Normal Sugar Level For Diabetic

Maintaining normal sugar levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes to prevent complications and manage the condition effectively. The goal of diabetes management is to keep blood glucose levels as close to normal as possible. This involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes, regular physical activity, and, if necessary, medication.
Understanding Blood Glucose Levels
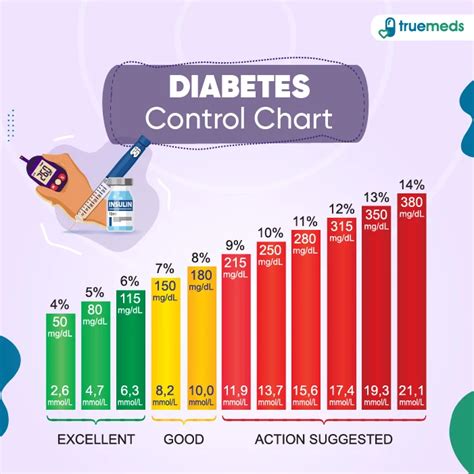
Blood glucose levels are measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) in the United States and in millimoles per liter (mmol/L) in most other countries. For people with diabetes, the American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends the following blood glucose targets:
- Before meals: 80 to 130 mg/dL (4.4 to 7.2 mmol/L)
- After meals (1-2 hours after beginning of meal): Less than 180 mg/dL (10.0 mmol/L)
- At bedtime: 100 to 140 mg/dL (5.6 to 7.8 mmol/L)
- A1c (average blood glucose over the past 2-3 months): Less than 7% for most adults
Factors Influencing Blood Sugar Levels
Several factors can influence blood sugar levels, including:
Diet: The types and amounts of food you eat can significantly affect your blood sugar levels. Foods high in carbohydrates, especially those with a high glycemic index, can cause blood sugar levels to rise more rapidly.
Physical Activity: Regular physical activity can help lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. The type and duration of activity can influence how much it affects blood glucose levels.
Medications: If you are taking diabetes medications, they can affect your blood glucose levels. It’s essential to follow your medication regimen as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
Stress: Stress can raise your blood sugar levels. Learning stress management techniques, such as deep breathing, exercise, or meditation, can help.
Sleep: Lack of quality sleep can affect blood sugar control and insulin sensitivity. Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels
Effective management of blood sugar levels involves a multimodal approach:
Monitoring: Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels helps you understand how different factors affect your levels and make informed decisions about your care.
Dietary Management: Focus on balanced meals that are low in added sugars, saturated fats, and sodium. Choose foods that are rich in nutrients and fiber, such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Physical Activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity, or a combination of both, per week. You should also incorporate strength-training activities, high-intensity interval training, and other forms of physical activity.
Medication Adherence: If you’re prescribed diabetes medications, take them as directed. Your healthcare provider may need to adjust your medications based on your blood glucose monitoring results and other factors.
Stress Management and Sleep: Engage in stress-reducing activities and prioritize getting enough quality sleep.
Complications of Unmanaged Diabetes
Unmanaged diabetes can lead to serious complications, including:
- Heart Disease and Stroke: High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and the nerves that control the heart.
- Kidney Damage: Diabetes is the leading cause of kidney failure.
- Nerve Damage (Neuropathy): High blood sugar can damage the nerves, causing pain, numbness, or weakness in the hands and feet.
- Vision Problems and Blindness: Diabetes can cause blindness due to damage to the blood vessels in the retina.
- Foot Damage: Nerve damage and poor blood flow can lead to serious foot problems, including infections and amputations.
Conclusion
Maintaining normal sugar levels is a critical aspect of diabetes management. By understanding the factors that influence blood glucose levels and implementing a comprehensive management plan that includes dietary changes, physical activity, medication adherence, stress management, and quality sleep, individuals with diabetes can reduce the risk of complications and improve their quality of life.
What are the normal blood sugar levels for someone with diabetes?
+For individuals with diabetes, the American Diabetes Association recommends blood glucose levels of 80 to 130 mg/dL before meals and less than 180 mg/dL after meals. The A1c goal for most adults is less than 7%.
How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of checking blood sugar levels depends on your treatment plan and the type of diabetes you have. Generally, it’s recommended to check before meals, after meals, at bedtime, and occasionally during the night.
What foods should I avoid to manage my blood sugar levels?
+It’s best to limit foods that are high in added sugars, saturated fats, and sodium. Examples include sugary drinks, fast food, and processed snacks. Instead, focus on whole, unprocessed foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
How does physical activity impact blood sugar levels?
+Regular physical activity can help lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week, along with strength-training activities and other forms of physical activity.
Why is sleep important for managing diabetes?
+Lack of quality sleep can affect blood sugar control and insulin sensitivity. Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night to help manage your diabetes.