What Level Of Blood Sugar
is considered normal, and how does it impact our overall health? Blood sugar levels, also known as blood glucose levels, are a critical measure of our body’s ability to regulate the amount of glucose in the bloodstream. Glucose is a type of sugar that serves as the primary source of energy for our cells, and it’s essential to maintain a healthy balance to prevent various health complications.
Normal Blood Sugar Levels
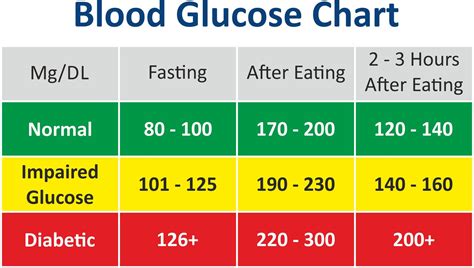
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends the following blood sugar levels as normal:
- Fasting blood sugar: Less than 100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L)
- After eating (postprandial): Less than 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L)
- 2 hours after eating: Less than 120 mg/dL (6.7 mmol/L)
It’s essential to note that these values can vary slightly depending on the individual, their age, and any underlying medical conditions. For example, pregnant women or people with certain medical conditions may have different target blood sugar levels.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
To better comprehend blood sugar levels, let’s explore how glucose is regulated in the body. When we eat, our body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. The pancreas, an organ located behind the stomach, releases insulin, a hormone that helps cells absorb glucose from the bloodstream. As glucose enters the cells, the blood sugar levels decrease.
Conversely, when we haven’t eaten for a while, the pancreas releases glucagon, a hormone that stimulates the liver to release stored glucose (glycogen) into the bloodstream, raising blood sugar levels. This elegant balance ensures that our cells receive the energy they need to function properly.
Impact of Blood Sugar Levels on Health
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial to prevent various health complications, including:
- Diabetes: Elevated blood sugar levels over an extended period can lead to the development of type 2 diabetes, which increases the risk of heart disease, kidney disease, and nerve damage.
- Cardiovascular disease: High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and nerves, increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease.
- Neuropathy: Prolonged high blood sugar levels can damage nerves, leading to numbness, tingling, and pain in the hands and feet.
- Kidney disease: High blood sugar levels can damage the kidneys, leading to chronic kidney disease and potentially even kidney failure.
Factors That Influence Blood Sugar Levels
Several factors can impact blood sugar levels, including:
- Diet: Consuming high-carbohydrate foods, sugary drinks, and saturated fats can raise blood sugar levels.
- Physical activity: Regular exercise, such as walking, can help lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as steroids and certain psychiatric medications, can raise blood sugar levels.
- Stress: Chronic stress can increase cortisol levels, which can raise blood sugar levels.
- Sleep: Poor sleep quality and duration can disrupt blood sugar regulation.
Strategies for Maintaining Healthy Blood Sugar Levels
Fortunately, there are several strategies that can help maintain healthy blood sugar levels:
- Eat a balanced diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods, such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water to help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Exercise regularly: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week.
- Manage stress: Engage in stress-reducing activities, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Get enough sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night to help regulate blood sugar levels.
What are the symptoms of high blood sugar levels?
+High blood sugar levels can cause symptoms such as increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow healing of cuts and wounds.
How can I check my blood sugar levels at home?
+You can check your blood sugar levels at home using a blood glucose meter, which involves pricking your finger with a lancet and placing a small drop of blood on a test strip.
What is the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
+Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system attacks the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, while type 2 diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by insulin resistance and impaired insulin secretion.
In conclusion, maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial to prevent various health complications. By understanding the factors that influence blood sugar levels and implementing strategies to maintain a healthy balance, we can reduce our risk of developing diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and other health conditions. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional if you have concerns about your blood sugar levels or overall health.