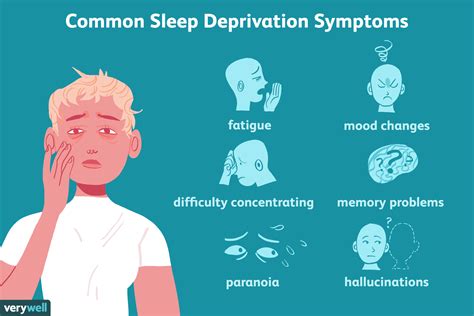
What Is A Sleep Deprivation

Sleep deprivation is a condition that occurs when an individual does not receive an adequate amount of sleep, resulting in a range of physical, emotional, and cognitive impairments. During sleep, the body repairs and regenerates tissues, builds bone and muscle, and strengthens the immune system. Sleep also plays a critical role in brain function, with research suggesting that it helps to clear waste from the brain, consolidate memories, and regulate emotions.
When we don’t get enough sleep, our bodies and brains suffer. Sleep deprivation can be acute, lasting for a short period, or chronic, lasting for an extended period. Chronic sleep deprivation is particularly concerning, as it can have long-term consequences for our health and wellbeing.
One of the primary effects of sleep deprivation is impaired cognitive function. When we’re tired, our reaction times slow, our attention wanders, and our ability to make decisions and solve problems is compromised. This can have serious consequences in everyday life, from decreased productivity at work to increased risk of accidents on the road.
Sleep deprivation also has a significant impact on our emotional wellbeing. When we’re tired, we’re more prone to irritability, anxiety, and depression. We may become more sensitive to stress, and our ability to regulate our emotions is impaired. This can lead to conflicts with others, decreased job satisfaction, and a reduced quality of life.
In addition to its effects on cognitive function and emotional wellbeing, sleep deprivation can also have physical consequences. Chronic sleep deprivation has been linked to an increased risk of obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. It can also weaken the immune system, making us more susceptible to illness and infection.
Sleep deprivation is not just a matter of feeling tired; it's a serious health concern that can have long-term consequences for our physical and mental health. By prioritizing sleep and making it a priority, we can reduce our risk of sleep deprivation and improve our overall wellbeing.
There are many potential causes of sleep deprivation, including lifestyle factors such as work schedules, family responsibilities, and social obligations. Certain medical conditions, such as sleep apnea, insomnia, and restless leg syndrome, can also disrupt sleep patterns. Additionally, the use of electronic devices before bed, consuming heavy meals close to bedtime, and engaging in stimulating activities before sleep can all interfere with our ability to get a good night’s rest.
To address sleep deprivation, it’s essential to establish a consistent sleep schedule and create a sleep-conducive environment. This can include avoiding caffeine and electronics before bedtime, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and making sure the bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool. It’s also crucial to prioritize sleep and make it a priority, just like any other essential aspect of our daily lives.
Understanding the Stages of Sleep
Sleep is a complex process that involves multiple stages, each with distinct characteristics and functions. There are two primary types of sleep: non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep.
NREM sleep is further divided into three stages, each characterized by decreasing brain activity and increasing depth of sleep. Stage 1 NREM sleep is the lightest stage of sleep, during which we drift in and out of consciousness. Stage 2 NREM sleep is characterized by a decrease in body temperature and heart rate, and stage 3 NREM sleep is the deepest stage of NREM sleep, during which it’s difficult to wake up.
REM sleep, on the other hand, is characterized by rapid eye movements, increased brain activity, and vivid dreams. During REM sleep, our brains are active and process memories, consolidate learning, and regulate emotions.
Improving Sleep Quality
- Establish a consistent sleep schedule and stick to it, even on weekends.
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine to signal to your brain that it's time to sleep.
- Avoid caffeine, electronics, and heavy meals close to bedtime.
- Make your bedroom a sleep sanctuary by ensuring it's dark, quiet, and cool.
- Prioritize sleep and make it a priority, just like any other essential aspect of your daily life.
By understanding the stages of sleep and taking steps to improve sleep quality, we can reduce our risk of sleep deprivation and improve our overall wellbeing. It’s essential to remember that sleep is a critical component of our overall health, and by prioritizing it, we can wake up feeling rested, refreshed, and ready to take on the day.
What are the primary effects of sleep deprivation?
+The primary effects of sleep deprivation include impaired cognitive function, emotional instability, and physical consequences such as increased risk of obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.
How can I improve my sleep quality?
+To improve sleep quality, establish a consistent sleep schedule, create a relaxing bedtime routine, avoid caffeine and electronics before bedtime, and make your bedroom a sleep sanctuary.
What are the stages of sleep?
+There are two primary types of sleep: non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. NREM sleep is further divided into three stages, and REM sleep is characterized by rapid eye movements, increased brain activity, and vivid dreams.
In conclusion, sleep deprivation is a serious health concern that can have significant consequences for our physical and mental health. By understanding the stages of sleep, establishing a consistent sleep schedule, and creating a sleep-conducive environment, we can reduce our risk of sleep deprivation and improve our overall wellbeing. Remember, sleep is a critical component of our overall health, and by prioritizing it, we can wake up feeling rested, refreshed, and ready to take on the day.