What Is Furosemide 40Mg Used For? Effective Relief
Furosemide, commonly known by its brand name Lasix, is a potent diuretic medication that has been widely used for decades to treat various conditions associated with fluid retention and edema. The 40mg dosage of furosemide is one of the most commonly prescribed strengths, offering effective relief for patients suffering from conditions that require the removal of excess fluid from the body.
At its core, furosemide works by inhibiting the sodium-potassium-chloride cotransporter in the ascending limb of the loop of Henle, which is a part of the kidney’s nephron. This inhibition leads to increased urine production, resulting in the reduction of fluid volume in the body and subsequent alleviation of edema and other symptoms associated with fluid overload.
Conditions Treated with Furosemide 40mg
Edema: Perhaps the most common use of furosemide 40mg is in the treatment of edema associated with congestive heart failure, liver disease (cirrhosis), and a kidney disorder called nephrotic syndrome. Edema is characterized by swelling caused by excess fluid trapped in the body’s tissues, which can be painful and limit mobility.
Hypertension: Furosemide can be used to treat high blood pressure. By reducing fluid volume and promoting diuresis, it helps lower blood pressure in some patients. However, its use in hypertension is more adjunctive, often used in conjunction with other antihypertensive medications.
Renal Impairment: In cases of acute renal failure, furosemide may be used to increase urine output, helping manage fluid balance. However, its effectiveness can depend on the underlying cause and severity of the renal impairment.
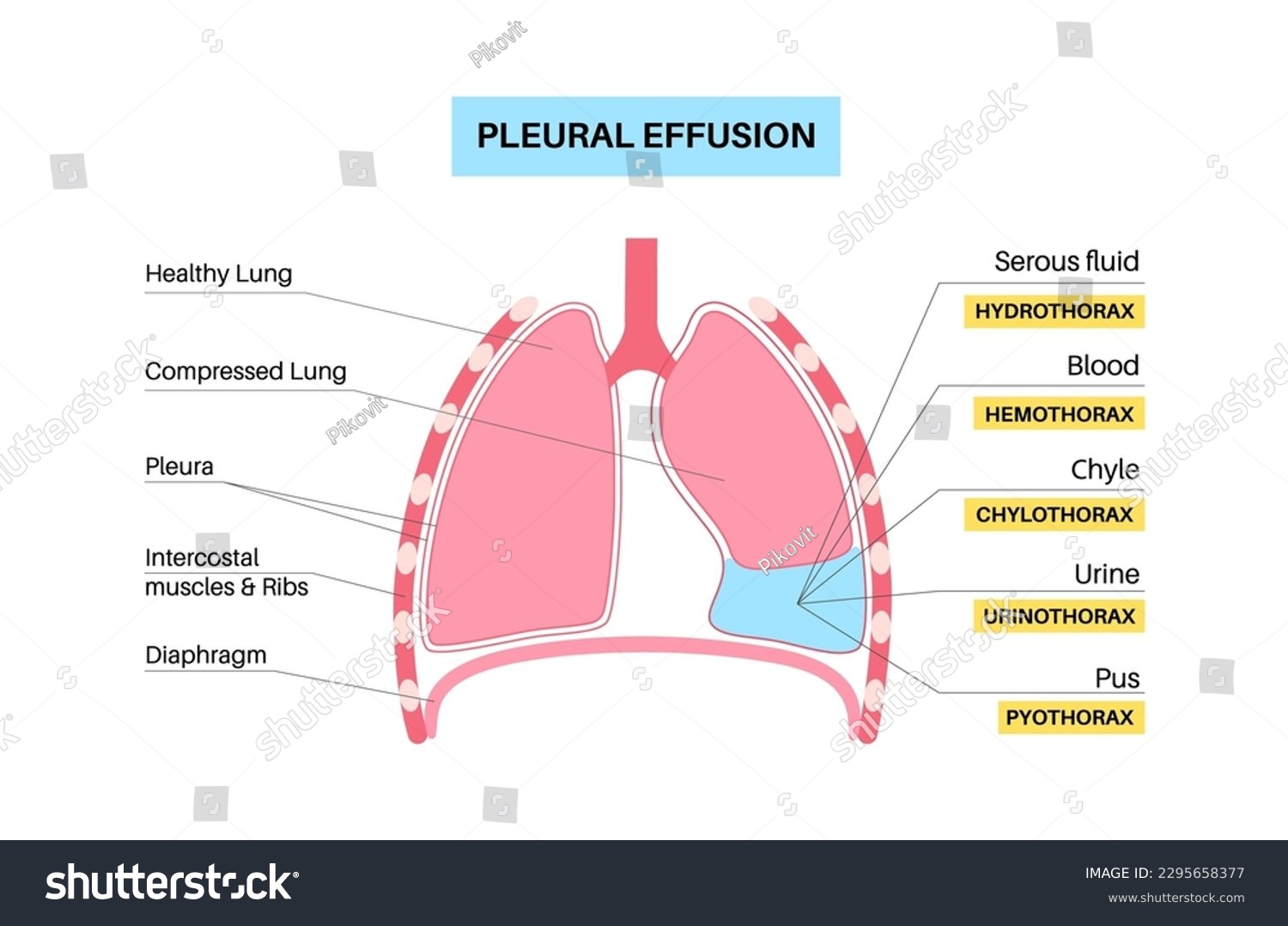
Pulmonary Edema: This is a condition where fluid accumulates in the lungs, making it difficult to breathe. Furosemide can provide rapid relief by promoting the removal of excess fluid.
Ascites: This condition involves fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity, often due to liver disease. Furosemide can help reduce this fluid buildup, alleviating discomfort and other associated symptoms.
Administration and Dosage
The dosage of furosemide can vary depending on the patient’s condition, age, and response to treatment. For adults, the typical starting dose for treating edema is 20-80 mg given as a single dose, and this can be adjusted based on the patient’s response. For hypertension, a lower dose may be used. The 40mg dosage of furosemide is quite common, offering a balance between efficacy and minimizing potential side effects for many conditions.
Side Effects and Considerations
While furosemide 40mg can provide significant relief for various conditions, it’s not without potential side effects. Common side effects include increased urination, dizziness, lightheadedness, and dehydration if the diuretic effect is too strong. Electrolyte imbalances, such as low potassium levels (hypokalemia), are also possible due to the increased urine output. Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s guidance closely, as the dosage may need adjustment to mitigate these effects.
Moreover, patients should be aware of signs of dehydration or electrolyte imbalance, such as excessive thirst, dark urine, decreased urine output, muscle pain or weakness, and fast or irregular heartbeat, and report them promptly to their healthcare provider.
In conclusion, furosemide 40mg is an effective medication for treating a range of conditions associated with fluid retention and edema. Its use should be tailored to the individual patient’s needs and monitored by a healthcare professional to ensure the benefits are maximized while minimizing potential side effects.
Practical Guidance for Patients
For those taking furosemide 40mg, here are some practical tips: - Stay hydrated: It’s a paradox that while furosemide helps remove excess fluid, dehydration can occur if the body loses too much fluid. Drinking water regularly can help. - Monitor urine output: Keep track of how much you urinate and report any significant changes to your healthcare provider. - Watch for signs of electrolyte imbalance: Muscle cramps, weakness, or heart palpitations can indicate low potassium or magnesium levels. - Follow up regularly: Regular check-ins with your healthcare provider can help adjust the dosage if necessary and manage side effects.
By understanding how furosemide 40mg works and being mindful of its potential effects and side effects, patients can better navigate their treatment plan and work towards managing their condition effectively.
What are the common side effects of furosemide 40mg?
+Common side effects include increased urination, dizziness, lightheadedness, and dehydration. Electrolyte imbalances, such as low potassium levels, can also occur.
How should I take furosemide 40mg for best results?
+Follow the exact dosage instructions provided by your healthcare provider, and stay hydrated by drinking water regularly. Monitor your urine output and watch for signs of dehydration or electrolyte imbalance.
Can I stop taking furosemide 40mg if I feel better?
+No, do not stop taking furosemide without consulting your healthcare provider. Stopping the medication abruptly can lead to a return of symptoms or worsening of your condition.