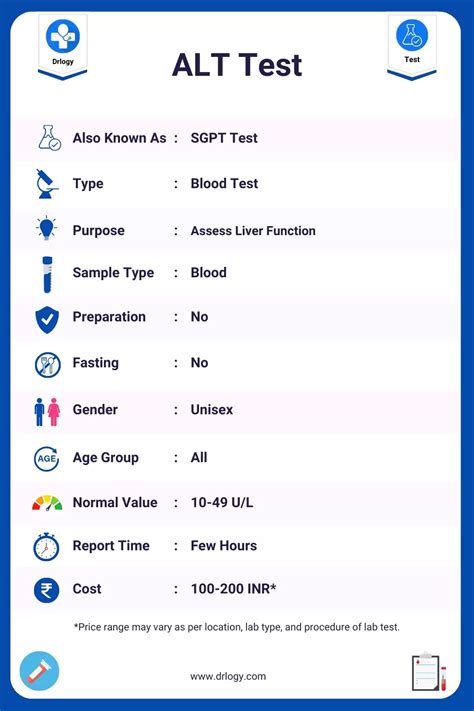
Alt Blood Test Normal Range
Elevations in the alanine transaminase (ALT) blood test can signify liver damage or inflammation, prompting healthcare providers to investigate further to determine the cause. The ALT test is a crucial component of a liver panel, which assesses liver health by measuring various enzymes and proteins in the blood. Understanding the normal range for ALT and the implications of abnormal results is essential for both healthcare providers and patients.
Normal Range for ALT
The normal range for ALT in the blood varies slightly among different laboratories but is generally considered to be between 0 and 40 units per liter (U/L) for adults. However, it’s essential to note that what is considered “normal” can vary based on the laboratory conducting the test, the equipment used, and the individual’s specific characteristics, such as age and sex. Some laboratories may define the upper limit of normal as slightly higher, up to 45 U/L or even 50 U/L in some cases, reflecting the variability in liver enzyme levels among healthy individuals.
Factors Influencing ALT Levels
Several factors can influence ALT levels, including but not limited to, age, gender, body mass index (BMI), and the presence of underlying medical conditions. For instance, ALT levels tend to be higher in men than in women and can increase with age. Individuals with a higher BMI may also have higher ALT levels due to the potential for fatty liver disease. It’s also crucial to consider that ALT levels can fluctuate and may be influenced by recent physical activity, diet, and other lifestyle factors.
Causes of Elevated ALT
Elevated ALT levels suggest liver cell damage but are not specific to any one cause. Common reasons for elevated ALT include:
- Viral Hepatitis: Infections such as hepatitis A, B, and C can cause liver inflammation, leading to elevated ALT levels.
- Fatty Liver Disease: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and alcoholic liver disease can cause ALT levels to rise.
- Medications and Toxins: Certain drugs, such as statins, and exposure to toxins can damage liver cells, increasing ALT levels.
- Autoimmune Hepatitis: A condition where the body’s immune system attacks liver cells.
- Muscle Diseases: While ALT is predominantly found in the liver, it is also present in smaller amounts in muscle tissue. Therefore, muscle diseases or injuries can also lead to elevated ALT levels, although this is less common.
Interpretation of ALT Results
Interpreting ALT results requires a comprehensive approach, considering the patient’s overall clinical picture, including symptoms, medical history, and other laboratory findings. Mild elevations in ALT may not always signify significant liver disease and can sometimes be transient. However, significantly elevated ALT levels or persistent mild elevations warrant further investigation.
Further Evaluation
If ALT levels are elevated, healthcare providers may order additional tests to determine the cause and extent of liver damage. These may include:
- Other Liver Enzymes: Aspartate transaminase (AST) and other components of the liver panel can provide more insight into liver health.
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI may be used to visually assess liver damage.
- Liver Biopsy: In some cases, a biopsy may be necessary to examine liver tissue more closely.
- Viral Hepatitis Tests: To diagnose hepatitis A, B, or C infections.
- Autoantibody Tests: For autoimmune hepatitis.
Management and Treatment
The management and treatment of elevated ALT levels depend on the underlying cause. For example, if the elevation is due to fatty liver disease, lifestyle modifications such as weight loss and exercise may be recommended. In cases of viral hepatitis, antiviral medications may be prescribed. If medications are suspected to be the cause, alternative treatments may be explored.
Prevention
Preventing liver damage is crucial for maintaining healthy ALT levels. This can be achieved through various means, including:
- Vaccinations: Against hepatitis A and B.
- Safe Alcohol Consumption: Limiting alcohol intake to recommended levels.
- Healthy Diet and Exercise: Maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding a diet high in saturated fats.
- Avoiding Toxins: Being cautious with chemicals and drugs that can harm the liver.
Conclusion
ALT blood tests are a valuable tool for assessing liver health, but understanding the results requires a nuanced approach. Both healthcare providers and patients should be aware of the normal range for ALT, the factors that can influence levels, and the potential causes and implications of elevations. By adopting preventive measures and seeking medical evaluation when necessary, individuals can protect their liver health and address any issues promptly.
What is the normal range for ALT in blood tests?
+The normal range for ALT (alanine transaminase) in blood tests is generally considered to be between 0 and 40 units per liter (U/L) for adults, though this can slightly vary among different laboratories.
What factors can influence ALT levels in the blood?
+Several factors can influence ALT levels, including age, gender, body mass index (BMI), and the presence of underlying medical conditions. Lifestyle factors such as diet and physical activity can also impact ALT levels.
What are common causes of elevated ALT levels?
+Elevated ALT levels can result from various conditions, including viral hepatitis, fatty liver disease, certain medications, autoimmune hepatitis, and muscle diseases. The specific cause needs to be determined through further medical evaluation.
How is elevated ALT managed and treated?
+Management and treatment of elevated ALT depend on the underlying cause. This can include lifestyle modifications, antiviral medications for hepatitis, alternative treatments if medications are the cause, and addressing any underlying conditions contributing to the elevation.
What preventive measures can be taken to maintain healthy ALT levels?
+Preventing liver damage is key to maintaining healthy ALT levels. This can be achieved through vaccinations against hepatitis A and B, safe alcohol consumption, a healthy diet and regular exercise, and avoiding toxins that can harm the liver.