Z Pack Antibiotics: Fast Relief From Bacterial Infections
The advent of antibiotics has revolutionized the treatment of bacterial infections, saving countless lives and alleviating suffering worldwide. Among the array of antibiotics available, Z Pack antibiotics have emerged as a popular and effective treatment option for various bacterial infections. But what exactly are Z Pack antibiotics, how do they work, and what are their benefits and potential drawbacks?
To understand the significance of Z Pack antibiotics, it’s essential to delve into the world of bacterial infections and the challenges they pose. Bacteria are microscopic organisms that can cause a wide range of infections, from mild to life-threatening. When bacteria invade the body, they can trigger an immune response, leading to inflammation, pain, and discomfort. If left untreated, bacterial infections can spread, causing severe complications and even death.
Introduction to Z Pack Antibiotics

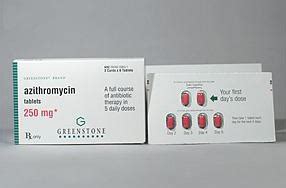
Z Pack antibiotics, also known as Zithromax, are a type of macrolide antibiotic that belongs to the azalide class. They contain the active ingredient azithromycin, which works by inhibiting the growth and multiplication of bacteria. Z Pack antibiotics are available in various forms, including capsules, tablets, and oral suspensions, making them convenient for patients to take.
The unique aspect of Z Pack antibiotics is their dosing schedule. The “Z Pack” refers to a specific dosing regimen, where the patient takes a higher dose of azithromycin on the first day, followed by a lower dose for the next four days. This dosing schedule allows for high concentrations of the antibiotic in the body, providing rapid relief from bacterial infections.
How Z Pack Antibiotics Work

Z Pack antibiotics work by binding to the bacterial ribosome, which is responsible for protein synthesis. By inhibiting protein synthesis, azithromycin prevents the bacteria from growing and multiplying, ultimately leading to their death. This mechanism of action makes Z Pack antibiotics effective against a wide range of bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections, skin infections, and sexually transmitted infections.
One of the key advantages of Z Pack antibiotics is their ability to concentrate in high levels in the tissues, providing targeted treatment of the infected area. This property, combined with their broad-spectrum activity, makes them an ideal choice for treating various bacterial infections.
Benefits of Z Pack Antibiotics
The benefits of Z Pack antibiotics are numerous. They offer:
- Rapid relief: Z Pack antibiotics provide quick relief from symptoms, reducing the duration and severity of bacterial infections.
- Convenience: The Z Pack dosing schedule is easy to follow, with a simple regimen that minimizes the risk of non-compliance.
- Broad-spectrum activity: Z Pack antibiotics are effective against a wide range of bacterial infections, making them a valuable treatment option.
- Low risk of resistance: Azithromycin has a low risk of resistance development, reducing the likelihood of treatment failure.
Potential Drawbacks and Side Effects
While Z Pack antibiotics are generally well-tolerated, they can cause side effects, including:
- Gastrointestinal issues: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain are common side effects of Z Pack antibiotics.
- Allergic reactions: Some patients may experience allergic reactions, such as rash, itching, or difficulty breathing.
- Cardiovascular issues: Z Pack antibiotics can cause changes in heart rhythm, particularly in patients with pre-existing heart conditions.
It’s essential to note that Z Pack antibiotics are not suitable for everyone, particularly those with certain medical conditions, such as liver or kidney disease. Patients should consult their healthcare provider to determine if Z Pack antibiotics are the right treatment option for their specific condition.
Common Uses of Z Pack Antibiotics
Z Pack antibiotics are commonly used to treat various bacterial infections, including:
- Respiratory tract infections: Bronchitis, pneumonia, and sinusitis are common indications for Z Pack antibiotics.
- Skin infections: Z Pack antibiotics are effective against skin infections, such as impetigo, folliculitis, and cellulitis.
- Sexually transmitted infections: Chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis are among the sexually transmitted infections that can be treated with Z Pack antibiotics.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Z Pack antibiotics offer a convenient and effective treatment option for various bacterial infections. Their broad-spectrum activity, rapid relief, and low risk of resistance development make them a valuable choice for patients. However, it’s crucial to weigh the benefits and potential drawbacks, considering individual patient needs and medical conditions. By working closely with healthcare providers, patients can determine if Z Pack antibiotics are the right treatment option for their specific condition, ensuring the best possible outcome.
What is the typical dosing schedule for Z Pack antibiotics?
+The typical dosing schedule for Z Pack antibiotics involves taking a higher dose on the first day, followed by a lower dose for the next four days.
What are the common side effects of Z Pack antibiotics?
+Common side effects of Z Pack antibiotics include gastrointestinal issues, allergic reactions, and cardiovascular issues.
Are Z Pack antibiotics suitable for everyone?
+No, Z Pack antibiotics are not suitable for everyone, particularly those with certain medical conditions, such as liver or kidney disease.
What are the common uses of Z Pack antibiotics?
+Z Pack antibiotics are commonly used to treat respiratory tract infections, skin infections, and sexually transmitted infections.
How do Z Pack antibiotics work?
+Z Pack antibiotics work by binding to the bacterial ribosome, inhibiting protein synthesis and preventing the growth and multiplication of bacteria.



