Blood Sugar Chart For Diabetes
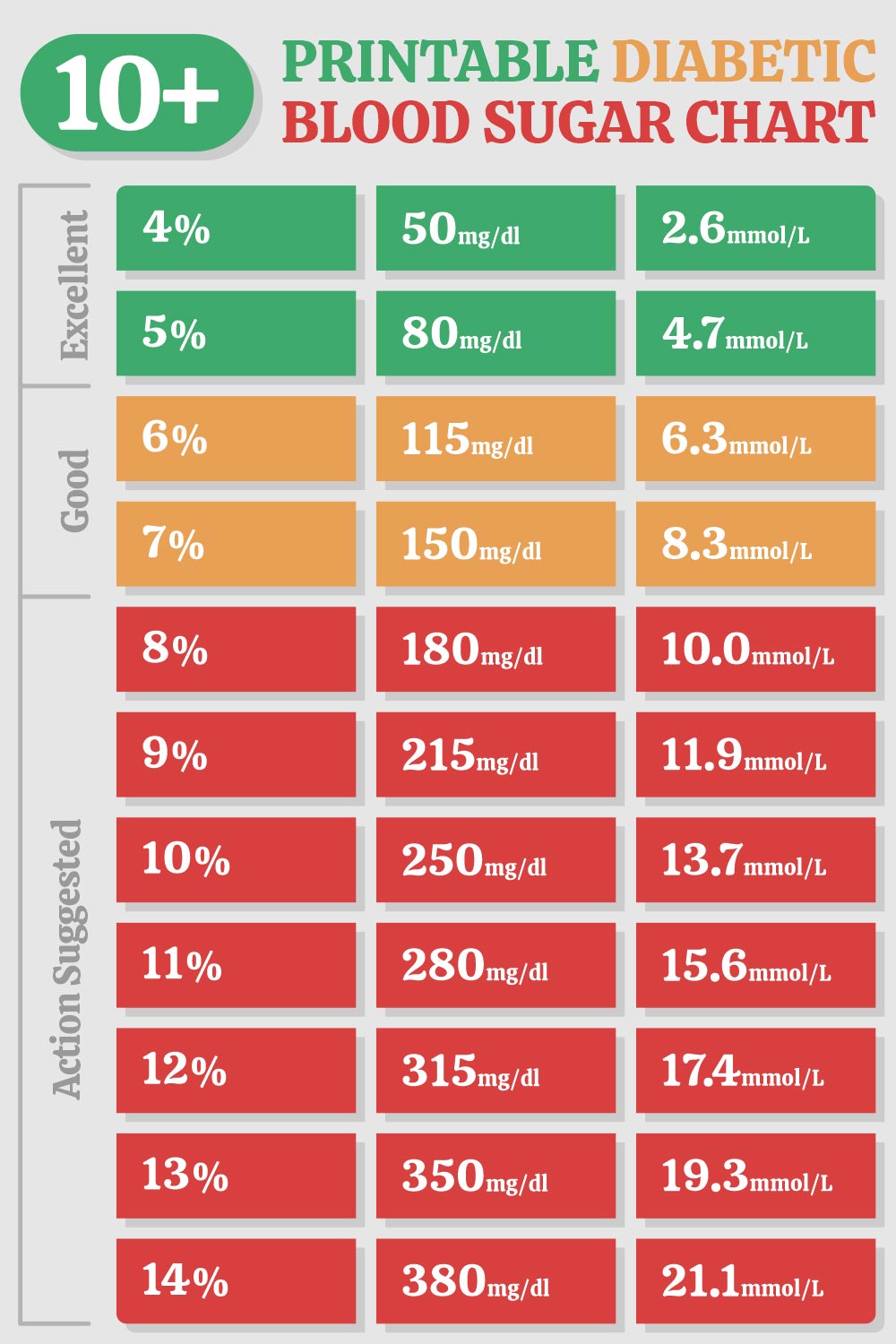
Managing diabetes requires a thorough understanding of blood sugar levels and how they fluctuate throughout the day. A blood sugar chart is a valuable tool for individuals with diabetes, as it helps track and manage glucose levels, making it easier to adjust diet, exercise, and medication regimens as needed. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the world of blood sugar charts, exploring what they are, how to use them, and the importance of monitoring blood sugar levels for effective diabetes management.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
Before diving into the specifics of a blood sugar chart, it’s essential to understand the concept of blood sugar levels. Blood sugar, or glucose, is the primary energy source for the body’s cells. It’s obtained from the food we eat and is regulated by the pancreas, which releases insulin and glucagon to maintain a healthy balance. In individuals with diabetes, this balance is disrupted, leading to high blood sugar levels if left unmanaged.
What is a Blood Sugar Chart?
A blood sugar chart, also known as a blood glucose log, is a tool used by individuals with diabetes to record their blood sugar levels at various times throughout the day. This chart typically includes columns for the date, time, blood glucose reading, medication taken, food consumed, and any notes about physical activity or other factors that might affect blood sugar levels.
How to Use a Blood Sugar Chart
Using a blood sugar chart effectively involves several steps:
Regular Monitoring: Check your blood sugar levels at the same times each day, typically before meals and at bedtime. Also, monitor after meals if possible, especially if you’re trying to understand how different foods affect your levels.
Record Keeping: Write down each reading in your chart, along with the time and any relevant details such as what you ate, any medication taken, and whether you engaged in physical activity.
Analysis: Regularly review your chart to identify patterns or trends. For example, you might notice that your blood sugar levels are higher in the morning or after consuming certain foods.
Adjustments: Based on your observations, make adjustments to your diet, exercise routine, or medication as advised by your healthcare provider. This could involve changing meal times, portions, or types of food, increasing physical activity, or adjusting medication dosages.
Importance of Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Monitoring blood sugar levels is crucial for several reasons:
Prevents Complications: High blood sugar levels over time can lead to serious health complications, including heart disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, and vision problems. Regular monitoring helps keep levels in check, reducing the risk of these complications.
Guides Treatment: Blood sugar charts provide valuable information for healthcare providers, helping them adjust treatment plans, including medication, diet, and exercise recommendations.
Enhances Awareness: By tracking blood sugar levels, individuals with diabetes become more aware of how different factors (food, exercise, stress, etc.) affect their glucose levels, empowering them to make better lifestyle choices.
Creating Your Own Blood Sugar Chart
While there are many templates available online, creating your own blood sugar chart can be as simple as setting up a table in a notebook or using a spreadsheet on your computer or mobile device. The key components to include are:
- Date and Time: When each reading was taken.
- Blood Glucose Reading: The actual level, usually measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or millimoles per liter (mmol/L).
- Medications: Any diabetes medications taken, including dosages.
- Food and Drinks: A brief description of meals and snacks consumed.
- Physical Activity: Notes on any exercise or significant physical activity.
- Notes: Any additional comments, such as stress levels, sleep quality, or other factors that might influence blood sugar levels.
Conclusion
A blood sugar chart is a powerful tool in the management of diabetes, offering a clear picture of how blood glucose levels fluctuate and respond to different factors. By regularly monitoring and recording blood sugar levels, individuals with diabetes can better understand their condition, make informed decisions about their care, and work towards maintaining healthy blood sugar levels. Remember, managing diabetes is a long-term commitment, and with the right tools and mindset, it’s possible to lead a full and active life.
What are normal blood sugar levels?
+Normal blood sugar levels are typically between 70 and 140 mg/dL, but these targets can vary depending on the individual and their specific health needs. It’s best to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized targets.
How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of checking blood sugar levels depends on the type of diabetes, treatment plan, and individual factors. Generally, it’s recommended to check levels at least four times a day: before breakfast, before lunch, before dinner, and at bedtime.


