Flu Warning Signs: Identify And Act Fast
The flu, also known as influenza, is a highly contagious respiratory illness that can affect anyone, regardless of age or health status. It’s essential to recognize the warning signs of the flu to take prompt action and prevent complications. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the common symptoms of the flu, explore the differences between the flu and other respiratory illnesses, and provide expert advice on when to seek medical attention.
Understanding the Flu
The flu is caused by the influenza virus, which spreads through the air when an infected person talks, coughs, or sneezes. It can also be transmitted by touching surfaces or objects contaminated with the virus and then touching one’s mouth, nose, or eyes. The flu can be severe, especially for vulnerable populations such as older adults, young children, and people with certain chronic health conditions.
Common Flu Symptoms
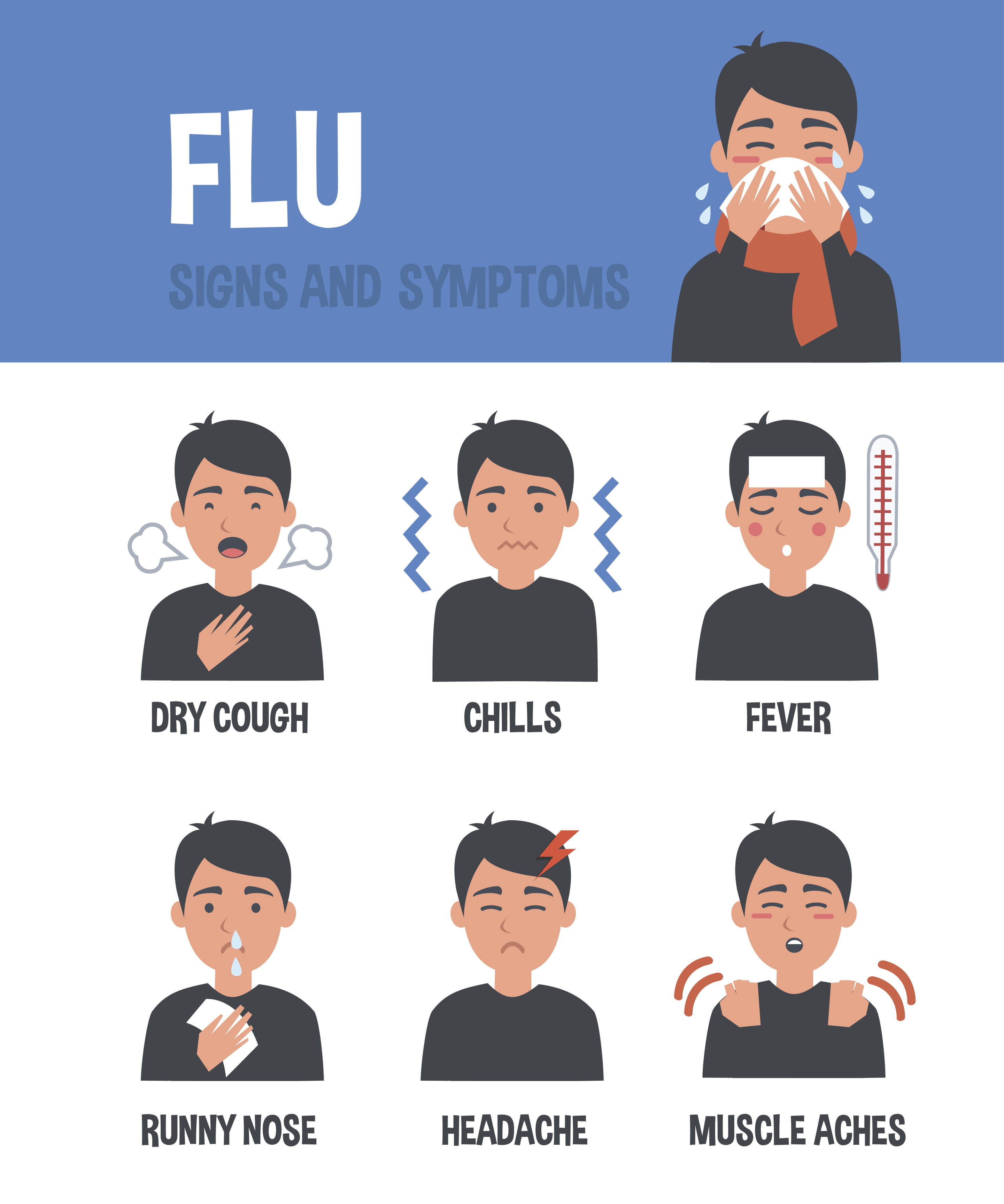
The symptoms of the flu can vary from person to person, but common warning signs include:
- Fever: A sudden and high fever, usually above 102°F (39°C), is often one of the first signs of the flu.
- Chills: Shivering and feeling cold, even if the body temperature is high, is a common symptom of the flu.
- Cough: A dry, hacking cough is a typical symptom of the flu, although it can be mild or severe.
- Sore Throat: Pain or discomfort in the throat, which can make swallowing difficult, is a common flu symptom.
- Runny or Stuffy Nose: Nasal congestion or a runny nose can occur due to the flu.
- Headache: A severe headache, often described as a dull, throbbing pain, is a common symptom of the flu.
- Fatigue: Feeling extremely weak, tired, or exhausted, even after resting, is a characteristic symptom of the flu.
- Muscle or Body Aches: Pain or discomfort in the muscles, back, or other parts of the body is common during the flu.
- Diarrhea and Vomiting: Although more common in children, diarrhea and vomiting can also occur in adults with the flu.
Understanding the Differences Between the Flu and Other Respiratory Illnesses
It’s essential to differentiate between the flu and other respiratory illnesses, such as the common cold or COVID-19, to ensure proper treatment and management. While the flu and COVID-19 share some similar symptoms, such as fever, cough, and fatigue, there are distinct differences:
- Onset of Symptoms: The flu typically comes on suddenly, with symptoms appearing within 1-3 days of exposure. COVID-19 symptoms can appear 2-14 days after exposure.
- Fever: The flu often causes a high fever, usually above 102°F (39°C), whereas COVID-19 may cause a lower-grade fever or no fever at all.
- Cough: The flu typically causes a dry, hacking cough, whereas COVID-19 can cause a more productive cough.
It's crucial to note that the flu can lead to severe complications, such as pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and even death, especially in high-risk individuals. If you or someone you know is experiencing severe flu symptoms or is at high risk for complications, it's essential to seek medical attention immediately.
High-Risk Groups
Certain groups are more susceptible to the flu and its complications, including:
- Older Adults: People 65 years and older are at high risk due to age-related weakening of the immune system.
- Young Children: Children under 5 years, especially those under 2 years, are more vulnerable due to their developing immune system.
- Pregnant Women: Pregnant women are at high risk due to changes in their immune system and increased risk of complications.
- People with Chronic Health Conditions: Those with conditions like heart disease, lung disease, or diabetes are more prone to flu complications.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you or someone you know is experiencing any of the following, seek medical attention immediately:
- Difficulty Breathing: Shortness of breath, wheezing, or feeling like you’re going to pass out.
- Chest Pain or Pressure: Severe chest pain or pressure, which can be a sign of a heart attack or other serious condition.
- Severe Headache: A sudden, severe headache, which can be a sign of a stroke or other neurological condition.
- Confusion or Disorientation: Feeling confused, disoriented, or losing consciousness.
- Severe Vomiting: Vomiting that is severe, bloody, or accompanied by abdominal pain.
- Fever Above 103°F (39.4°C): A fever that is extremely high and does not respond to treatment.
What to Do If You Think You Have the Flu
- Stay home and avoid contact with others to prevent the spread of the virus.
- Rest and stay hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids.
- Use over-the-counter medications, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, to help alleviate symptoms like fever and headache.
- Practice good hygiene, such as washing your hands frequently and covering your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing.
- Seek medical attention if you experience any severe symptoms or if you are at high risk for complications.
Prevention and Treatment
While there is no cure for the flu, there are steps you can take to prevent it and manage symptoms:
- Get Vaccinated: The flu vaccine is the most effective way to prevent the flu and its complications.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Wash your hands frequently, avoid close contact with others, and avoid touching your eyes, nose, and mouth.
- Stay Healthy: Maintain a healthy lifestyle by getting enough sleep, exercising regularly, and eating a balanced diet.
What are the most common flu symptoms?
+The most common flu symptoms include fever, chills, cough, sore throat, runny or stuffy nose, headache, fatigue, and muscle or body aches.
How can I prevent the flu?
+To prevent the flu, get vaccinated, practice good hygiene, stay healthy, and avoid close contact with others who are sick.
When should I seek medical attention for the flu?
+Seek medical attention immediately if you experience difficulty breathing, chest pain or pressure, severe headache, confusion or disorientation, severe vomiting, or a fever above 103°F (39.4°C).
In conclusion, recognizing the warning signs of the flu and taking prompt action can help prevent complications and ensure proper treatment. By understanding the common symptoms, differences between the flu and other respiratory illnesses, and high-risk groups, you can take the necessary steps to protect yourself and your loved ones. Remember to seek medical attention immediately if you or someone you know is experiencing severe flu symptoms or is at high risk for complications.