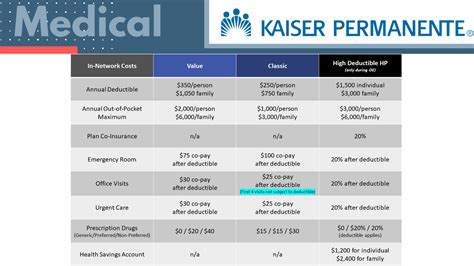
Shoulder Replacement Surgery: Relieve Chronic Pain
Chronic shoulder pain can be debilitating, affecting every aspect of daily life. For individuals suffering from severe shoulder arthritis, fractures, or rotator cuff injuries, shoulder replacement surgery often emerges as a viable solution to alleviate pain and restore mobility. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of shoulder replacement surgery, exploring its types, benefits, potential risks, and what to expect during the recovery process.
Understanding Shoulder Anatomy and Conditions Leading to Surgery
The shoulder joint, also known as the glenohumeral joint, is a ball-and-socket joint that consists of three bones: the humerus (upper arm bone), the scapula (shoulder blade), and the clavicle (collarbone). The joint is stabilized by muscles, tendons, and ligaments, allowing for a wide range of motion. However, conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, avascular necrosis, severe fractures, and rotator cuff tears can lead to chronic pain and reduced mobility, necessitating surgical intervention.
Types of Shoulder Replacement Surgery
Shoulder replacement surgery is not a one-size-fits-all solution; it comes in different forms, each tailored to address specific conditions and needs:
- Total Shoulder Replacement: This involves replacing the arthritic joint surfaces with a highly polished metal ball attached to a stem and a plastic socket. It’s the most common type of shoulder replacement surgery, suitable for patients with severe arthritis.
- Stemmed Hemiarthroplasty: In this procedure, only the ball of the joint is replaced with a metal component. It’s typically recommended for patients with severe fractures or those who have a healthy glenoid (shoulder socket) but a damaged humerus.
- Resurfacing Hemiarthroplasty: This involves capping the head of the humerus with a metal cap, without a stem. It’s an option for younger patients with early-stage arthritis or those with minimal bone loss.
- Reverse Total Shoulder Replacement: This innovative procedure is often used for patients with torn rotator cuffs or severe arthritis. It reverses the position of the ball and socket, providing more stable movement and strength to the shoulder.
Benefits of Shoulder Replacement Surgery
The primary goal of shoulder replacement surgery is to alleviate chronic pain and improve mobility and function. Other benefits include:
- Significant Pain Relief: Most patients experience considerable reduction in pain, allowing them to return to their daily activities without the burden of constant discomfort.
- Improved Mobility: Surgery can restore a wide range of motion, enabling patients to move their shoulders more freely and perform tasks that were previously challenging.
- Durability: With proper care, shoulder replacement implants can last for many years, providing long-term relief and improved quality of life.
Potential Risks and Complications
As with any surgical procedure, shoulder replacement surgery comes with potential risks and complications, including:
- Infection: As with any surgery, there is a risk of infection, which can be treated with antibiotics but may require additional surgery in severe cases.
- Nerve Damage: There is a small risk of nerve damage during surgery, which can lead to numbness, tingling, or weakness in the arm.
- Prosthesis Failure: Although rare, the artificial components can wear out or loosen over time, requiring revision surgery.
- Blood Clots: Patients are at risk of developing blood clots in the legs, which can travel to the lungs and cause a pulmonary embolism.
Recovery Process
The recovery from shoulder replacement surgery is a gradual process that requires patience, dedication, and a well-structured rehabilitation plan. Immediate post-surgery care typically involves:
- Pain Management: Effective pain control is crucial in the early stages of recovery, often managed through a combination of medication and ice.
- Immobilization: Patients are usually required to wear a sling for several weeks to protect the shoulder and allow the tissues to heal.
- Physical Therapy: A structured physical therapy program is essential for regaining strength, mobility, and function. Exercises are progressed gradually, from simple movements to more complex actions.
Long-Term Outcomes and Expectations
Most patients can expect significant improvements in pain and function, with the majority being able to return to their normal activities within a few months. It’s essential to have realistic expectations and understand that:
- Full Recovery Time: It can take up to a year or more for the shoulder to reach its maximum strength and improvement.
- Activity Modifications: Some activities, especially those involving heavy lifting or repetitive motions, may need to be modified or avoided to prolong the life of the implant.
- Follow-Up Care: Regular follow-up appointments with the surgeon are crucial for monitoring the implant’s condition and addressing any concerns or complications early.
Conclusion
Shoulder replacement surgery offers a beacon of hope for individuals plagued by chronic shoulder pain, providing a pathway to regain mobility, reduce discomfort, and enhance the overall quality of life. With advancements in surgical techniques and implant technology, the outcomes of shoulder replacement surgery continue to improve, making it a viable option for those seeking relief from debilitating shoulder conditions. As with any significant medical decision, it’s vital to consult with a qualified healthcare professional to discuss the potential benefits and risks and determine the best course of action for individual circumstances.
What are the primary indications for shoulder replacement surgery?
+The primary indications include severe arthritis (osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis), severe fractures, and rotator cuff arthropathy. Patients experiencing chronic pain and significant loss of function despite conservative treatments may be candidates for shoulder replacement surgery.
How long does it take to recover from shoulder replacement surgery?
+Recovery from shoulder replacement surgery is a gradual process. Most patients can expect to wear a sling for 2-6 weeks and undergo physical therapy for several months. Full recovery, with maximum strength and improvement, can take up to a year or more.
What are the potential risks and complications of shoulder replacement surgery?
+Potential risks and complications include infection, nerve damage, prosthesis failure, and blood clots. Although these complications are rare, they can have significant implications for the patient’s recovery and long-term outcome.
Can shoulder replacement surgery be performed on an outpatient basis?
+Yes, in some cases, shoulder replacement surgery can be performed on an outpatient basis, depending on the patient’s overall health, the complexity of the procedure, and the surgeon’s preference. However, many patients still require a short hospital stay for monitoring and initial recovery.
How long do shoulder replacement implants last?
+The longevity of shoulder replacement implants varies depending on several factors, including the patient’s activity level, weight, and overall health, as well as the quality of the implant and surgical technique. On average, implants can last for 10 to 20 years or more before they may need to be revised.