricular (AV) block, also known as complete heart block, is a serious cardiac condition where the electrical signals between the heart’s upper and lower chambers are completely disrupted. This condition can lead to severe symptoms, including fainting, dizziness, and even heart failure. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the treatment options for third-degree AV block, exploring both traditional and innovative approaches.
Understanding Third-Degree AV Block
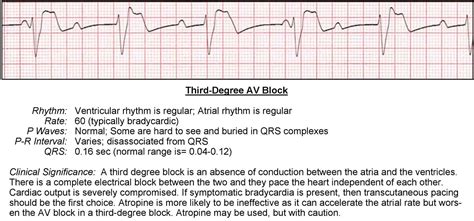
Before discussing treatment, it’s essential to understand the condition. Third-degree AV block occurs when the electrical impulses generated by the heart’s natural pacemaker, the sinoatrial (SA) node, are unable to reach the ventricles. This disruption in communication leads to a complete blockage of electrical signals, causing the heart to beat at a slower rate than normal. In some cases, the ventricles may even beat independently of the atria, a phenomenon known as ventricular escape rhythm.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Third-degree AV block can manifest with a range of symptoms, including:
- Fainting or near-fainting (syncope)
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Fatigue or weakness
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain or discomfort
Diagnosing third-degree AV block typically involves an electrocardiogram (ECG), which can detect the abnormal heart rhythm. Other diagnostic tests, such as echocardiography or cardiac catheterization, may also be performed to rule out underlying conditions.
Treatment Options
Treatment for third-degree AV block depends on the underlying cause, severity of symptoms, and overall health of the patient. The primary goal is to restore a normal heart rhythm and prevent complications.
1. Pacemaker Implantation
The most common treatment for third-degree AV block is the implantation of a pacemaker, a small device that generates electrical impulses to regulate the heart’s rhythm. There are different types of pacemakers, including:
- Single-chamber pacemakers: These devices stimulate either the atria or ventricles.
- Dual-chamber pacemakers: These devices stimulate both the atria and ventricles, mimicking the natural heart rhythm.
Pacemaker implantation is typically performed under local anesthesia and sedation. The procedure involves inserting the pacemaker leads (thin, flexible wires) through a vein in the chest and connecting them to the pacemaker generator, which is usually implanted under the skin.
2. Medications
In some cases, medications may be used to manage symptoms or treat underlying conditions that contribute to third-degree AV block. These medications may include:
- Atropine: To increase heart rate in emergency situations
- Isoproterenol: To increase heart rate and contractility
- Beta blockers: To slow the heart rate and reduce symptoms
3. Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT)
CRT is a type of pacemaker that helps coordinate the beating of the left and right ventricles, improving the heart’s efficiency and reducing symptoms. CRT is typically reserved for patients with severe heart failure and third-degree AV block.
4. His-Bundle Pacing
His-bundle pacing is a newer approach that involves implanting a pacemaker lead directly into the His bundle, a group of specialized fibers that conduct electrical impulses from the atria to the ventricles. This approach can help maintain a more natural heart rhythm and may reduce the risk of complications.
Complications and Risks
As with any medical treatment, there are potential complications and risks associated with third-degree AV block treatment. These may include:
- Pacemaker malfunction or failure
- Infection or bleeding at the implantation site
- Damage to surrounding tissues or nerves
- Allergic reactions to medications
Conclusion
Third-degree AV block is a serious cardiac condition that requires prompt and effective treatment. Pacemaker implantation is the most common treatment, but medications, CRT, and His-bundle pacing may also be used. It’s essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine the best treatment approach and manage potential complications. By understanding the treatment options and taking proactive steps, individuals with third-degree AV block can lead active and healthy lives.
It's crucial to note that third-degree AV block can be a life-threatening condition if left untreated. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.
What are the symptoms of third-degree AV block?
+Symptoms may include fainting, dizziness, fatigue, shortness of breath, and chest pain or discomfort.
How is third-degree AV block diagnosed?
+Diagnosis typically involves an electrocardiogram (ECG) and may include additional tests such as echocardiography or cardiac catheterization.
What is the treatment for third-degree AV block?
+Treatment usually involves pacemaker implantation, but may also include medications, cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT), or His-bundle pacing.
The key to managing third-degree AV block is prompt and effective treatment. By understanding the treatment options and working closely with a healthcare provider, individuals can lead active and healthy lives.