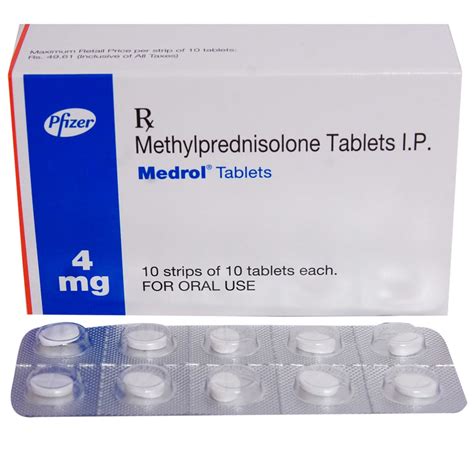
Methylprednisolone 4 Mg
Methylprednisolone is a synthetic corticosteroid that exhibits potent anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive properties. It belongs to the class of glucocorticoids, which are steroid hormones that play crucial roles in regulating the body’s immune response, inflammation, and metabolism. The medication is widely used in various medical conditions to reduce inflammation, suppress the immune system, and replace deficient steroid hormones in the body.
Mechanism of Action
Methylprednisolone works by binding to specific receptors in the body, which then influence the expression of various genes involved in the inflammatory response. This binding process leads to a decrease in the production of inflammatory mediators, such as prostaglandins and leukotrienes, which are key players in the inflammation process. Additionally, methylprednisolone inhibits the migration of white blood cells to sites of inflammation, further reducing the inflammatory response.
Uses
Methylprednisolone is used to treat a wide range of conditions, including but not limited to:
- Allergic reactions: It is effective in managing severe allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis, and in treating conditions like allergic rhinitis and asthma.
- Autoimmune diseases: Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and multiple sclerosis, where the body’s immune system attacks its own tissues, can be managed with methylprednisolone.
- Inflammatory conditions: It is used to treat various inflammatory conditions, including bursitis, tendonitis, and gout.
- Respiratory diseases: Methylprednisolone can help manage respiratory conditions like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma.
- Blood diseases: Certain blood disorders, such as thrombocytopenia and autoimmune hemolytic anemia, may be treated with this medication.
Dosage and Administration
The dosage of methylprednisolone varies widely depending on the specific condition being treated, the severity of the condition, and the patient’s response to the medication. It can be administered orally, intravenously, or intramuscularly. For oral administration, doses can range from a few milligrams to several hundred milligrams per day, divided into multiple doses.
A dose of 4 mg of methylprednisolone is considered relatively low and might be used for maintaining therapy in certain conditions or for treating mild to moderate inflammatory or allergic reactions. This dosage can be part of a tapering regimen after higher doses have been used to control acute inflammation or an allergic response.
Side Effects and Precautions
Like all corticosteroids, methylprednisolone can cause a variety of side effects, which are more common with higher doses and prolonged use. Common side effects include:
- Weight gain
- Mood changes
- Increased appetite
- Sleep disturbances
- Increased blood sugar levels
- Osteoporosis
- Cataracts
- Glaucoma
It is essential to use methylprednisolone under the guidance of a healthcare provider, as it can have significant side effects, especially with long-term use. Patients should be monitored closely for signs of adrenal insufficiency, osteoporosis, and other potential side effects.
Interaction with Other Medications
Methylprednisolone can interact with various medications, either by enhancing their effects or by increasing the risk of side effects. These include:
- Blood thinners: Methylprednisolone can increase the risk of bleeding when used with anticoagulants.
- Diabetes medications: It can affect blood sugar levels, necessitating adjustments in diabetes medication.
- Hepatotoxic medications: The risk of liver damage may increase when methylprednisolone is used with other hepatotoxic drugs.
Conclusion
Methylprednisolone is a powerful corticosteroid with a wide range of applications in medicine. Its ability to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system makes it a valuable treatment option for numerous conditions. However, due to its potential for significant side effects, especially with prolonged use, it is crucial to use methylprednisolone under the close supervision of a healthcare provider. Patients should be aware of the potential interactions with other medications and monitor their condition closely to minimize the risk of adverse effects.
What is the primary use of methylprednisolone?
+Methylprednisolone is primarily used to treat inflammatory conditions and autoimmune diseases by reducing inflammation and suppressing the immune system.
How does methylprednisolone work?
+Methylprednisolone works by binding to specific receptors, influencing gene expression related to inflammation, and inhibiting the production of inflammatory mediators and the migration of white blood cells to sites of inflammation.
What are the common side effects of methylprednisolone?
+Common side effects include weight gain, mood changes, increased appetite, sleep disturbances, and increased blood sugar levels. Long-term use can lead to more serious side effects such as osteoporosis, cataracts, and glaucoma.
Expert Insights
When considering the use of methylprednisolone, it’s essential to weigh the potential benefits against the risks, particularly for long-term therapy. The medication’s potency and the individual’s response to it play crucial roles in determining the optimal dosage and treatment duration.
Key Takeaways

- Methylprednisolone is a synthetic corticosteroid useful in managing inflammatory and autoimmune conditions. - Its dosage and administration method can vary significantly based on the condition being treated. - Monitoring for side effects and potential interactions with other medications is critical during therapy. - The medication should be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider to minimize risks and maximize benefits.