What Is Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Test? Accurate Results
The Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) test is a pivotal diagnostic tool employed by healthcare professionals to assess the functioning of the thyroid gland. This gland, situated in the neck, plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism, energy production, and overall hormonal balance through the production of thyroid hormones, primarily thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). The TSH test is fundamental in evaluating how well the thyroid is operating and is typically the first line of investigation when thyroid dysfunction is suspected.
How TSH Works
TSH is a hormone produced by the pituitary gland, a small endocrine gland located at the base of the brain. The primary function of TSH is to stimulate the thyroid gland to produce and release T4 and T3 into the bloodstream. These thyroid hormones are crucial for various bodily functions, including heart rate, digestion, muscle strength, and metabolism regulation. The level of TSH in the blood is a reflection of how well the thyroid is responding to the pituitary gland’s signals. In a healthy individual, the pituitary gland adjusts the amount of TSH it produces based on the levels of T4 and T3 in the blood. This feedback loop ensures that the thyroid hormones remain within a narrow, healthy range.
Interpreting TSH Test Results
The interpretation of TSH test results is nuanced and requires consideration of the clinical context, including symptoms, medical history, and other diagnostic findings. Generally, TSH levels are interpreted as follows:
- Normal Range: This typically falls between 0.4 and 4.5 milliunits per liter (mU/L), though reference ranges can slightly vary between laboratories. A TSH level within this range usually indicates that the thyroid is functioning properly.
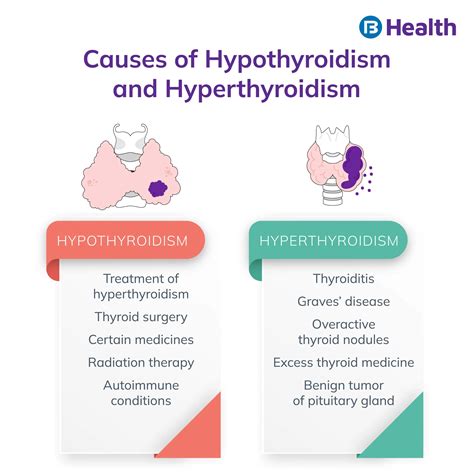
- Elevated TSH: Levels above the normal range may indicate hypothyroidism, a condition where the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones. This can be due to various causes, including autoimmune diseases like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, thyroid surgery, or radiation therapy.
- Low TSH: Levels below the normal range can suggest hyperthyroidism, where the thyroid produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones. This could be due to conditions like Graves’ disease, thyroid nodules, or excessive intake of thyroid hormone medication.
Factors Influencing TSH Test Results
Several factors can influence TSH test results, leading to either false positives or false negatives. These include:
- Medications: Certain drugs, such as lithium, amiodarone, and high doses of iodine-containing contrast agents, can affect thyroid function and thus TSH levels.
- Pregnancy: Thyroid hormone requirements increase during pregnancy, and TSH levels may be lower due to the effect of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) on the thyroid.
- Age: TSH levels naturally increase with age.
- Time of Day: TSH levels can vary throughout the day, typically peaking at night.
- Non-Thyroidal Illness: Severe illness can transiently alter TSH levels.
Ensuring Accurate Results
To ensure accurate TSH test results, it’s essential to:
- Follow Pre-Test Instructions: This may include fasting or avoiding certain medications.
- Choose the Right Test: In some cases, free T4 (FT4) and free T3 (FT3) tests may also be necessary for a comprehensive assessment.
- Consider Repeat Testing: If results are borderline or if symptoms persist despite normal results, repeating the test after an appropriate interval may be advisable.
- Clinical Correlation: Always interpret TSH results in the context of clinical symptoms and other diagnostic findings.
In conclusion, the TSH test is a critical tool for evaluating thyroid function. Understanding the nuances of TSH levels and the factors that can influence test results is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective management of thyroid disorders. Healthcare providers play a vital role in interpreting these results within the context of each patient’s unique clinical scenario, ensuring that thyroid conditions are diagnosed and treated appropriately.
What does an elevated TSH level indicate?
+An elevated TSH level typically indicates that the thyroid gland is not producing enough thyroid hormones, a condition known as hypothyroidism. This can be due to various causes, including autoimmune diseases, thyroid surgery, or radiation therapy.
How often should TSH tests be repeated?
+The frequency of TSH testing depends on the individual's health status and the presence of thyroid disorders. For those with a history of thyroid issues or on thyroid hormone replacement therapy, regular monitoring as advised by a healthcare provider is necessary.
Can medications affect TSH test results?
+Yes, certain medications can influence TSH levels. These include lithium, amiodarone, and high doses of iodine-containing contrast agents. It's crucial to inform your healthcare provider about all medications you're taking before undergoing a TSH test.
By understanding the intricacies of the TSH test and its results, individuals can better navigate the diagnosis and management of thyroid-related conditions, ensuring optimal thyroid health and overall well-being.