Diabetes Eyesight Test Guide: Protect Vision
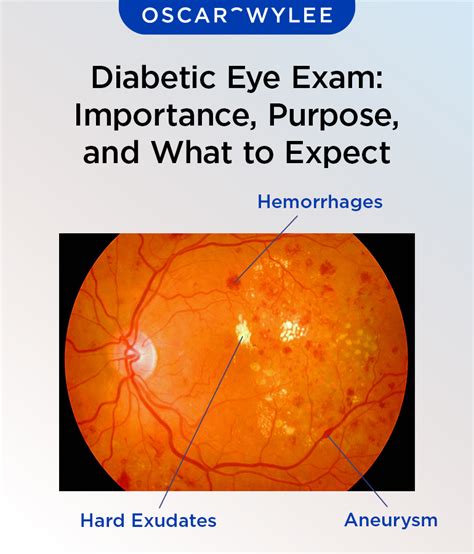
As the world grapples with the escalating prevalence of diabetes, a silent yet devastating complication has emerged: diabetic eye disease. This condition, which encompasses a range of vision-threatening disorders, including diabetic retinopathy, macular edema, and cataracts, can lead to irreversible blindness if left undiagnosed or untreated. The importance of regular eyesight tests for individuals with diabetes cannot be overstated, as early detection and management are crucial in preventing or delaying the onset of vision loss. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of diabetic eye care, exploring the warning signs, diagnostic tests, treatment options, and preventative measures that can help protect vision and ensure a better quality of life for those affected by this condition.
Understanding Diabetic Eye Disease
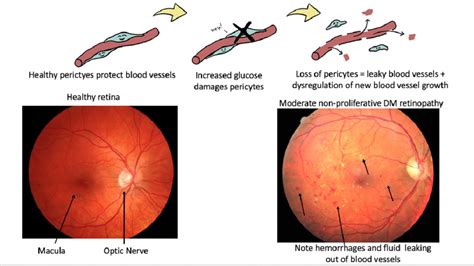
Diabetic eye disease is a broad term that encompasses several eye conditions that can occur in people with diabetes. These conditions include:
- Diabetic Retinopathy: A condition characterized by damage to the blood vessels in the retina, which can lead to vision loss and blindness.
- Macular Edema: A condition where fluid builds up in the macula, the part of the retina responsible for central vision, causing vision distortion and blindness.
- Cataracts: A condition where the lens of the eye becomes cloudy, affecting vision.
- Glaucoma: A condition where the pressure in the eye increases, damaging the optic nerve and leading to vision loss.
Warning Signs of Diabetic Eye Disease

While diabetic eye disease can progress without noticeable symptoms in its early stages, there are several warning signs that may indicate the presence of a problem. These include:
- Blurred Vision: Difficulty seeing clearly or experiencing double vision.
- Floaters: Seeing spots or floaters in your field of vision.
- Flashes of Light: Experiencing sudden flashes of light or seeing sparks.
- Vision Loss: Sudden or gradual loss of vision.
- Eye Pain: Feeling pain or pressure in the eyes.
Diabetic Eyesight Test Guide
Regular eye exams are essential for individuals with diabetes, as they can help detect diabetic eye disease in its early stages, when treatment is most effective. The following tests are typically included in a comprehensive diabetic eye exam:
- Visual Acuity Test: A test that measures the sharpness of your vision.
- Dilated Eye Exam: A test where the pupils are dilated to allow the doctor to examine the retina and optic nerve.
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT): A non-invasive test that uses light waves to take pictures of the retina and optic nerve.
- Fluorescein Angiography: A test that uses a special dye to highlight the blood vessels in the retina.
Treatment Options for Diabetic Eye Disease
While there is no cure for diabetic eye disease, several treatment options are available to manage the condition and prevent further vision loss. These include:
- Laser Surgery: A procedure that uses a laser to destroy abnormal blood vessels in the retina.
- Intraocular Injections: Medications injected into the eye to reduce swelling and prevent vision loss.
- Vitrectomy: A surgical procedure that removes the vitreous gel and any blood that has leaked into the eye.
- Cataract Surgery: A surgical procedure that removes the cloudy lens and replaces it with an artificial one.
Preventative Measures

While diabetic eye disease can be treated, prevention is still the best approach. The following measures can help reduce the risk of developing diabetic eye disease:
- Control Blood Sugar Levels: Keeping blood sugar levels within a healthy range can help prevent damage to the blood vessels in the eyes.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of developing diabetic eye disease.
- Exercise Regularly: Regular physical activity can help improve blood flow and overall health.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking can increase the risk of developing diabetic eye disease.
- Get Regular Eye Exams: Regular eye exams can help detect diabetic eye disease in its early stages, when treatment is most effective.
FAQ Section
What are the symptoms of diabetic eye disease?
+The symptoms of diabetic eye disease can include blurred vision, floaters, flashes of light, vision loss, and eye pain. However, in its early stages, diabetic eye disease may not have any noticeable symptoms, which is why regular eye exams are essential.
How often should I get my eyes checked if I have diabetes?
+If you have diabetes, it is recommended that you get your eyes checked at least once a year, or as directed by your eye doctor. Regular eye exams can help detect diabetic eye disease in its early stages, when treatment is most effective.
Can diabetic eye disease be treated?
+Yes, diabetic eye disease can be treated. Treatment options may include laser surgery, intraocular injections, vitrectomy, and cataract surgery. The goal of treatment is to prevent further vision loss and manage the condition.
Can I prevent diabetic eye disease?
+While diabetic eye disease cannot be completely prevented, there are measures that can help reduce the risk of developing the condition. These include controlling blood sugar levels, maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, and getting regular eye exams.
Conclusion
Diabetic eye disease is a devastating complication of diabetes that can lead to irreversible vision loss if left undiagnosed or untreated. Regular eyesight tests are essential for individuals with diabetes, as they can help detect the condition in its early stages, when treatment is most effective. By understanding the warning signs, diagnostic tests, treatment options, and preventative measures, individuals with diabetes can take proactive steps to protect their vision and ensure a better quality of life. Remember, early detection and management are key to preventing or delaying the onset of vision loss. Don’t wait until it’s too late – schedule your eye exam today and take the first step towards protecting your vision.