Diabetic Normal Values
Understanding diabetic normal values is crucial for managing diabetes effectively. Diabetes, a chronic health condition characterized by elevated levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood, affects millions worldwide. Proper management involves monitoring and maintaining blood glucose levels within a target range to prevent complications. Here, we’ll delve into the normal values for diabetes management, including blood glucose levels, hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) levels, and other relevant metrics.
Blood Glucose Levels
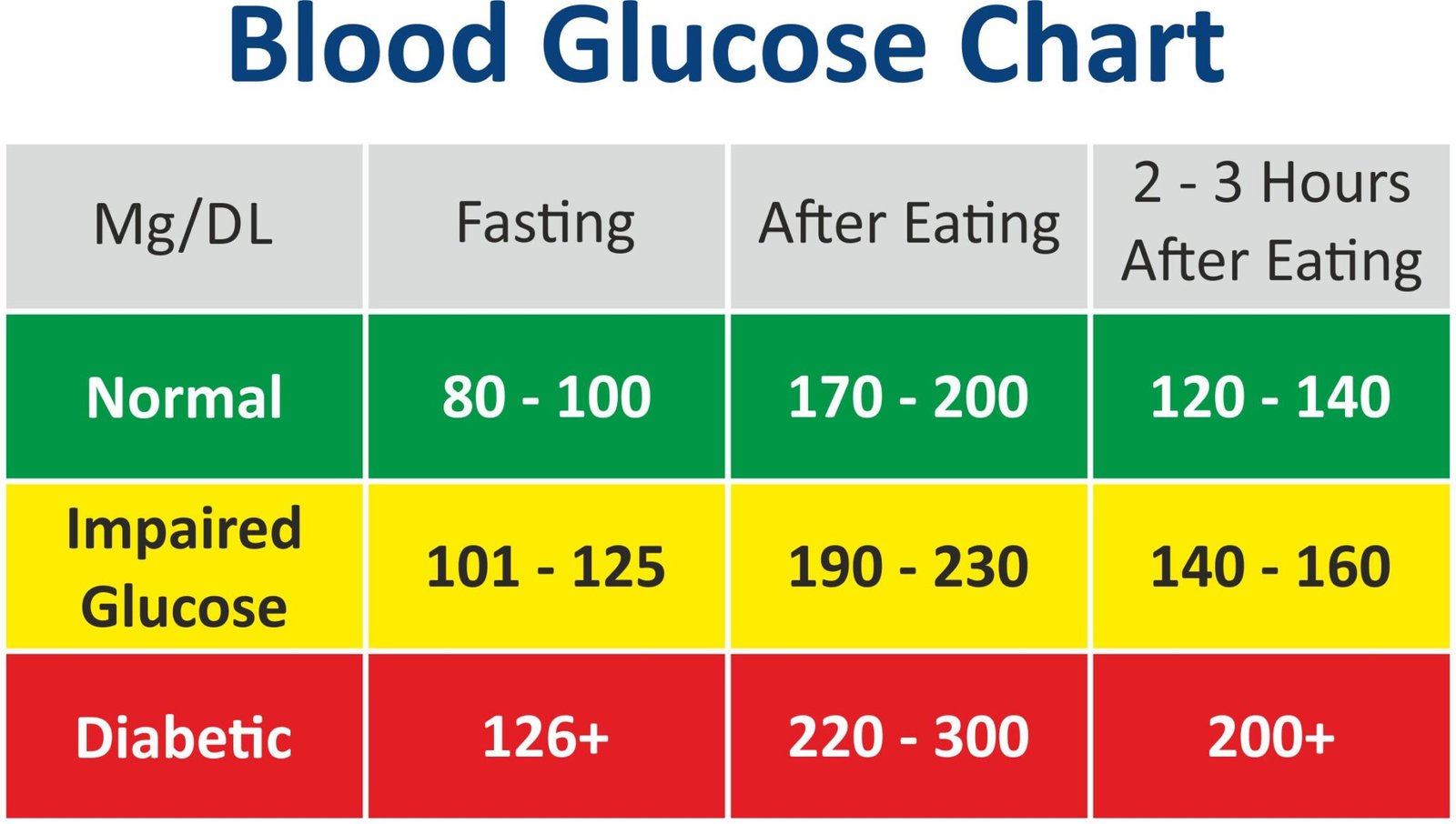
Blood glucose levels are measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or millimoles per liter (mmol/L). The normal values for blood glucose depend on the time of day and when you last ate.
- Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS): This is your blood glucose level after an overnight fast of at least 8 hours. Normal fasting blood sugar levels are between 70 to 99 mg/dL (3.9 to 5.5 mmol/L).
- Postprandial (After Meal) Blood Sugar: This is your blood glucose level 1-2 hours after eating. Normal postprandial blood sugar levels are less than 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L).
For individuals with diabetes, the American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends the following target blood glucose levels:
- Before Meals: 70 to 130 mg/dL (3.9 to 7.2 mmol/L)
- After Meals (1-2 hours): Less than 180 mg/dL (10 mmol/L)
Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c)
HbA1c is a blood test that provides information about your average levels of blood glucose over the past 3 months. It’s a crucial indicator for diabetes management.
- Normal HbA1c Levels: Less than 5.7% (39 mmol/mol)
- Prediabetes: 5.7% to 6.4% (39 to 46 mmol/mol)
- Diabetes: 6.5% or above (48 mmol/mol or above)
For people with diabetes, the ADA recommends an HbA1c goal of less than 7% (53 mmol/mol) for most adults. However, this goal may be adjusted based on individual characteristics, such as duration of diabetes, life expectancy, resources, and support system.
Other Important Metrics
- Blood Pressure: Managing blood pressure is crucial for people with diabetes to reduce the risk of heart disease and kidney disease. The ADA recommends a blood pressure goal of less than 140⁄90 mmHg.
- Cholesterol Levels: Dyslipidemia (abnormal amounts of lipids) is common in diabetes and increases the risk of cardiovascular disease. Targets may vary, but generally, LDL (“bad”) cholesterol should be less than 100 mg/dL, and triglycerides should be less than 150 mg/dL.
- Body Mass Index (BMI): Maintaining a healthy weight is important for managing diabetes. A BMI between 18.5 and 24.9 is considered normal.
Lifestyle and Medication Management
Achieving and maintaining these normal values often requires a combination of lifestyle modifications and, when necessary, medication.
- Diet: Eating a balanced diet that is low in added sugars, saturated fats, and sodium, and high in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help manage blood glucose levels.
- Physical Activity: Regular physical activity, such as walking, can help lower blood glucose levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Medications: Various medications, including metformin, sulfonylureas, and insulin, can be prescribed to help manage blood glucose levels.
Monitoring and Adjustments
Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels, HbA1c, and other metrics is essential to make adjustments to your treatment plan as needed. Work closely with your healthcare provider to set realistic targets, understand your medications, and make lifestyle changes to achieve optimal diabetes management.
Conclusion
Managing diabetes involves understanding and working towards achieving normal values for blood glucose levels, HbA1c, and other health metrics. By combining lifestyle modifications with medication (when prescribed), individuals with diabetes can reduce the risk of complications and improve their quality of life. Regular monitoring and adjustments, along with support from healthcare providers, are key to successful diabetes management.
What is the normal range for fasting blood sugar levels?
+Normal fasting blood sugar levels are between 70 to 99 mg/dL (3.9 to 5.5 mmol/L).
How often should I check my blood glucose levels?
+The frequency of checking blood glucose levels depends on your diabetes treatment plan and the type of diabetes you have. Generally, it’s recommended to check levels at least four times a day (before meals and before bedtime) if you’re taking insulin.
What does an HbA1c level of 7% mean?
+An HbA1c level of 7% indicates that your average blood glucose levels over the past 3 months were within the target range for most adults with diabetes, suggesting good control of your condition.