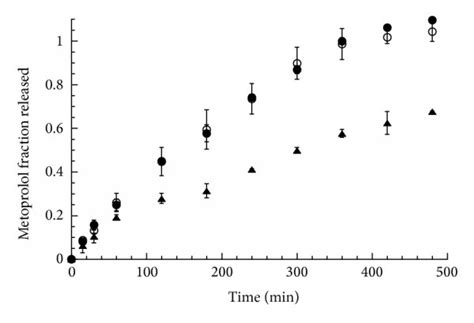
Metoprolol Time Release
Metoprolol, a beta-blocker medication, is widely used to treat various cardiovascular conditions, including high blood pressure, chest pain (angina), and certain heart-related issues. The time-release formulation of metoprolol, often referred to as metoprolol succinate, is designed to release the medication slowly over a period of time, providing a consistent and controlled release of the active ingredient into the bloodstream. This formulation is intended to improve patient compliance by reducing the number of doses taken per day, typically to just once daily, and to maintain a steady level of the medication in the body throughout the day.
Introduction to Time-Release Formulations
Time-release formulations, also known as sustained-release or extended-release formulations, are designed to release the active ingredient of a drug over an extended period, contrasting with immediate-release formulations that release the drug more quickly. This design helps in maintaining a constant drug concentration for a longer period with fewer doses, which can improve patient adherence to medication regimens. In the case of metoprolol, the time-release version helps in managing conditions that require consistent medication levels over 24 hours, such as hypertension and heart failure.
How Metoprolol Time Release Works
Metoprolol succinate, the time-release version of metoprolol, works by slowing the heart rate and reducing its workload. This action decreases the heart’s demand for oxygen, which is particularly beneficial for patients with angina. By controlling the heart rate and reducing blood pressure, metoprolol also helps in reducing the risk of heart attacks and strokes in patients with high blood pressure or those who have had a heart attack.
The mechanism of action of metoprolol involves the selective blockade of beta-1 adrenergic receptors, which are predominantly found in the heart. This selectivity means that metoprolol has less effect on airway resistance and peripheral blood vessels compared to non-selective beta-blockers, making it a favorable choice for patients with respiratory conditions such as asthma.
Benefits of Metoprolol Time Release
- Improved Patient Compliance: The once-daily dosing regimen of metoprolol succinate can enhance patient adherence compared to multiple daily doses required by immediate-release formulations.
- Consistent Medication Levels: The slow and consistent release of metoprolol ensures that therapeutic drug levels are maintained throughout the day, providing stable control over heart rate and blood pressure.
- Reduced Peak-to-Trough Fluctuations: By releasing the medication slowly, time-release formulations minimize the peak-to-trough fluctuations in drug concentration, potentially reducing the risk of side effects associated with high drug levels.
- Enhanced Efficacy and Safety: For many patients, the controlled release of metoprolol can lead to improved management of their condition, reducing the risk of complications associated with hypertension and heart disease.
Potential Side Effects and Considerations
While metoprolol time release is generally well-tolerated, potential side effects include fatigue, dizziness, shortness of breath, and vivid dreams or nightmares. It’s also important to note that beta-blockers like metoprolol can mask the symptoms of low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) and may interfere with the body’s natural response to stress, making it crucial for patients to monitor their condition closely while on this medication.
Interactions and Precautions
Metoprolol can interact with various medications, including other beta-blockers, certain antidepressants, and over-the-counter cough and cold medicines. Patients should inform their healthcare provider about all medications they are taking before starting metoprolol. Additionally, patients with certain conditions, such as severe bradycardia (slow heart rate), heart block, or cardiogenic shock, should use metoprolol with caution or under close medical supervision.
Conclusion
Metoprolol time release offers a convenient and effective way to manage cardiovascular conditions, providing consistent drug levels and improved patient compliance. However, as with any medication, it’s crucial to follow the prescribed regimen, monitor for potential side effects, and be aware of possible interactions with other medications. By understanding how metoprolol time release works and its benefits, patients can work closely with their healthcare providers to optimize their treatment plan and improve their cardiovascular health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary difference between metoprolol tartrate and metoprolol succinate?
+Metoprolol tartrate is an immediate-release formulation, while metoprolol succinate is a time-release formulation. The main difference lies in how the medication is released into the body, with metoprolol tartrate releasing more quickly and metoprolol succinate releasing slowly over time.
Can I stop taking metoprolol time release suddenly if I feel better?
+No, you should not stop taking metoprolol time release suddenly without consulting your healthcare provider. Abruptly stopping beta-blockers can lead to withdrawal symptoms and potentially serious heart problems. Your healthcare provider will advise you on how to safely discontinue the medication if necessary.
How long does it take for metoprolol time release to start working?
+The effects of metoprolol time release can be noticed within a few hours of the first dose, but it may take several weeks to achieve its full blood pressure-lowering effect. Consistency in taking the medication as prescribed is crucial for its effectiveness.